Prog Med Phys.
2015 Dec;26(4):223-228. 10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.223.
Evaluation of Dosimetric Characteristics of a Double-focused Dynamic Micro-Multileaf Collimator (DMLC)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Presbyterian Medical Center of Korea, Jeonju, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiation Oncology, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Incheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Medical Physics, Kyonggi University of Korea, Suwon, Korea.
- 6Department of Medical Physics, Kyonggi University of Korea, Suwon, Korea. ynkang33@gmail.com
- KMID: 2151755
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.223
Abstract
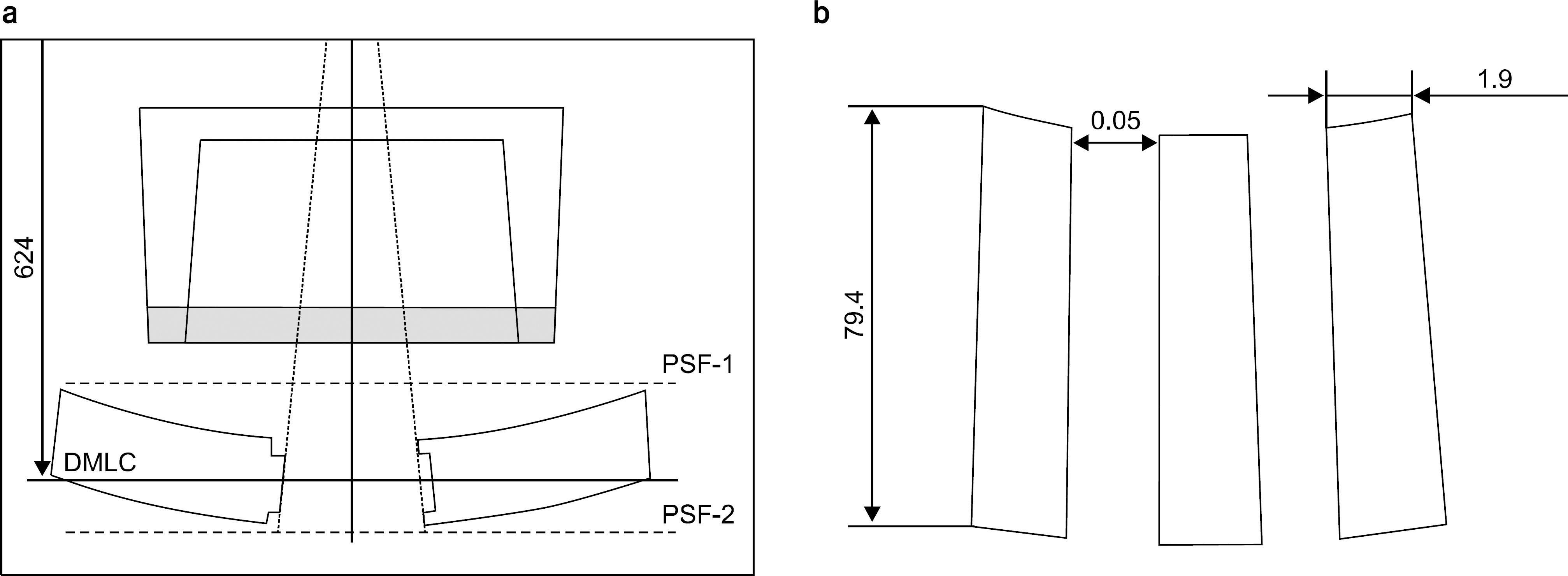
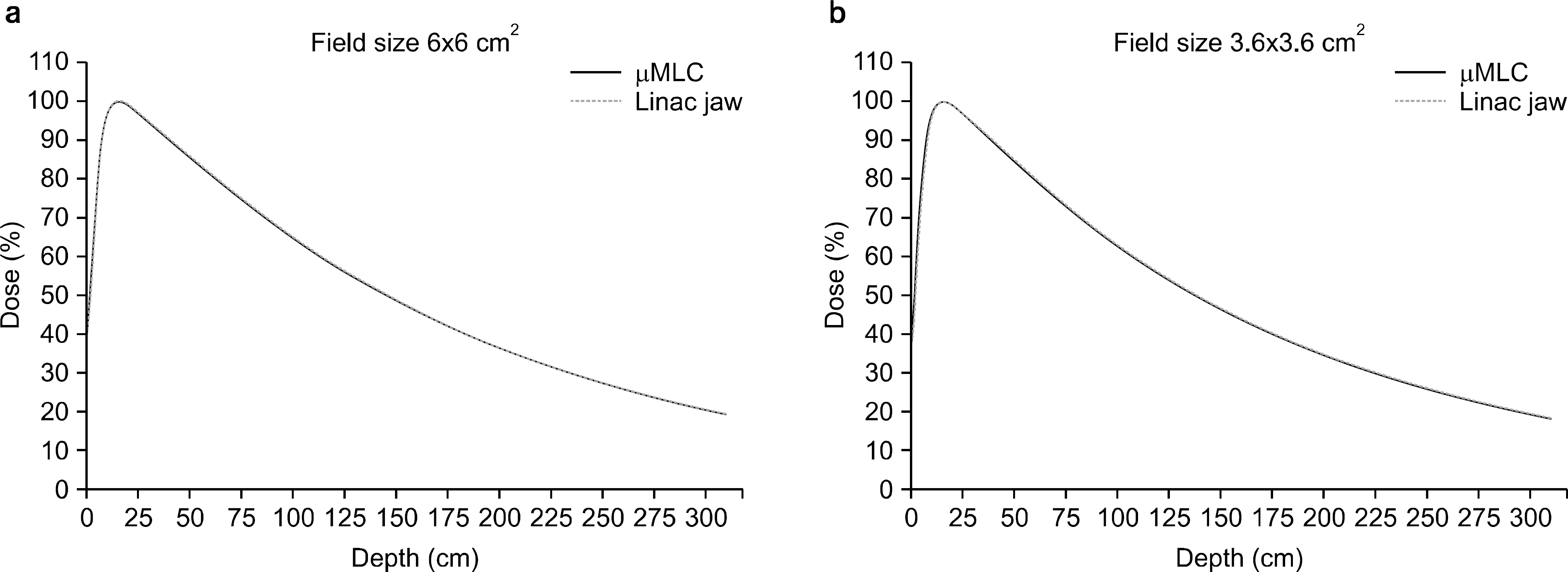
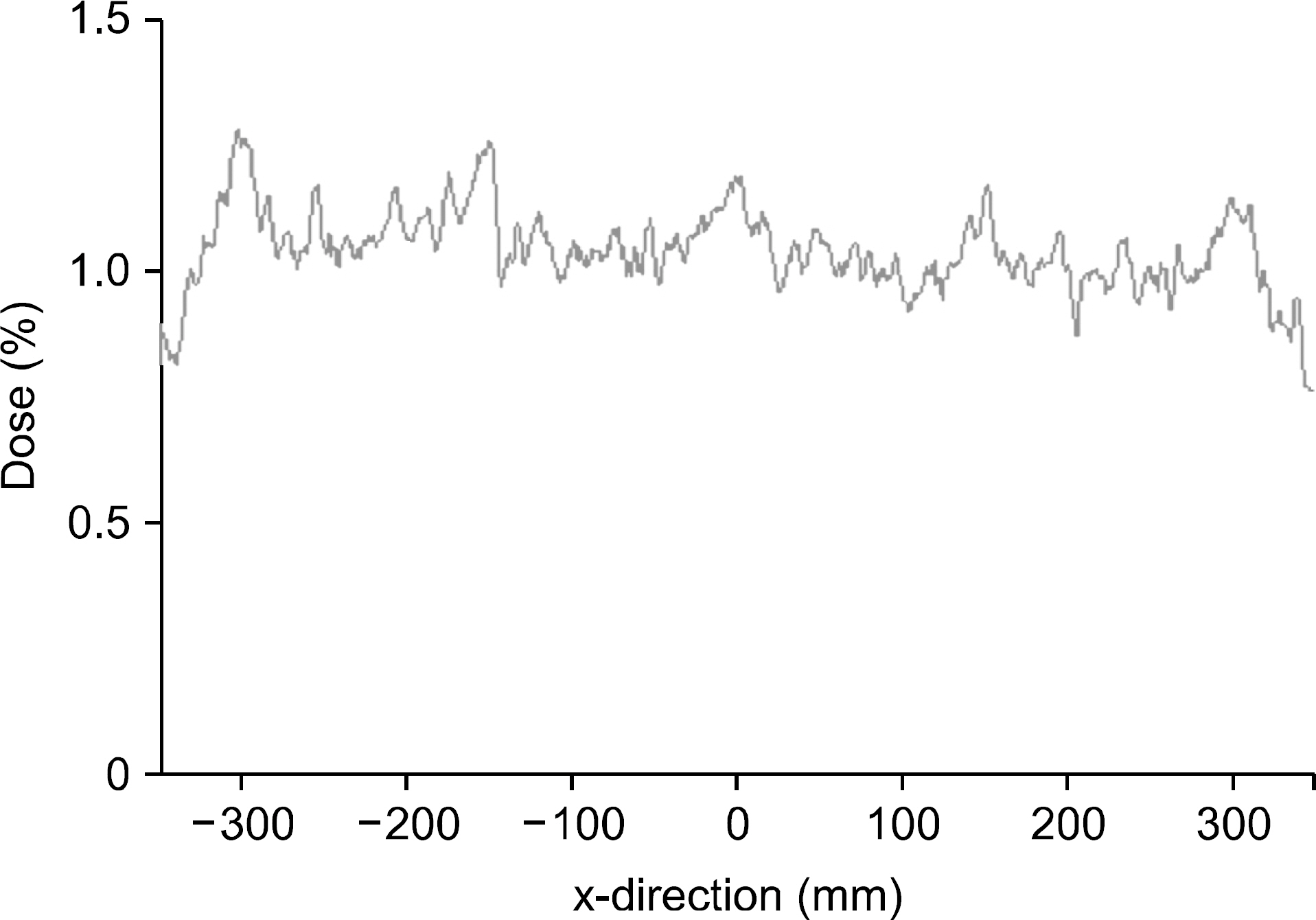
- Double-focused micro-Multileaf Collimator (microMLC) is able to create radiation fields having sharper dose gradients at the field edges than common MLC. Therefore, microMLC has been used for the stereotactic radio-surgery (SRS) and Stereotactic Radiotherapy (SRT). We evaluated the dosimetric characteristics of a double-focused Dynamic-microMLC (DMLC) attached to the Elekta Synergy linear accelerator. For this study, the dosimetric parameters including, Percent Depth Dose (PDD), Leaf leakage and penumbra, have been measured by using of the radiochromic films (GafChromic EBT2), EDGE diode detector and three-dimensional water phantom. All datas were measured on 6 MV x-ray. As a result, The DMLC shows transmission below to 1% and because of double-focused construction of the DMLC, the penumbras of fields with DMLC are independent from the field sizes. In this paper, the resulting dosimetric evaluations proved the applicability of the DMLC attached to the Elekta Synergy linear accelerator.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Bortfeld T, Oelfke U, Nill S. What is the optimum leaf width of a multileaf collimator? Med Phys. 27(11):2494–502. 2000.
Article2. Fischer M, Todorovic M, Drud E, and Cremers F, Commissioning of a double-focused micro multileaf collimator (μMLC). J Appl Clin Med Phys. 11(2):81–91. 2010.3. AAPM Report No. 72: Basic Applications of Multileaf Collimators, Report of Task Group 50 (. 2001.4. Meeks SL, Bova FJ, Kim S, Tome WA, and Buatti JM, Dosimetric characteristics of a double-focused miniature multileaf collimator. Med Phys. 26(5):729–733. 1999.5. Galal MM, Keogh S, and Khalil S. Dosimetric and mechanical characteristics of a commercial dynamic μMLC used in SRS. Med Phys. 38(7):4225. 2011.
Article6. Gonzalez W, Lallena AM, Alfonso R. Monte Carlo simulation of the dynamic micro-multileaf collimator of a LINAC Elekta Precise using PENELOPE. Phys Med Biol. 56(11):3417–3431. 2011.7. Yu CX. Design considerations for the sides of multileaf collimator leaves. Phys Med Biol. 43:1335–1342. 1998.
Article8. Bayouth JE, Morrill SM. MLC dosimetric characteristics for small field and IMRT applications. Med Phys. 30(9):2545–52. 2003.
Article9. Garcia-Garduno OA, Celis MA, Manuel J, et al. Radiation transmission, leakage and beam penumbra measurements of a micro-multileaf collimator using GafChromic EBT Film. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 9(3):2802. 2008.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dosimetric Characteristics of Dynamic Wedge Techinique
- Dosimetric Characteristics on Penumbra Regions of the multileaf Collimator as Compared with the Lead Alloy Block
- Feasibility Study of Vertical Multileaf Collimator for Determination of Irradiation Size
- Dosimetric Characteristics of Multileaf Collimator-based Intensity-modulated Arc Therapy for Stereotactic Radiosurgery
- Partial Block Technique for Radiation Therapy of Lung Cancer with Dynamic Multi-leaf Collimator