J Rheum Dis.
2013 Feb;20(1):24-29. 10.4078/jrd.2013.20.1.24.
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: Analysis of Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. ysong@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Health Policy Management, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3WCU Department of Molecular Medicine and Biopharmaceutical Sciences, Medical Research Center, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2223045
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2013.20.1.24
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
There are currently limited treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). In the process of pursuing further treatment strategies for this subgroup of patients, it is prudent to study what medications have been commonly prescribed, particularly for disease modifying anti-rheumatic agents (DMARDs) in Korea.
METHODS
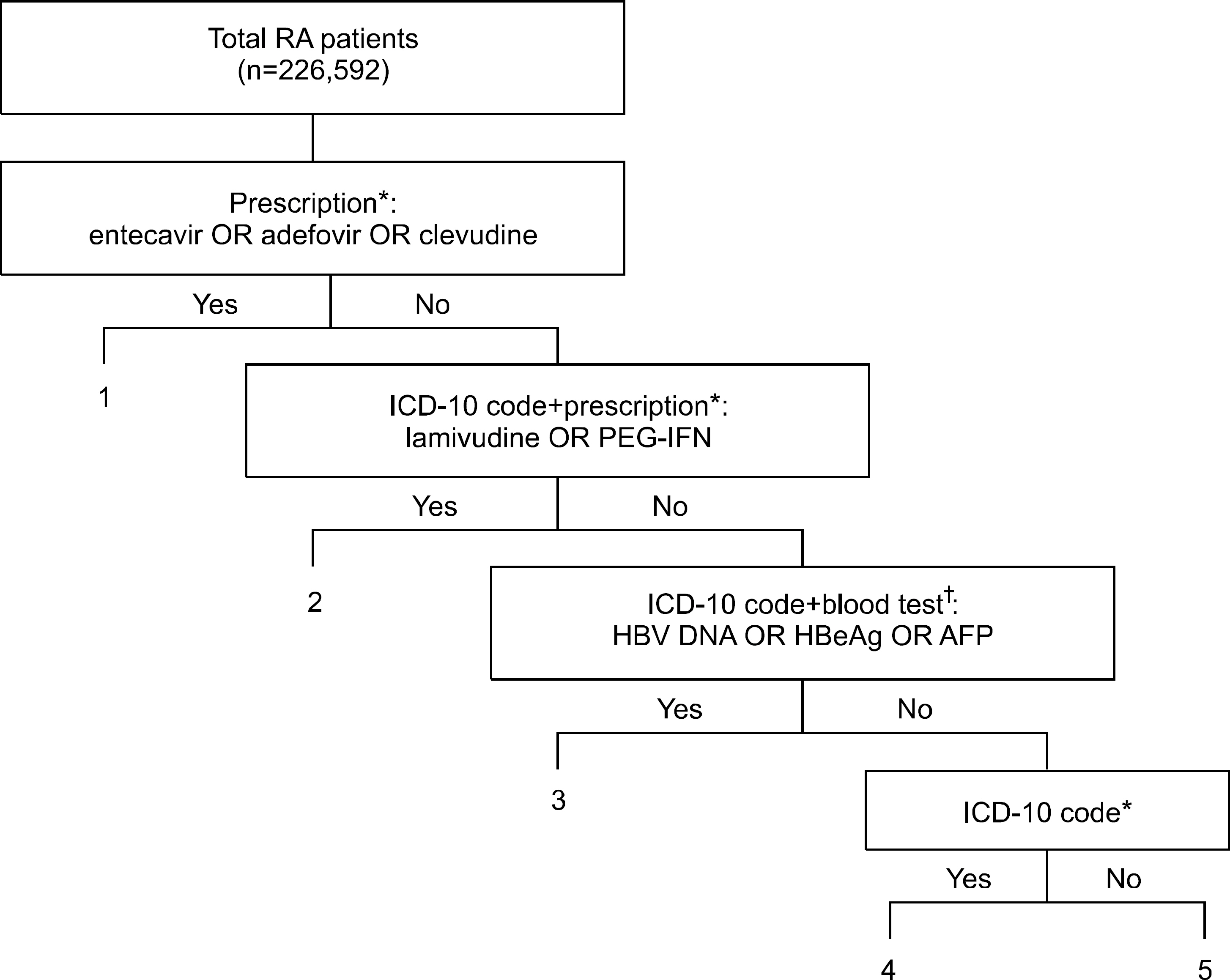
We analyzed the Korean National Health Insurance claims database (2007~2009) of RA patients through co-working with the Clinical Research Center for RA (CRCRA). Patients with CHB were defined by an algorithm including prescription information, blood tests, and the ICD-10 code.
RESULTS
There were 8,677 CHB patients (3.8%) among 226,592 RA patients in the database. The age distribution or gender difference in CHB patients was comparable to the general RA population. Hydroxychloroquine was the most frequently (66.2%) prescribed DMARD. Thirty four percent of CHB patients had been prescribed with methotrexate (MTX) during the study period; most of them without concomitant anti-viral treatment. About 3% of RA patients with CHB were prescribed with TNF inhibitors.
CONCLUSION
Apart from the published expert recommendations, MTX still seems to be one of the main DMARDs prescribed to Korean RA patients with CHB. This is most likely due to the lack of evidence-based, effective treatment strategies for this subgroup of patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Disease Characteristics and Change in Arthritis Activity according to Treatment in Hepatitis B Surface Antigen-positive Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: a Retrospective Chart Review Study
Yeonghee Eun, In Young Kim, Hyemin Jeong, Hyungjin Kim, Jaejoon Lee, Moon Seok Choi, Eunmi Koh, Hoon-Suk Cha
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(23):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e168.
Reference
-
References
1. Saag KG, Teng GG, Patkar NM, Anuntiyo J, Finney C, Curtis JR, et al. American College of Rheumatology. American College of Rheumatology 2008 recommendations for the use of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 59:762–84.
Article2. Jeong S, Yim HW, Bae SH, Lee WC. Changes of hepatitis B surface antigen seroprevalence in Korea, 1998–2005. Korean J Epidemiol. 2008; 30:119–27.
Article3. Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, Curtis JR, Kavanaugh AF, Kremer JM, et al. 2012 update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012; 64:625–39.
Article4. Sung YK, Cho SK, Choi CB, Bae SC. Prevalence and incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in South Korea. Rheumatol Int. 2012; [Epub ahead of print].
Article5. Kwon JM, Cho SK, Kim JH, Lee EK. Medical costs for Korean patients with rheumatoid arthritis based on the national claims database. Rheumatol Int. 2012; 32:2893–9.
Article6. Hur NW, Choi CB, Uhm WS, Bae SC. The prevalence and trend of arthritis in Korea: results from Korea National health and nutrition examination surveys. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2008; 15:11–26.
Article7. Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B: update 2009. Hepatology. 2009; 50:661–2.
Article8. Liaw YF, Leung N, Kao JH, Piratvisuth T, Gane E, Han KH, et al. Chronic Hepatitis B Guideline Working Party of the Asian-Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver. Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B: a 2008 update. Hepatol Int. 2008; 2:263–83.
Article9. European Association For The Study Of The Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2009; 50:227–42.10. Hoofnagle JH. Reactivation of hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2009; 49(5 Suppl):S156–65.
Article11. Mori S. Past hepatitis B virus infection in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving biological and/or nonbiological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Mod Rheumatol. 2011; 21:621–7.
Article12. Flowers MA, Heathcote J, Wanless IR, Sherman M, Reynolds WJ, Cameron RG, et al. Fulminant hepatitis as a consequence of reactivation of hepatitis B virus infection after discontinuation of low-dose methotrexate therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1990; 112:381–2.
Article13. Ryu HH, Lee EY, Shin K, Choi IA, Lee YJ, Yoo B, et al. Hepatitis B virus reactivation in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis patients treated with anti-TNF α agents: a retrospective analysis of 49 cases. Clin Rheumatol. 2012; 31:931–6.14. Lan JL, Chen YM, Hsieh TY, Chen YH, Hsieh CW, Chen DY, et al. Kinetics of viral loads and risk of hepatitis B virus reactivation in hepatitis B core antibody-positive rheumatoid arthritis patients undergoing anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha therapy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70:1719–25.
Article15. Sung YK, Cho SK, Choi CB, Park SY, Shim J, Ahn JK, et al. Korean Observational Study Network for Arthritis (KORONA): establishment of a prospective multicenter cohort for rheumatoid arthritis in South Korea. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 41:745–51.
Article16. Furst DE, Keystone EC, Braun J, Breedveld FC, Burmester GR, De Benedetti F, et al. Updated consensus statement on biological agents for the treatment of rheumatic diseases, 2010. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70(Suppl 1):i2–36.
Article17. Kim YJ, Bae SC, Sung YK, Kim TH, Jun JB, Yoo DH, et al. Possible reactivation of potential hepatitis B virus occult infection by tumor necrosis factor-alpha blocker in the treatment of rheumatic diseases. J Rheumatol. 2010; 37:346–50.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis Following Peginterferon Alpha-2A and Ribavirin Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis C
- Sensitivity of Medical Insurance Claims Data Using Population-based Cancer Registry Data
- Medical Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Synovial Chondromatosis in Knee Masquerading as Tuberculosis Arthritis
- Clinical Study Using Healthcare Claims Database