Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2016 Jun;9(2):98-103. 10.21053/ceo.2015.00542.
Methodology for Intraoperative Laser Doppler Vibrometry Measurements of Ossicular Chain Reconstruction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology, Medical University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland. mlachowska@wum.edu.pl
- KMID: 2165050
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2015.00542
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Despite the increasing number of research concerning the applications of the Laser Doppler Vibrometry (LDV) in medicine, its usefulness is still under discussion. The aim of this study is to present a methodology developed in our Department for the LDV intraoperative assessment of ossicular chain reconstruction.
METHODS
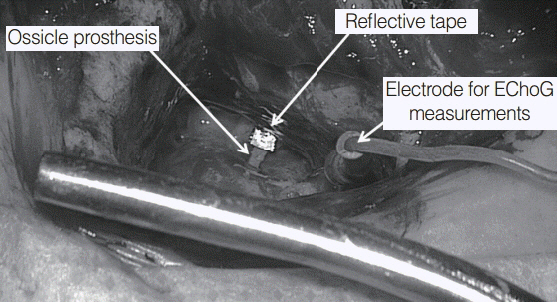
Ten patients who underwent "second look" tympanoplasty were involved in the study. The measurements of the acoustic conductivity of the middle ear were performed using the LDV system. Tone bursts with carrier frequencies of 500, 1,000, 2,000, and 4,000 Hz set in motion the ossicular chain. The study was divided into four experiments that examined the intra- and interindividual reproducibility, the utility of the posterior tympanotomy, the impact of changes in the laser beam angle, and the influence of reflective tape presence on measurements.
RESULTS
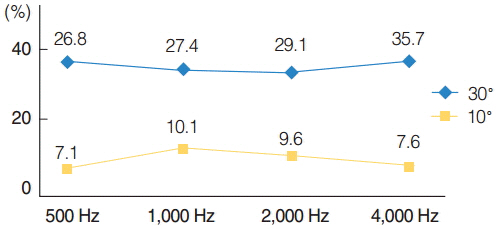
There were no statistically significant differences between the two measurements performed in the same patient. However, interindividual differences were significant. In all cases, posterior tympanotomy proved to be useful for LDV measurements of the ossicular prosthesis vibrations. In most cases, changing the laser beam angle decreased signal amplitude about 1.5% (not significant change). The reflective tape was necessary to achieve adequate reflection of the laser beam.
CONCLUSION
LDV showed to be a valuable noncontact intraoperative tool for measurements of the middle ear conductive system mobility with a very good intraindividual repeatability. Neither a small change in the angle of the laser beam nor performing the measurements through posterior tympanotomy showed a significant influence on the results. Reflective tape was necessary to obtain good quality responses in LDV measurements.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Whittemore KR Jr, Merchant SN, Poon BB, Rosowski JJ. A normative study of tympanic membrane motion in humans using a laser Doppler vibrometer (LDV). Hear Res. 2004; Jan. 187(1-2):85–104.
Article2. Dai C, Gan RZ. Change of middle ear transfer function in otitis media with effusion model of guinea pigs. Hear Res. 2008; Sep. 243(1-2):78–86.
Article3. Rosowski JJ, Merchant SN, Ravicz ME. Middle ear mechanics of type IV and type V tympanoplasty: I. model analysis and predictions. Am J Otol. 1995; Sep. 16(5):555–64.4. Zenner HP, Freitag HG, Linti C, Steinhardt U, Rodriguez Jorge J, Preyer S, et al. Acoustomechanical properties of open TTP titanium middle ear prostheses. Hear Res. 2004; Jun. 192(1-2):36–46.
Article5. Huber A, Linder T, Ferrazzini M, Schmid S, Dillier N, Stoeckli S, et al. Intraoperative assessment of stapes movement. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001; Jan. 110(1):31–5.
Article6. Huttenbrink KB. Mechanics of the ear ossicle chain in static pressures. I. The normal middle ear. Laryngol Rhinol Otol (Stuttg). 1988; Feb. 67(2):45–52.7. Merchant SN, Ravicz ME, Puria S, Voss SE, Whittemore KR Jr, Peake WT, et al. Analysis of middle ear mechanics and application to diseased and reconstructed ears. Am J Otol. 1997; Mar. 18(2):139–54.8. Niemczyk K, Sokolowski J, Bartoszewicz R, Morawski K, Bruzgielewicz A, Rygalska B. The methodology of measurements of ossicular chain movability during tympanoplasty using Laser Doppler vibrometry. Otolaryngol Pol. 2012; Mar-Apr. 66(2):126–31.9. Heiland KE, Goode RL, Asai M, Huber AM. A human temporal bone study of stapes footplate movement. Am J Otol. 1999; Jan. 20(1):81–6.10. Kirikae I. The structure and function of the middle ear. Tokyo: University of Tokyo Press;1960.11. Chien W, Ravicz ME, Merchant SN, Rosowski JJ. The effect of methodological differences in the measurement of stapes motion in live and cadaver ears. Audiol Neurootol. 2006; Mar. 11(3):183–97.
Article12. Rosowski JJ, Mehta RP, Merchant SN. Diagnostic utility of laser-Doppler vibrometry in conductive hearing loss with normal tympanic membrane. Otol Neurotol. 2003; Mar. 24(2):165–75.
Article13. Ruggero MA, Temchin AN. Middle-ear transmission in humans: wideband, not frequency-tuned? Acoust Res Lett Online. 2003; Mar. 4:53–8.
Article14. Sokołowski J, Niemczyk K, Bartoszewicz R, Morawski K, Bruzgielewicz A. Method of ossicular chain valuation. Experimental measurement and clinical application. Otolaryngol Pol. 2009; Sep-Oct. 63(5):432–6.15. Goode RL, Ball G, Nishihara S, Nakamura K. Laser Doppler vibrometer (LDV): a new clinical tool for the otologist. Am J Otol. 1996; Nov. 17(6):813–22.16. Asai M, Heiland KE, Huber AM, Goode RL. Evaluation of a cement incus replacement prosthesis in a temporal bone model. Acta Otolaryngol. 1999. 119(5):p. 573–6.17. Asai M, Huber AM, Goode RL. Analysis of the best site on the stapes footplate for ossicular chain reconstruction. Acta Otolaryngol. 1999. 119(3):p. 356–61.18. Huber AM, Schwab C, Linder T, Stoeckli SJ, Ferrazzini M, Dillier N, et al. Evaluation of eardrum laser doppler interferometry as a diagnostic tool. Laryngoscope. 2001; Mar. 111(3):501–7.
Article19. Chien W, Rosowski JJ, Ravicz ME, Rauch SD, Smullen J, Merchant SN. Measurements of stapes velocity in live human ears. Hear Res. 2009; Mar. 249(1-2):54–61.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Multiple Ossicular Chain Disruption After Penetrating Injury and Tympanic Membrane Healing
- Ossicular chain reconstruction: the TORP and PORP
- Variability of Measurements of the Optic Nerve Head and Peripapillary Retinal Blood Flow by Scanning Laser Doppler Flowmetry
- Post-Traumatic Conductive Hearing Loss
- USE OF LASER DOPPLER FLOWMETRY FOR ESTIMATION OF BURN DEPTH