J Clin Neurol.
2014 Oct;10(4):334-341. 10.3988/jcn.2014.10.4.334.
Up-Regulation of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products in the Skin Biopsy Specimens of Patients with Severe Diabetic Neuropathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pathology, Seoul Metropolitan Government Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Seoul Metropolitan Government Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. nrhong@gmail.com
- 4Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Seoul Metropolitan Government Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul Metropolitan Government Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2287513
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2014.10.4.334
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) may contribute to the development of diabetic neuropathy. To assess its relevance in humans, this study examined the expression of RAGE in the skin biopsy samples of patients with diabetes mellitus, and investigated its correlation with intraepidermal nerve-fiber density (IENFD) and clinical measures of neuropathy severity.
METHODS
Forty-four patients who either had type 2 diabetes or were prediabetes underwent clinical evaluation and a 3-mm skin punch biopsy. The clinical severity of their neuropathy was assessed using the Michigan Diabetic Neuropathy Score. IENFD was measured along with immunohistochemical staining for RAGE in 29 skin biopsy samples. The expression of RAGE was also quantified by real-time reverse-transcription PCR in the remaining 15 patients.
RESULTS
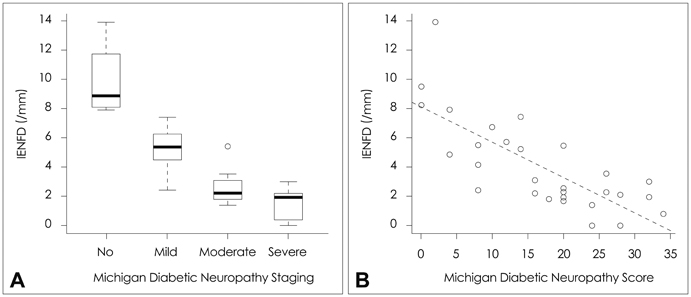
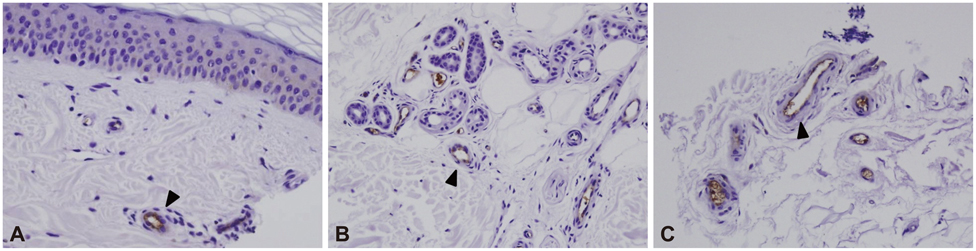
RAGE was localized mostly in the dermal and subcutaneous vascular endothelia. The staining was more intense in patients with a lower IENFD (p=0.004). The quantity of RAGE mRNA was significantly higher in patients with severe neuropathy than in those with no or mild neuropathy (p=0.003). The up-regulation of RAGE was related to dyslipidemia and diabetic nephropathy. There was a trend toward decreased sural nerve action-potential amplitude and slowed peroneal motor-nerve conduction with increasing RAGE expression.
CONCLUSIONS
The findings of this study demonstrate up-regulation of RAGE in skin biopsy samples from patients with diabetic neuropathy, supporting a pathogenic role of RAGE in the development of diabetic neuropathy.
MeSH Terms
-
Biopsy*
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetic Nephropathies
Diabetic Neuropathies*
Dyslipidemias
Glycosylation End Products, Advanced*
Humans
Michigan
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Prediabetic State
Rage
RNA, Messenger
Skin*
Sural Nerve
Up-Regulation*
Advanced Glycosylation End Product-Specific Receptor
Glycosylation End Products, Advanced
RNA, Messenger
Figure
Reference
-
1. Callaghan BC, Cheng HT, Stables CL, Smith AL, Feldman EL. Diabetic neuropathy: clinical manifestations and current treatments. Lancet Neurol. 2012; 11:521–534.
Article2. Gordois A, Scuffham P, Shearer A, Oglesby A, Tobian JA. The health care costs of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in the US. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:1790–1795.
Article3. Bril V. Treatments for diabetic neuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2012; 17:Suppl 2. 22–27.
Article4. Feldman EL. Oxidative stress and diabetic neuropathy: a new understanding of an old problem. J Clin Invest. 2003; 111:431–433.
Article5. Geraldes P, King GL. Activation of protein kinase C isoforms and its impact on diabetic complications. Circ Res. 2010; 106:1319–1331.
Article6. Lauria G, Cornblath DR, Johansson O, McArthur JC, Mellgren SI, Nolano M, et al. EFNS guidelines on the use of skin biopsy in the diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy. Eur J Neurol. 2005; 12:747–758.
Article7. England JD, Gronseth GS, Franklin G, Carter GT, Kinsella LJ, Cohen JA, et al. Practice Parameter: evaluation of distal symmetric polyneuropathy: role of autonomic testing, nerve biopsy, and skin biopsy (an evidence-based review). Report of the American Academy of Neurology, American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2009; 72:177–184.
Article8. Joint Task Force of the EFNS and the PNS. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on the use of skin biopsy in the diagnosis of small fiber neuropathy. Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2010; 15:79–92.9. Quattrini C, Tavakoli M, Jeziorska M, Kallinikos P, Tesfaye S, Finnigan J, et al. Surrogate markers of small fiber damage in human diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes. 2007; 56:2148–2154.
Article10. Shun CT, Chang YC, Wu HP, Hsieh SC, Lin WM, Lin YH, et al. Skin denervation in type 2 diabetes: correlations with diabetic duration and functional impairments. Brain. 2004; 127(Pt 7):1593–1605.
Article11. Polydefkis M, Hauer P, Sheth S, Sirdofsky M, Griffin JW, McArthur JC. The time course of epidermal nerve fibre regeneration: studies in normal controls and in people with diabetes, with and without neuropathy. Brain. 2004; 127(Pt 7):1606–1615.
Article12. Løseth S, Stålberg E, Jorde R, Mellgren SI. Early diabetic neuropathy: thermal thresholds and intraepidermal nerve fibre density in patients with normal nerve conduction studies. J Neurol. 2008; 255:1197–1202.
Article13. Wada R, Yagihashi S. Role of advanced glycation end products and their receptors in development of diabetic neuropathy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005; 1043:598–604.
Article14. Yan SF, Barile GR, D'Agati V, Du Yan S, Ramasamy R, Schmidt AM. The biology of RAGE and its ligands: uncovering mechanisms at the heart of diabetes and its complications. Curr Diab Rep. 2007; 7:146–153.
Article15. Misur I, Zarković K, Barada A, Batelja L, Milicević Z, Turk Z. Advanced glycation endproducts in peripheral nerve in type 2 diabetes with neuropathy. Acta Diabetol. 2004; 41:158–166.
Article16. Wautier MP, Chappey O, Corda S, Stern DM, Schmidt AM, Wautier JL. Activation of NADPH oxidase by AGE links oxidant stress to altered gene expression via RAGE. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 280:E685–E694.
Article17. Bierhaus A, Haslbeck KM, Humpert PM, Liliensiek B, Dehmer T, Morcos M, et al. Loss of pain perception in diabetes is dependent on a receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Clin Invest. 2004; 114:1741–1751.
Article18. Haslbeck KM, Schleicher E, Bierhaus A, Nawroth P, Haslbeck M, Neundörfer B, et al. The AGE/RAGE/NF-(kappa)B pathway may contribute to the pathogenesis of polyneuropathy in impaired glucose tolerance (IGT). Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2005; 113:288–291.
Article19. Vincent AM, Perrone L, Sullivan KA, Backus C, Sastry AM, Lastoskie C, et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end products activation injures primary sensory neurons via oxidative stress. Endocrinology. 2007; 148:548–558.
Article20. Toth C, Rong LL, Yang C, Martinez J, Song F, Ramji N, et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGEs) and experimental diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes. 2008; 57:1002–1017.
Article21. Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:Suppl 1. S5–S20.22. Wilkinson CP, Ferris FL 3rd, Klein RE, Lee PP, Agardh CD, Davis M, et al. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:1677–1682.
Article23. Feldman EL, Stevens MJ, Thomas PK, Brown MB, Canal N, Greene DA. A practical two-step quantitative clinical and electrophysiological assessment for the diagnosis and staging of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 1994; 17:1281–1289.
Article24. Berglund SR, Schwietert CW, Jones AA, Stern RL, Lehmann J, Goldberg Z. Optimized methodology for sequential extraction of RNA and protein from small human skin biopsies. J Invest Dermatol. 2007; 127:349–353.
Article25. Fleige S, Pfaffl MW. RNA integrity and the effect on the real-time qRT-PCR performance. Mol Aspects Med. 2006; 27:126–139.
Article26. Chello M, Spadaccio C, Lusini M, Covino E, Blarzino C, De Marco F, et al. Advanced glycation end products in diabetic patients with optimized glycaemic control and their effects on endothelial reactivity: possible implications in venous graft failure. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2009; 25:420–426.
Article27. Ball TB, Plummer FA, HayGlass KT. Improved mRNA quantitation in LightCycler RT-PCR. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2003; 130:82–86.
Article28. Franke S, Sommer M, Rüster C, Bondeva T, Marticke J, Hofmann G, et al. Advanced glycation end products induce cell cycle arrest and proinflammatory changes in osteoarthritic fibroblast-like synovial cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009; 11:R136.
Article29. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001; 25:402–428.
Article30. Yuan JS, Reed A, Chen F, Stewart CN Jr. Statistical analysis of real-time PCR data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006; 7:85.
Article31. Wiggin TD, Sullivan KA, Pop-Busui R, Amato A, Sima AA, Feldman EL. Elevated triglycerides correlate with progression of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes. 2009; 58:1634–1640.
Article32. Neeper M, Schmidt AM, Brett J, Yan SD, Wang F, Pan YC, et al. Cloning and expression of a cell surface receptor for advanced glycosylation end products of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992; 267:14998–15004.
Article33. Wendt T, Harja E, Bucciarelli L, Qu W, Lu Y, Rong LL, et al. RAGE modulates vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis in a murine model of type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis. 2006; 185:70–77.
Article34. Soro-Paavonen A, Watson AM, Li J, Paavonen K, Koitka A, Calkin AC, et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) deficiency attenuates the development of atherosclerosis in diabetes. Diabetes. 2008; 57:2461–2469.
Article35. Bierhaus A, Illmer T, Kasper M, Luther T, Quehenberger P, Tritschler H, et al. Advanced glycation end product (AGE)-mediated induction of tissue factor in cultured endothelial cells is dependent on RAGE. Circulation. 1997; 96:2262–2271.
Article36. Quehenberger P, Bierhaus A, Fasching P, Muellner C, Klevesath M, Hong M, et al. Endothelin 1 transcription is controlled by nuclear factor-kappaB in AGE-stimulated cultured endothelial cells. Diabetes. 2000; 49:1561–1570.
Article37. Schmidt AM, Stern DM. RAGE: a new target for the prevention and treatment of the vascular and inflammatory complications of diabetes. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2000; 11:368–375.
Article38. Nishikawa T, Edelstein D, Du XL, Yamagishi S, Matsumura T, Kaneda Y, et al. Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three pathways of hyperglycaemic damage. Nature. 2000; 404:787–790.
Article39. Lin J, Bierhaus A, Bugert P, Dietrich N, Feng Y, Vom Hagen F, et al. Effect of R-(+)-alpha-lipoic acid on experimental diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia. 2006; 49:1089–1096.
Article40. Hur J, Sullivan KA, Pande M, Hong Y, Sima AA, Jagadish HV, et al. The identification of gene expression profiles associated with progression of human diabetic neuropathy. Brain. 2011; 134(Pt 11):3222–3235.
Article41. Haslbeck KM, Neundörfer B, Schlötzer-Schrehardtt U, Bierhaus A, Schleicher E, Pauli E, et al. Activation of the RAGE pathway: a general mechanism in the pathogenesis of polyneuropathies? Neurol Res. 2007; 29:103–110.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of Advanced Glycation End Products in Diabetic Vascular Complications
- Advanced Glycation End Products and Diabetic Complications
- Inhibition of advanced glycation end product formation by burdock root extract
- Letter: The Association between Serum Endogenous Secretory Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products and Vertebral Fractures in Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2012;27:289-94, Cheol Ho Lee et al.)
- Response: The Association between Serum Endogenous Secretory Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products and Vertebral Fractures in Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2012;27:289-94, Cheol Ho Lee et al.)