J Clin Neurol.
2008 Jun;4(2):94-98. 10.3988/jcn.2008.4.2.94.
Severe Episodic Memory Impairment in a Patient With Clinical Features Compatible With Corticobasal Degeneration
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. neuropark@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2178929
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2008.4.2.94
Abstract
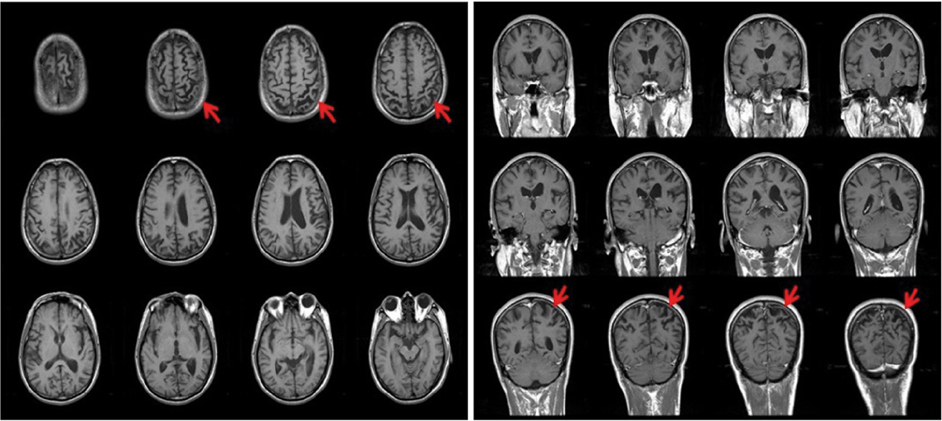
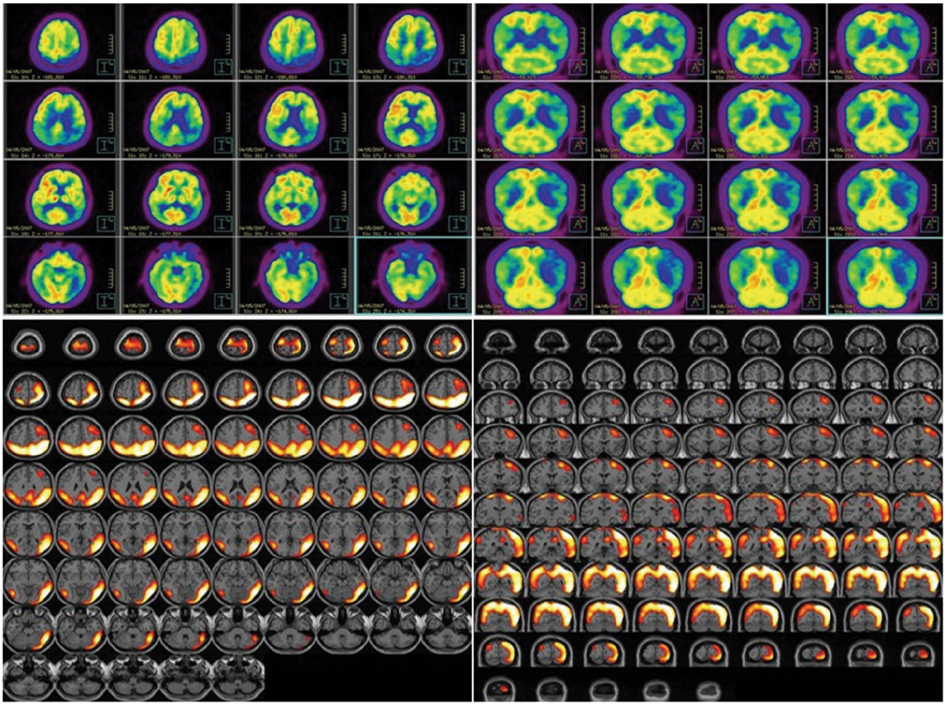
- Corticobasal degeneration (CBD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by asymmetric parkinsonism associated with apraxia, cortical sensory loss, and alien-limb phenomenon. Neuropsychological testing in patients with CBD typically shows deficits in executive functions, praxis, language, and visuospatial functioning, but not in memory. We report a CBD patient with severely impaired memory function but relatively mild motor symptoms. Detailed neuropsychological assessment showed significant verbal and visual memory deficits accompanied by frontal executive dysfunctions. Our observations indicate that CBD can in rare cases present with severe episodic memory impairment associated with frontal executive dysfunctions in the early stage of illness.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Riley DE, Lang AE, Lewis A, Resch L, Ashby P, Hornykiewicz O, et al. Cortical-basal ganglionic degeneration. Neurology. 1990. 40:1203–1212.
Article2. Boeve BF, Maraganore DM, Parisi JE, Ahlskog JE, Graff-Radford N, Caselli RJ, et al. Pathologic heterogeneity in clinically diagnosed corticobasal degeneration. Neurology. 1999. 53:795–800.
Article3. Piao YS, Hayashi S, Wakabayashi K, Kakita A, Aida I, Yamada M, et al. Cerebellar cortical tau pathology in progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 2002. 103:469–474.
Article4. Soliveri P, Monza D, Paridi D, Radice D, Grisoli M, Testa D, et al. Cognitive and magnetic resonance imaging aspects of corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology. 1999. 53:502–507.
Article5. Riley D, Lang AE. Corticobasal degeneration. Clinical diagnostic criteria. Adv Neurol. 2000. 82:29–34.6. Wenning GK, Litvan I, Jankovic J, Granata R, Mangone CA, McKee A, et al. Natural history and survival of 14 patients with corticobasal degeneration confirmed at postmortem examination. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998. 64:184–189.
Article7. Rinne JO, Lee MS, Thompson PD, Marsden CD. Corticobasal degeneration. A clinical study of 36 cases. Brain. 1994. 117:1183–1196.
Article8. Grimes DA, Lang AE, Bergeron CB. Dementia as the most common presentation of cortical-basal ganglionic degeneration. Neurology. 1999. 53:1969–1974.
Article9. Schneider JA, Watts RL, Gearing M, Brewer RP, Mirra SS. Corticobasal degeneration: neuropathologic and clinical heterogeneity. Neurology. 1997. 48:959–969.
Article10. Pillon B, Blin J, Vidailhet M, Deweer B, Sirigu A, Dubois B, et al. . Neurology. 1995. 45:1477–1483.11. Massman PJ, Kreiter KT, Jankovic J, Doody RS. Neuropsychological functioning in cortical-basal ganglionic degeneration: Differentiation from Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1996. 46:720–726.
Article12. Pillon B, Dubois B. Memory and executive processes in corticobasal degeneration. Adv Neurol. 2000. 82:91–101.13. Graham NL, Bak TH, Hodges JR. Corticobasal degeneration as a cognitive disorder. Mov Disord. 2003. 18:1224–1232.
Article14. Caine D. Posterior cortical atrophy: a review of the literature. Neurocase. 2004. 10:382–385.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Corticobasal Degeneration Presenting as Non-Fluent/Agrammatic Primary Progressive Aphasia: A Case Report
- Clinical Syndrome of Corticobasal Degeneration
- Memory Impairment in Dementing Patients
- Time Perception and Memory in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Preliminary Study
- Primary Progressive Aphasia and the Left Hemisphere Language Network