Prog Med Phys.
2015 Dec;26(4):201-207. 10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.201.
Evaluation of 3DVH Software for the Patient Dose Analysis in TomoTherapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. tknam@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea.
- KMID: 2151752
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.201
Abstract
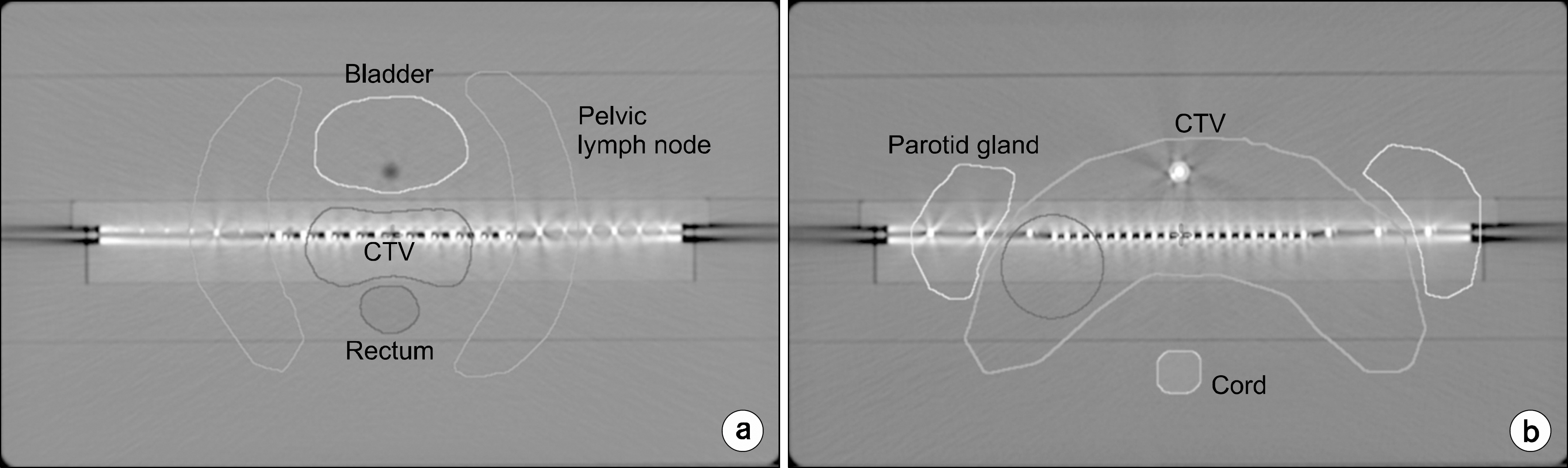
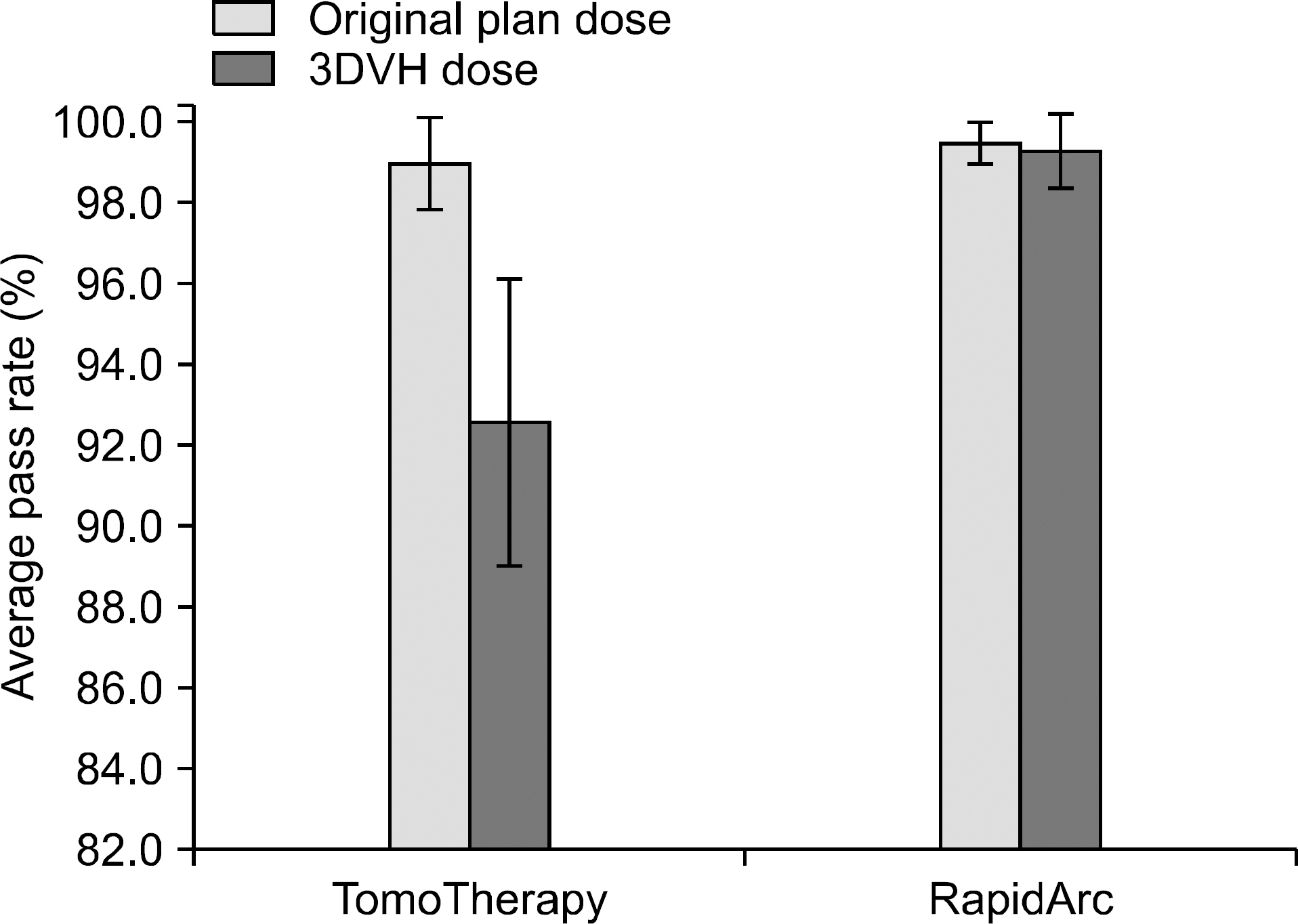
- The new function of 3DVH software for dose calculation inside the patient undergoing TomoTherapy treatment by applying the measured data obtained by ArcCHECK was recently released. In this study, the dosimetric accuracy of 3DVH for the TomoTherapy DQA process was evaluated by the comparison of measured dose distribution with the dose calculated using 3DVH. The 2D diode detector array MapCHECK phantom was used for the TomoTherapy planning of virtual patient and for the measurement of the compared dose. The average pass rate of gamma evaluation between the measured dose in the MapCHECK phantom and the recalculated dose in 3DVH was 92.6+/-3.5%, and the error was greater than the average pass rate, 99.0+/-1.2%, in the gamma evaluation results with the dose calculated in TomoTherapy planning system. The error was also greater than that in the gamma evaluation results in the RapidArc analysis, which showed the average pass rate of 99.3+/-0.9%. The evaluated accuracy of 3DVH software for TomoTherapy DQA process in this study seemed to have some uncertainty for the clinical use. It is recommended to perform a proper analysis before using the 3DVH software for dose recalculation of the patient in the TomoTherapy DQA process considering the initial application stage in clinical use.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ezzell GA, Galvin JM, Low D, et al. Guidance document on delivery, treatment planning, and clinical implementation of IMRT: Report of the IMRT subcommittee of the AAPM radiation therapy committee. Med Phys. 30(8):2089–115. 2003.
Article2. Palta JR, Liu C, Li JG. Quality assurance of Intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 71:(. (1 Suppl):):. S108–12. 2008.
Article3. Ezzell GA, Burmeister JW, Dogan N, et al. IMRT commissioning: Multiple institution planning and dosimetry comparisons, a report from AAPM Task Group 119. Med Phys. 36(11):5359–73. 2009.
Article4. Korevaar EW, Wauben DJ, Langendijk JA, et al. Clinical introduction of linac head-mounted 2D detector array based quality assurance system in head and neck IMRT. Radiother Oncol. 100(3):446–52. 2011.5. Nelms BE, Zhen H, Tome WA. Per-beam, planar IMRT QA passing rates do not predict relevant patient dose errors. Med Phys. 38(2):1037–44. 2011.6. Van Elmpt W, Nijsten S, Mijnheer B, et al. The next step in patient-specific QA: 3D dose verification of conformal and intensitymodulated RT based on EPID dosimetry and Monte Carlo dose calculations. Radiother Oncol. 86(1):86–92. 2008.
Article7. Olch AJ. Evaluation of the accuracy of 3DVH software estimates of dose to virtual ion chamber and film in composite IMRT QA. Med Phys. 39(1):81–6. 2012.
Article8. Nelms BE, Opp D, Robinson J, et al. VMAT QA: measurement-guided 4D dose reconstruction on a patient. Med Phys. 39(7):4228–38. 2012.
Article9. Carrasco P, Jornet N, Latorre A, et al. 3D DVH-based metric analysis versus per-beam planar analysis in IMRT pretreatment verification. Med Phys. 39(8):5040–9. 2012.
Article10. Stasi M, Bresciani S, Miranti A, et al. Pretreatment patient-specific IMRT quality assurance: a correlation study between gamma index and patient clinical dose volume histogram. Med Phys. 39(12):7626–34. 2012.
Article11. Nakaguchi Y, Araki F, Maruyama M, et al. Dose verification of IMRT by use of a COMPASS transmission detector. Radiol Phys Technol. 5(1):63–70. 2012.
Article12. Visser R, Wauben DJ, De Groot M, et al. Efficient and reliable 3D dose quality assurance for IMRT by combining independent dose calculations with measurements. Med Phys. 40(2):021710–1. -6 (. 2013.
Article13. Opp D, Nelms BE, Zhang G, et al. Validation of measurement-guided 3D VMAT dose reconstruction on a heterogeneous anthropomorphic phantom. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 14(1):70–84. 2013.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis on the Calculated Dose in the Lung Radiation Surgery Planning Using TomoTherpay
- Qualitative Evaluation of 2D Dosimetry System for Helical Tomotherapy
- Evaluation of Dynamic Delivery Quality Assurance Process for Internal Target Volume Based RapidArc
- Analysis on the Effect of Field Width in the Delineation of Planning Target Volume for TomoTherapy
- Dosimetric Analysis on the Effect of Target Motion in the Delivery of Conventional IMRT, RapidArc and Tomotherapy