J Korean Surg Soc.
2013 Apr;84(4):252-255. 10.4174/jkss.2013.84.4.252.
Gastrojejuno-colic fistula after gastrojejunostomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Dankook University Hospital, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. ysjee@dkuh.co.kr
- KMID: 2212471
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2013.84.4.252
Abstract
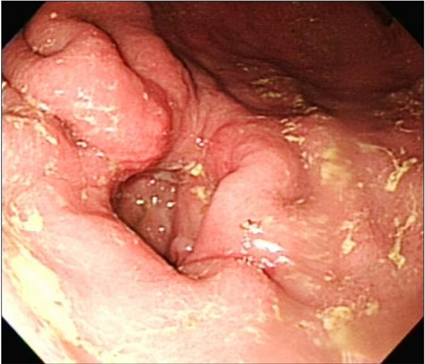
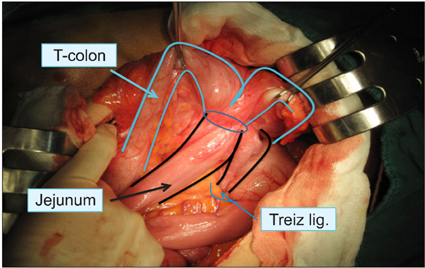
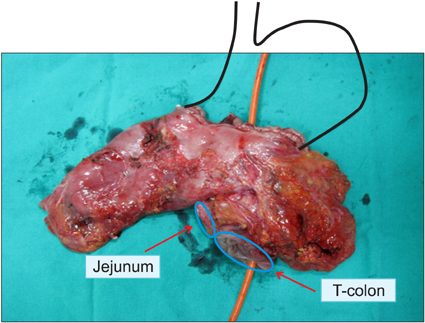
- Gastrojejunocolic fistula is a rare condition after gastrojejunostomy. It is severe complications of gastrojejunostomy, which results an inadequate resection or incomplete vagotomy during peptic ulcer surgery. The symptoms are diarrhea, upper abdominal pain, bleeding, vomiting and weight loss. A 55-year-old man with chronic diarrhea and weight loss for 6 months visited Dankook University Hospital. The patient had received a truncal vagotomy and gastrojejunostomy for duodenal ulcer obstruction 15 years previously. The patient underwent gastroscopy and upper gastrointestinal series evaluations, which detected the gastrojejunocolic fistula. After improving of malnutrition, an exploratory laparotomy was undertaken, which revealed that the gastrojejunostomy site and the T-colon formed adhesion and fistula. En block resection of the distal stomach and T-colon included the gastrojejunocolic fistula, and Roux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy was performed. Recovery was uneventful and the patient remained well at the follow-up. We report a gastrojejunocolic fistula, which is a rare case after gastrojejunostomy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kece C, Dalgic T, Nadir I, Baydar B, Nessar G, Ozdil B, et al. Current diagnosis and management of gastrojejunocolic fistula. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2010. 4:173–177.2. Takemura M, Hamano G, Nishioka T, Takii M, Mayumi K, Ikebe T. One-stage laparoscopic-assisted resection of gastrojejunocolic fistula after gastrojejunostomy for duodenal ulcer: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2011. 5:543.3. Chung DP, Li RS, Leong HT. Diagnosis and current management of gastrojejunocolic fistula. Hong Kong Med J. 2001. 7:439–441.4. D'Amata G, Rahili A, Karimdjee-Soilihi B, Gelsi E, Avallone S, Benchimol D. Gastrojejunocolic fistula after gastric surgery for duodenal ulcer: case report. G Chir. 2006. 27:360–362.5. Cody JH, DiVincenti FC, Cowick DR, Mahanes JR. Gastrocolic and gastrojejunocolic fistulae: report of twelve cases and review of the literature. Ann Surg. 1975. 181:376–380.6. Matsuo S, Eto T, Ohara O, Miyazaki J, Tsunoda T, Kanematsu T. Gastrocolic fistula originating from transverse colon cancer: report of a case and review of the Japanese literature. Surg Today. 1994. 24:1085–1089.7. Choi SW, Yang JM, Kim SS, Kang SH, Ro HJ, Song KS, et al. A case of combined gastrojejunal and gastrocolic fistula secondary to gastric cancer. J Korean Med Sci. 1996. 11:437–439.8. Pfeiffer DB. The surgical treatment of gastrojejunocolic fistula. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1941. 72:282–289.9. Subramaniasivam N, Ananthakrishnan N, Kate V, Smile SR, Jagdish S, Srinivasan K. Gastrojejunocolic fistula following surgery for peptic ulcer. Trop Gastroenterol. 1997. 18:183–187.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cholecysto - Duodeno - Colic Fistula : Report of One Case
- Post traumatic reno-colic fistula and intrarenal aneurysm: case report
- Case of Malignant Duodeno-Colic Fistula Showing Typical Endoscopic Findings
- A Case of Gastro-colic Fistula with Peritonitis Due to Ingested Magnets
- Gastro-umbilical Fistula as a Rare Complication of Benign Gastric Ulcer Perforation: A Case Report