Cancer Res Treat.
2010 Dec;42(4):203-209.
Cisplatin-Based Combination Chemotherapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Single Center Experience before the Sorafenib Era
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. jhkimmd@snu.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Systemic chemotherapy is the only option for patients with unresectable/metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who are not candidates for local/regional treatment. However, the response to such treatment and survival are poor, especially in hepatitis B virus (HBV) endemic areas. The aim of this study was to determine the efficacy of cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy and identify a subgroup of advanced HCC patients with favorable responses.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The medical records of all consecutive patients with unresectable/metastatic HCC who received cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy between January 2003 and October 2009 were reviewed. Time to progression (TTP) and overall survival (OS) were determined using Kaplan-Meier analysis. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to identify prognostic factors for TTP and OS.
RESULTS
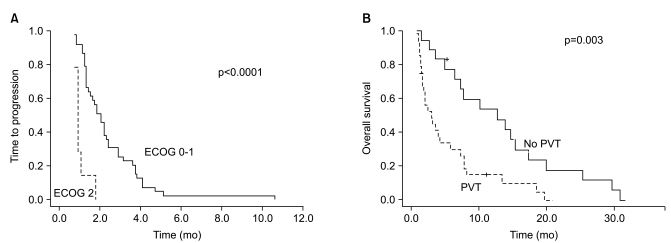
Data for 46 patients were analyzed. First-line chemotherapies consisted of cisplatin-based combination treatment with doxorubicin, fluoropyrimidines and gemcitabine. The response rate for all patients was 4.3%. The median TTP and OS were 1.8 (95%confidence interval [CI], 1.1 to 2.5) and 7.2 (95% CI, 3.0 to 11.5) months, respectively. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS), Child classification, Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) score and portal vein thrombosis (PVT) were identified by univariate analyses as prognostic factors for TTP and OS. ECOG PS (hazard ratio [HR], 4.51; 95% CI, 1.61 to 12.6; p=0.004) and PVT (HR, 2.12; 95% CI, 1.10 to 4.11; p=0.026) were independent prognostic factors for TTP.
CONCLUSION
Cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy in patients with advanced HCC has a low response rate and short TTP regardless of the chemotherapy regimen used. Patients with a good ECOG PS and without PVT can be considered candidates for cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Carcinoma, Hepatocellular
Child
Deoxycytidine
Doxorubicin
Drug Therapy, Combination
Hepatitis B virus
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Liver Neoplasms
Medical Records
Multivariate Analysis
Niacinamide
Phenylurea Compounds
Platinum
Portal Vein
Prognosis
Thrombosis
Thymine Nucleotides
Deoxycytidine
Doxorubicin
Niacinamide
Phenylurea Compounds
Platinum
Thymine Nucleotides
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nowak AK, Chow PK, Findlay M. Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a review. Eur J Cancer. 2004; 40:1474–1484. PMID: 15196530.
Article2. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:378–390. PMID: 18650514.
Article3. Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:25–34. PMID: 19095497.
Article4. Sciarrino E, Simonetti RG, Le Moli S, Pagliaro L. Adriamycin treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma: experience with 109 patients. Cancer. 1985; 56:2751–2755. PMID: 2413981.
Article5. Okada S, Okazaki N, Nose H, Shimada Y, Yoshimori M, Aoki K. A phase 2 study of cisplatin in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 1993; 50:22–26. PMID: 7678453.
Article6. Lee J, Park JO, Kim WS, Park SH, Park KW, Choi MS, et al. Phase II study of doxorubicin and cisplatin in patients with metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2004; 54:385–390. PMID: 15248028.
Article7. Parikh PM, Fuloria J, Babu G, Doval DC, Awasthy BS, Pai VR, et al. A phase II study of gemcitabine and cisplatin in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Trop Gastroenterol. 2005; 26:115–118. PMID: 16512457.8. Lee JO, Lee KW, Oh DY, Kim JH, Im SA, Kim TY, et al. Combination chemotherapy with capecitabine and cisplatin for patients with metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2009; 20:1402–1407. PMID: 19502532.
Article9. Ikeda M, Okusaka T, Ueno H, Takezako Y, Morizane C. A phase II trial of continuous infusion of 5-fluorouracil, mitoxantrone, and cisplatin for metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2005; 103:756–762. PMID: 15637692.
Article10. Lai CL, Wu PC, Chan GC, Lok AS, Lin HJ. Doxorubicin versus no antitumor therapy in inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective randomized trial. Cancer. 1988; 62:479–483. PMID: 2839280.
Article11. Yeo W, Mok TS, Zee B, Leung TW, Lai PB, Lau WY, et al. A randomized phase III study of doxorubicin versus cisplatin/interferon alpha-2b/doxorubicin/fluorouracil (PIAF) combination chemotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005; 97:1532–1538. PMID: 16234567.12. Kang BL, Yuh YJ, Kim SR, Song HS, Lee SN, Shin DB, et al. A phase II study of doxorubicin and cisplatin combination chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Med. 2005; 68:203–210.13. Kong XB, Yang ZK, Liang LJ, Huang JF, Lin HL. Overexpression of P-glycoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical implication. World J Gastroenterol. 2000; 6:134–135. PMID: 11819542.14. Katiyar S, Dash BC, Thakur V, Guptan RC, Sarin SK, Das BC. P53 tumor suppressor gene mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma patients in India. Cancer. 2000; 88:1565–1573. PMID: 10738214.
Article15. Park JW. Practice guideline for diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Hepatol. 2004; 10:88–98. PMID: 15218342.16. American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 2002. 6th ed. New York: Springer.17. A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435 patients: the Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) investigators. Hepatology. 1998; 28:751–755. PMID: 9731568.18. Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer. National Cancer Institute of the United States. National Cancer Institute of Canada. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000; 92:205–216. PMID: 10655437.
Article19. The Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) Investigators. Prospective validation of the CLIP score: a new prognostic system for patients with cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2000; 31:840–845. PMID: 10733537.20. Farinati F, Rinaldi M, Gianni S, Naccarato R. How should patients with hepatocellular carcinoma be staged? Validation of a new prognostic system. Cancer. 2000; 89:2266–2273. PMID: 11147597.21. Levy I, Sherman M. Staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: assessment of the CLIP, Okuda, and Child-Pugh staging systems in a cohort of 257 patients in Toronto. Gut. 2002; 50:881–885. PMID: 12010894.
Article22. Ueno S, Tanabe G, Sako K, Hiwaki T, Hokotate H, Fukukura Y, et al. Discrimination value of the new western prognostic system (CLIP score) for hepatocellular carcinoma in 662 Japanese patients. Cancer of the Liver Italian Program. Hepatology. 2001; 34:529–534. PMID: 11526539.23. Leung TW, Tang AM, Zee B, Yu SC, Lai PB, Lau WY, et al. Factors predicting response and survival in 149 patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated by combination cisplatin, interferon-alpha, doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy. Cancer. 2002; 94:421–427. PMID: 11905412.
Article24. Zhang XB, Wang JH, Yan ZP, Qian S, Du SS, Zeng ZC. Hepatocellular carcinoma with main portal vein tumor thrombus: treatment with 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy after portal vein stenting and transarterial chemoembolization. Cancer. 2009; 115:1245–1252. PMID: 19156918.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatments Other than Sorafenib for Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Can metronomic chemotherapy be an alternative to sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma?
- A Case of Achieving Complete Remission with Combination of Sorafenib and Tegafur in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Progression of Disease after Sorafenib Therapy
- Treatment options after sorafenib failure in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- Sorafenib-induced Pancreatic Pseudocyst in a Patient with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Rare Adverse Event