Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2016 Jun;19(2):147-151. 10.5223/pghn.2016.19.2.147.
Living Related Liver Transplantation in an Infant with Neonatal Hemochromatosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kojs@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2328177
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2016.19.2.147
Abstract
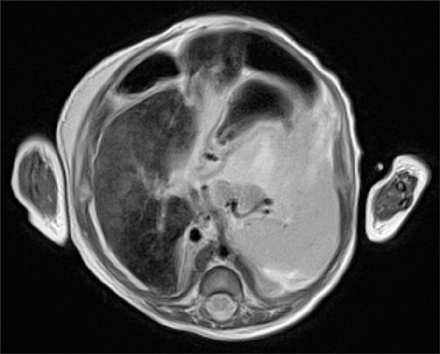
- Neonatal hemochromatosis (NH) is a severe neonatal liver injury that is confirmed by extra-hepatic iron accumulation. Although a recent study described treating NH with exchange transfusions and intravenous immunoglobulin, liver transplantation should be considered for patients with severe liver failure that does not respond to other medical treatment. Herein, we report the case of a two-month-old female infant who presented with persistent ascites and hyperbilirubinemia. Her laboratory findings demonstrated severe coagulopathy, high indirect and direct bilirubin levels, and high ferritin levels. Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging presented low signal intensity in the liver on T2-weighted images, suggesting iron deposition. The infant was diagnosed with NH as a result of the clinical findings and after congenital infection and metabolic diseases were excluded. The infant was successfully treated with a living-donor liver transplantation. Living related liver transplantation should be considered as a treatment option for NH in infants.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Whitington PF. Fetal and infantile hemochromatosis. Hepatology. 2006; 43:654–660.
Article2. Lopriore E, Mearin ML, Oepkes D, Devlieger R, Whitington PF. Neonatal hemochromatosis: management, outcome, and prevention. Prenat Diagn. 2013; 33:1221–1225.
Article3. Whitington PF. Gestational alloimmune liver disease and neonatal hemochromatosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2012; 32:325–332.
Article4. Pan X, Kelly S, Melin-Aldana H, Malladi P, Whitington PF. Novel mechanism of fetal hepatocyte injury in congenital alloimmune hepatitis involves the terminal complement cascade. Hepatology. 2010; 51:2061–2068.
Article5. Whitington PF, Kelly S. Outcome of pregnancies at risk for neonatal hemochromatosis is improved by treatment with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Pediatrics. 2008; 121:e1615–e1621.
Article6. Whitington PF, Hibbard JU. High-dose immunoglobulin during pregnancy for recurrent neonatal haemochromatosis. Lancet. 2004; 364:1690–1698.
Article7. Bailey D, Colantonio D, Kyriakopoulou L, Cohen AH, Chan MK, Armbruster D, et al. Marked biological variance in endocrine and biochemical markers in childhood: establishment of pediatric reference intervals using healthy community children from the CALIPER cohort. Clin Chem. 2013; 59:1393–1405.
Article8. Soldin OP, Dahlin JR, Gresham EG, King J, Soldin SJ. IMMULITE 2000 age and sex-specific reference intervals for alpha fetoprotein, homocysteine, insulin, insulin-like growth factor-1, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, C-peptide, immunoglobulin E and intact parathyroid hormone. Clin Biochem. 2008; 41:937–942.
Article9. Deugnier Y, Turlin B. Pathology of hepatic iron overload. Semin Liver Dis. 2011; 31:260–271.
Article10. Whitington PF, Kelly S, Ekong UD. Neonatal hemochromatosis: fetal liver disease leading to liver failure in the fetus and newborn. Pediatr Transplant. 2005; 9:640–645.
Article11. Knisely AS, O'Shea PA, Stocks JF, Dimmick JE. Oropharyngeal and upper respiratory tract mucosal-gland siderosis in neonatal hemochromatosis: an approach to biopsy diagnosis. J Pediatr. 1988; 113:871–874.
Article12. Magliocca KR, Lewis EL, Bhattacharyya I, Cohen DM, Dixon LR. Labial salivary gland biopsy in the investigation of neonatal hemochromatosis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 69:2592–2594.
Article13. Hayes AM, Jaramillo D, Levy HL, Knisely AS. Neonatal hemochromatosis: diagnosis with MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992; 159:623–625.
Article14. Debray FG, de Halleux V, Guidi O, Detrembleur N, Gaillez S, Rausin L, et al. Neonatal liver cirrhosis without iron overload caused by gestational alloimmune liver disease. Pediatrics. 2012; 129:e1076–e1079.
Article15. Rand EB, Karpen SJ, Kelly S, Mack CL, Malatack JJ, Sokol RJ, et al. Treatment of neonatal hemochromatosis with exchange transfusion and intravenous immunoglobulin. J Pediatr. 2009; 155:566–571.
Article16. Sheflin-Findling S, Annunziato RA, Chu J, Arvelakis A, Mahon D, Arnon R. Liver transplantation for neonatal hemochromatosis: analysis of the UNOS database. Pediatr Transplant. 2015; 19:164–169.
Article17. Sundaram SS, Alonso EM, Whitington PF. Liver transplantation in neonates. Liver Transpl. 2003; 9:783–788.
Article18. Rodrigues F, Kallas M, Nash R, Cheeseman P, D'Antiga L, Rela M, et al. Neonatal hemochromatosis--medical treatment vs. transplantation: the king's experience. Liver Transpl. 2005; 11:1417–1424.
Article19. Nijagal A, Fleck S, Hills NK, Feng S, Tang Q, Kang SM, et al. Decreased risk of graft failure with maternal liver transplantation in patients with biliary atresia. Am J Transplant. 2012; 12:409–419.
Article20. Sanada Y, Kawano Y, Miki A, Aida J, Nakamura K, Shimomura N, et al. Maternal grafts protect daughter recipients from acute cellular rejection after pediatric living donor liver transplantation for biliary atresia. Transpl Int. 2014; 27:383–390.
Article