Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2012 Apr;5(Suppl 1):S14-S18.
Acoustic Analysis of Speech of Cochlear Implantees and Its Implications
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Speech-Language Pathology, Ali Yavar Jung National Institute for Hearing Handicapped, Mumbai, India. a_kant15@yahoo.co.in
- 2Hinduja Hospital, Mumbai, India.
- 3G.A.E.T. Center, Mumbai, India.
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Cochlear implantees have improved speech production skills compared with those using hearing aids, as reflected in their acoustic measures. When compared to normal hearing controls, implanted children had fronted vowel space and their /s/ and /integral/ noise frequencies overlapped. Acoustic analysis of speech provides an objective index of perceived differences in speech production which can be precursory in planning therapy. The objective of this study was to compare acoustic characteristics of speech in cochlear implantees with those of normal hearing age matched peers to understand implications.
METHODS
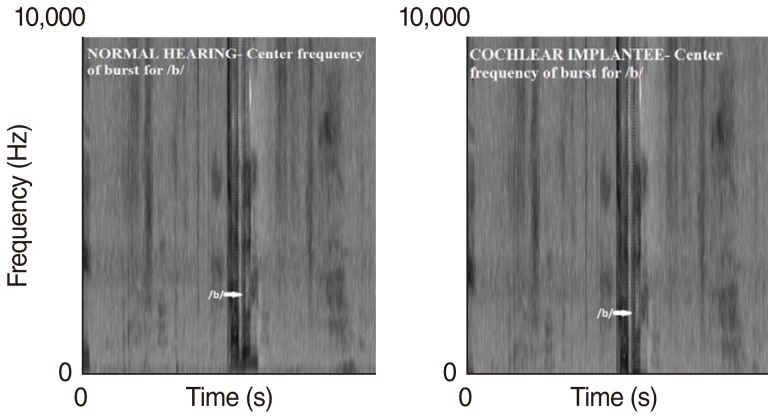
Group 1 consisted of 15 children with prelingual bilateral severe-profound hearing loss (age, 5-11 years; implanted between 4-10 years). Prior to an implant behind the ear, hearing aids were used; prior & post implantation subjects received at least 1 year of aural intervention. Group 2 consisted of 15 normal hearing age matched peers. Sustained productions of vowels and words with selected consonants were recorded. Using Praat software for acoustic analysis, digitized speech tokens were measured for F1, F2, and F3 of vowels; centre frequency (Hz) and energy concentration (dB) in burst; voice onset time (VOT in ms) for stops; centre frequency (Hz) of noise in /s/; rise time (ms) for affricates. A t-test was used to find significant differences between groups.
RESULTS
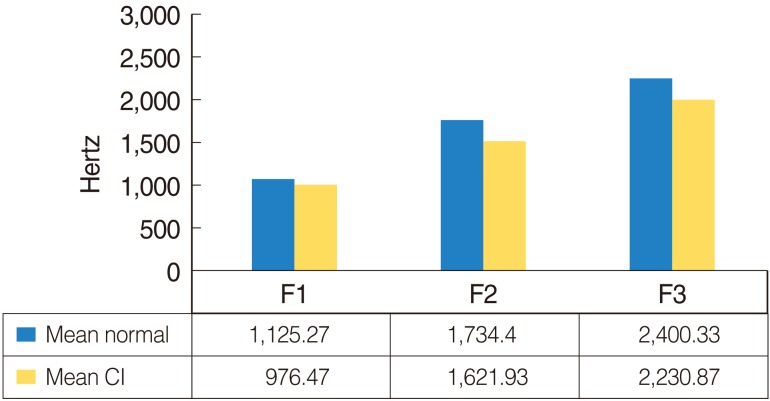
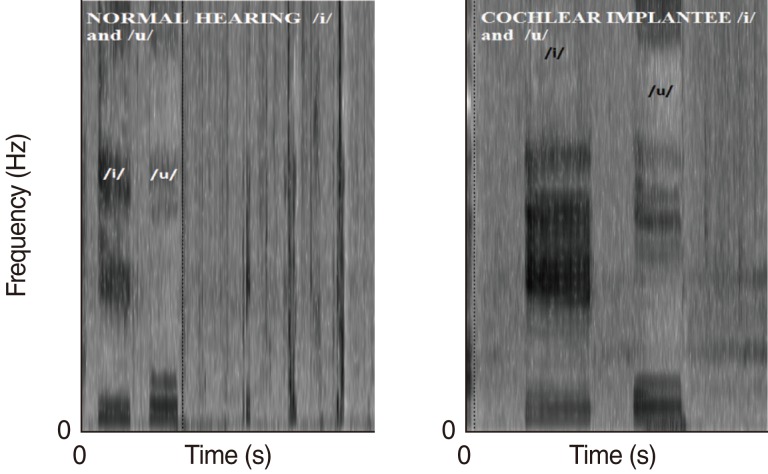
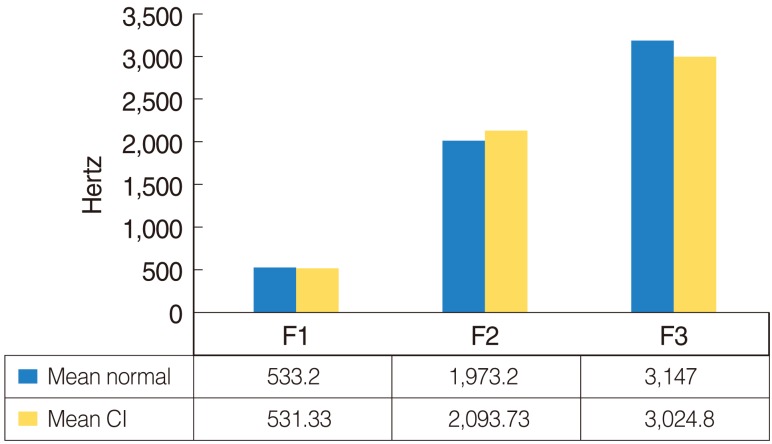
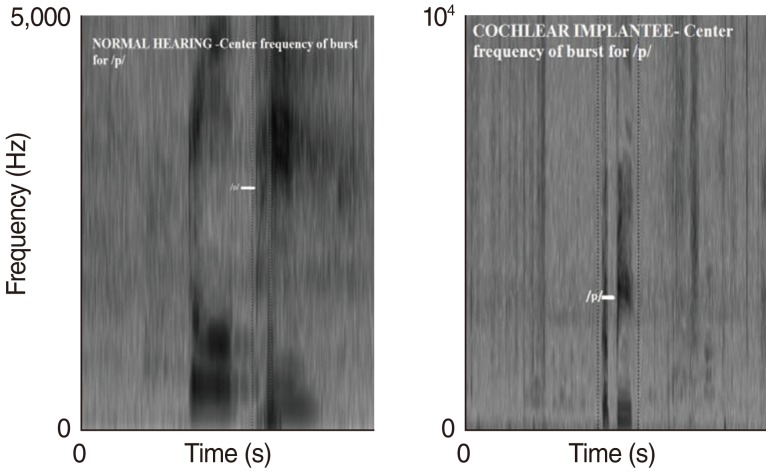
Significant differences were found in VOT for /b/, F1 and F2 of /e/, and F3 of /u/. No significant differences were found for centre frequency of burst, energy concentration for stops, centre frequency of noise in /s/, or rise time for affricates. These findings suggest that auditory feedback provided by cochlear implants enable subjects to monitor production of speech sounds.
CONCLUSION
Acoustic analysis of speech is an essential method for discerning characteristics which have or have not been improved by cochlear implantation and thus for planning intervention.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hudgins C, Numbers F. An investigation of the intelligibility of the speech of deaf and normal subjects. Genet Psychol Monogr. 1942; 25:289–392.2. Smith CR. Residual hearing and speech production in deaf children. J Speech Hear Res. 1975; 12. 18(4):795–811. PMID: 1207108.
Article3. Tobey E, Geers A, Brenner C. Speech production results: speech feature acquisition. Volta Rev. 1994; 11. 96(5):109–129.4. Tye-Murray N. Articulatory organizational strategies and the roles of audition. Volta Rev. 1992; 7. 94(3):243–259.5. Osberger MJ, Robbins AM, Berry SW, Todd SL, Hesketh LJ, Sedey A. Analysis of the spontaneous speech samples of children with cochlear implants or tactile aids. Am J Otol. 1991; 12 Suppl:151–164. PMID: 2069176.6. Fourakis M. Tempo, stress, and vowel reduction in American English. J Acoust Soc Am. 1991; 10. 90(4 Pt 1):1816–1827. PMID: 1960277.
Article7. Angelocci AA, Kopp GA, Holbrook A. The vowel formants of deaf and normal-hearing eleven- to fourteen-year-old boys. J Speech Hear Disord. 1964; 5. 29:156–160. PMID: 14147499.
Article8. Monsen RB. Second formant transitions of selected consonant-vowel combinations in the speech of deaf and normal-hearing children. J Speech Hear Res. 1976; 6. 19(2):279–289. PMID: 979202.
Article9. Monsen RB. Normal and reduced phonological space in the production of vowels by deaf adolescents. J Acoust Soc Am. 1976; 4. 59(S1):S86.
Article10. Kent RD, Read S. The acoustic analysis of speech. 1992. San Diego (CA): Singular Publishing.11. Uchanski RM, Geers AE. Acoustic characteristics of the speech of young cochlear implant users: a comparison with normal-hearing age-mates. Ear Hear. 2003; 2. 24(1 Suppl):90S–105S. PMID: 12612484.
Article12. Liker M, Mildner V, Sindija B. Acoustic analysis of the speech of children with cochlear implants: a longitudinal study. Clin Linguist Phon. 2007; 1. 21(1):1–11. PMID: 17364613.
Article13. Svirsky MA, Tobey EA. Effect of different types of auditory stimulation on vowel formant frequencies in multichannel cochlear implant users. J Acoust Soc Am. 1991; 6. 89(6):2895–2904. PMID: 1918629.
Article14. Stevens KN. Denes PB, David EE, editors. The quantal nature of speech: Evidence from articulatory - acoustic data. Human communication: a unified view. 1972. New York: McGraw-Hill;p. 51–66.15. Halle M, Hughes GW, Radley JP. Acoustic properties of stop consonants. J Acoust Soc Am. 1957; 1. 29(1):107–116.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Nasalance in Cochlear Implantees
- Preoperative Voice Parameters Affect the Postoperative Speech Intelligibility in Patients with Cochlear Implantation
- Definition and Clinical Implication of Temporal Fine Structure
- Acoustic Change Complex: Clinical Implications
- A Case of Electric Acoustic Stimulation Cochlear Implantation in Partial Deafness with Residual Low-Frequency Hearing