Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2012 Sep;15(3):160-165.
The Use of Radionuclide Salivagram and Videofluoroscopic Swallow Study in the Evaluation of Aspiration Pneumonia in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kmkim@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the abilities of radionuclide salivagrams (RS) and videofluoroscopic swallow studies (VFSS) to diagnose aspiration in children with aspiration pneumonia.
METHODS
The records of children who were referred to the Asan Medical Center between April, 2006 and April, 2012 and who underwent both VFSS and RS to evaluate their recurrent aspiration pneumonia were reviewed (n=67). The aspiration positivity rates of the two tests were determined. The agreement between the tests was assessed by using the kappa statistic.
RESULTS
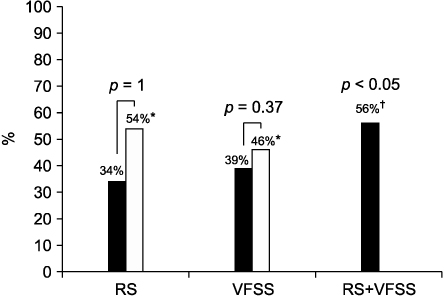
VFSS was more frequently positive (n=26, 39%) than RS (n=23, 34%) (p=0.68). In the 11 children who repeat two test, Repeated examination increased positive rate in each tests (n=11), repeated RS (54%, p=1) is more frequent positive than repeated VFSS (46%, p=0.37). If a cumulative positive test had been defined as at least one positive result, the positive rate of two test was 56% (p<0.05). There was a fair agreement between RS and VFSS (kappa=0.26).
CONCLUSION
The RS and VFSS positivity rates in children with aspiration pneumonia were similar but there was fair agreement between the two tests. This result suggests that these investigations to demonstrate aspiration are not interchangeable but complementary.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Boesch RP, Daines C, Willging JP, Kaul A, Cohen AP, Wood RE, et al. Advances in the diagnosis and management of chronic pulmonary aspiration in children. Eur Respir J. 2006. 28:847–861.
Article2. Lee SH, Jang JY, Yoon IJ, Kim KM. Usefulness of multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH metry in children with suspected gastroesophageal reflux disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008. 52:9–15.3. Stoeckli SJ, Huisman TA, Seifert B, Martin-Harris BJ. Interrater reliability of videofluoroscopic swallow evaluation. Dysphagia. 2003. 18:53–57.
Article4. Allewelt M, Schüler P, Bölcskei PL, Mauch H, Lode H. Study Group on Aspiration Pneumonia. Ampicillin + sulbactam vs clindamycin +/- cephalosporin for the treatment of aspiration pneumonia and primary lung abscess. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004. 10:163–170.
Article5. Treves ST, Baker A, Fahey FH, Cao X, Davis RT, Drubach LA, et al. Nuclear medicine in the first year of life. J Nucl Med. 2011. 52:905–925.
Article6. Chau KH, Kung CM. Patient dose during videofluoroscopy swallowing studies in a Hong Kong public hospital. Dysphagia. 2009. 24:387–390.
Article7. Gillies JD, Seshia SS. Vegetative state following coma in childhood: evolution and outcome. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1980. 22:642–648.
Article8. Heyman S, Respondek M. Detection of pulmonary aspiration in children by radionuclide "salivagram". J Nucl Med. 1989. 30:697–699.9. Levin K, Colon A, DiPalma J, Fitzpatrick S. Using the radionuclide salivagram to detect pulmonary aspiration and esophageal dysmotility. Clin Nucl Med. 1993. 18:110–114.
Article10. Cook SP, Lawless S, Mandell GA, Reilly JS. The use of the salivagram in the evaluation of severe and chronic aspiration. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1997. 41:353–361.
Article11. Heyman S. Volume-dependent pulmonary aspiration of a swallowed radionuclide bolus. J Nucl Med. 1997. 38:103–104.12. Bar-Sever Z, Connolly LP, Treves ST. The radionuclide salivagram in children with pulmonary disease and a high risk of aspiration. Pediatr Radiol. 1995. 25:Suppl 1. S180–S183.
Article13. Huxley EJ, Viroslav J, Gray WR, Pierce AK. Pharyngeal aspiration in normal adults and patients with depressed consciousness. Am J Med. 1978. 64:564–568.
Article14. Baikie G, South MJ, Reddihough DS, Cook DJ, Cameron DJ, Olinsky A, et al. Agreement of aspiration tests using barium videofluoroscopy, salivagram, and milk scan in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2005. 47:86–93.
Article15. Mirrett PL, Riski JE, Glascott J, Johnson V. Videofluoroscopic assessment of dysphagia in children with severe spastic cerebral palsy. Dysphagia. 1994. 9:174–179.
Article16. Rogers B, Arvedson J, Buck G, Smart P, Msall M. Characteristics of dysphagia in children with cerebral palsy. Dysphagia. 1994. 9:69–73.
Article17. Kahrilas PJ, Logemann JA. Volume accommodation during swallowing. Dysphagia. 1993. 8:259–265.
Article18. Lazarus CL, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ, Pajak T, Lazar R, et al. Effects of bolus volume, viscosity, and repeated swallows in nonstroke subjects and stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1993. 74:1066–1070.
Article19. Morton RE, Bonas R, Fourie B, Minford J. Videofluoroscopy in the assessment of feeding disorders of children with neurological problems. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1993. 35:388–395.
Article20. Kuhlemeier KV, Yates P, Palmer JB. Intra- and interrater variation in the evaluation of videofluorographic swallowing studies. Dysphagia. 1998. 13:142–147.
Article21. Ekberg O, Nylander G, Fork FT, Sjöberg S, Birch-Iensen M, Hillarp B. Interobserver variability in cineradiographic assessment of pharyngeal function during swallow. Dysphagia. 1988. 3:46–48.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study and Radionuclide Salivagram for Aspiration Pneumonia in Children With Swallowing Difficulty
- Evaluation of Salivary Aspiration in Brain-Injured Patients With Tracheostomy
- Correlation of Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study Findings With Radionuclide Salivagram in Chronic Brain-Injured Patients
- The Correlation Between Clinical Characteristics and Radionuclide Salivagram Findings in Patients With Brain Lesions: A Preliminary Study
- Detection of Saliva Aspiration Using Salivagram in Bedridden Patients with Brain Lesion