J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2007 Dec;14(4):431-435.
A Case of Isoniazid Induced Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea. ckhlms@wonkwang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, School of Medicine, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea.
- 3Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea.
Abstract
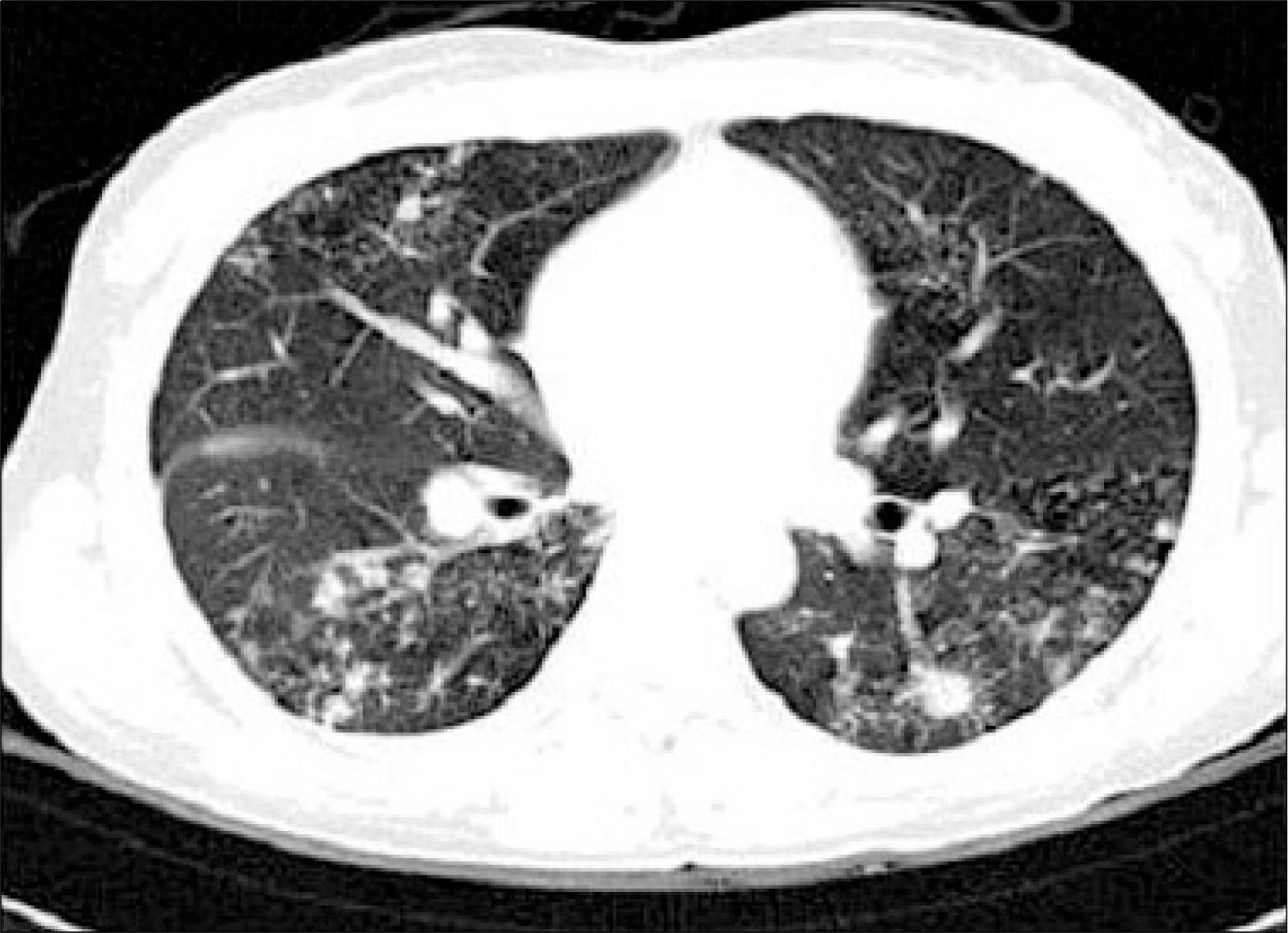
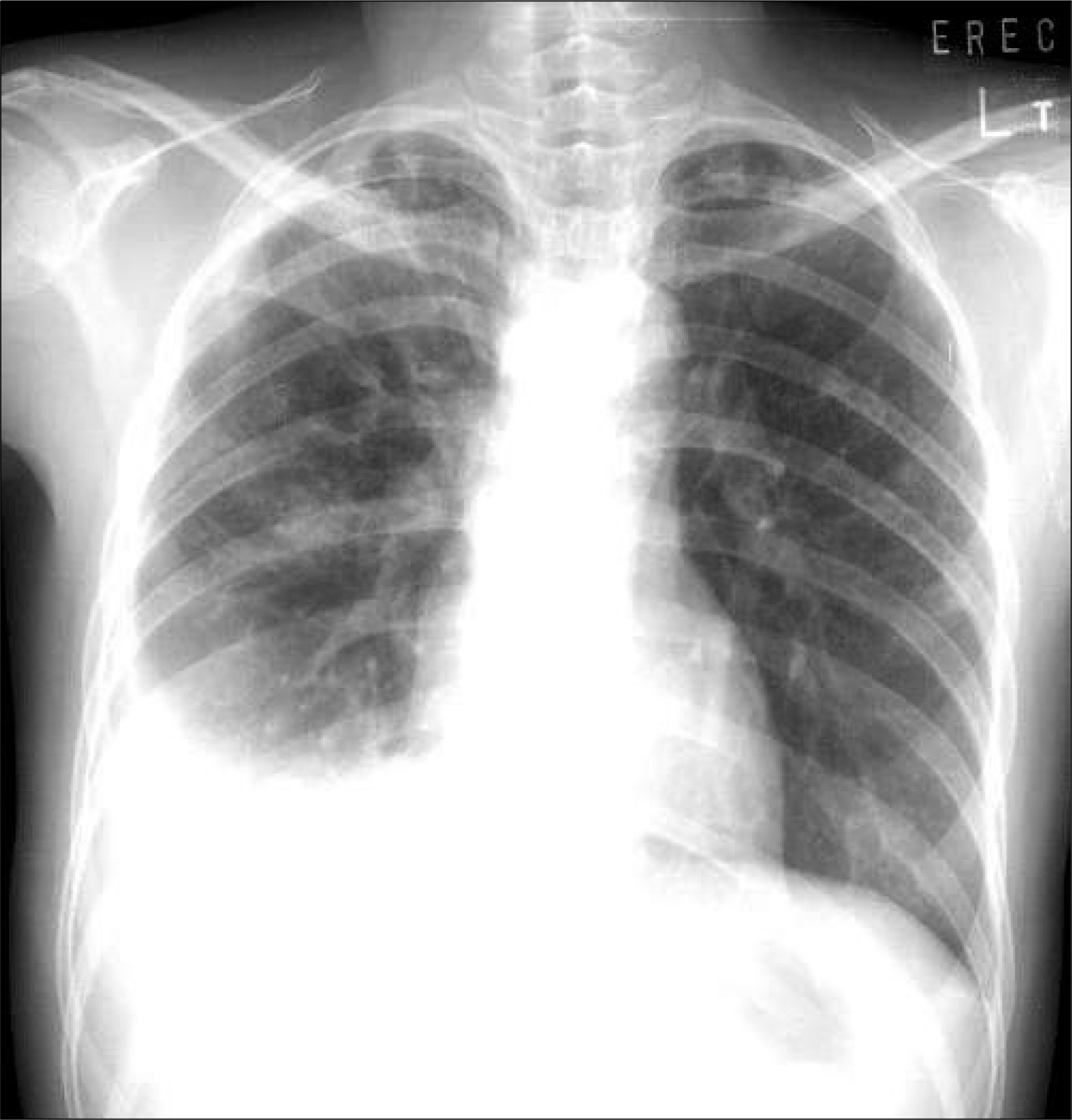
- Many drugs have been known to induce lupus-like syndrome, composing approximately 10% of all SLE cases. Isoniazid-induced lupus erythematosus affects either sex equally and the most common presenting feature is arthralgia or arthritis with anemia. Fever and pleuritis occur in approximately half of the cases, and pericarditis in approximately 30% of cases. We discribe a 28-year-old woman receiving antituberculous medications including isoniazid for one month. She was hospitalized with fever, arthralgia and newly developed pleural effusion The analysis of pleural fluid and serum revealed an elevated level of antinuclear antibody. We suspected of drug induced lupus and stopped isoniazid medication. After discontinuation of isoniazid and short course of prednisolone treatment, her symptoms and pleural effusion disappeared. This case is to our knowledge, the fist report of isoniazid induced SLE in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Hoffman BJ. Sensitivity to sulfadiazine resembling acute disseminated lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol Syphilis. 1945. 51:190–2.
Article2). Lee SL., CHase PH. Drug-induced systemic lupus erythematosus: a critical review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1975. 5:83–103.3). Weinstein A. Drug-induced systemic lupus erythematosus. Prog Clin Immunol. 1980. 4:1–21.4). Rothfield NF., Bierer WF., Garfield JW. Isoniazid induction of antinuclear antibodies. A prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1978. 88:650–2.5). Atzeni F., Marrazza MG., Sarzi-Puttini P., Carrabba M. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus. Reumatismo. 2003. 55:147–54.
Article6). Antonov D., Kazandjieva J., Etugov D., Gospodinov D., Tsankov N. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus. Clin Dermatol. 2004. 22:157–66.
Article7). Hess E. Drug-related lupus. N Engl J Med. 1988. 318:1460–2.
Article8). Yung RL., Richardson BC. Drug-induced lupus. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1994. 20:61–86.
Article9). Siddiqui MA., Khan IA. Isoniazid-induced lupus erythematosus presenting with cardiac tamponade. Am J Ther. 2002. 9:163–5.
Article10). Kang MJ., Lee YH., Lee JS. Etanercept-induced systemic lupus erythematosus in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:946–9.
Article11). Mario SP., Robert L., Ignacio G. Systemic lupus erythematosus induced by isoniazid. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992. 51:1085–7.12). Rider V., Abdou NI. Gender differences in autoimmunity: molecular basis for estrogen effects in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Immunopharmacol. 2001. 1:1009–24.
Article13). Jiang X., Khursigara G., Rubin RL. Transformation of lupus-inducing drugs to cytotoxic products by activated neutrophils. Science. 1994. 266:810–3.
Article14). Fazano CS., Bertin P. The pharmacological management of drug-induced rheumatic disorders. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2001. 10:1623–31.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adalimumab-induced Lupus Erythematosus Profundus in a Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient
- A Case of Transverse Myelitis as a First Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- A Case Of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Associated With Hyperthyroidism And Severe Retinopathy
- A Case of Lupus Enteritis That Developed during the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Multiple Dermatofibromas in a woman with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus