J Korean Diabetes.
2011 Jun;12(2):80-82. 10.4093/jkd.2011.12.2.80.
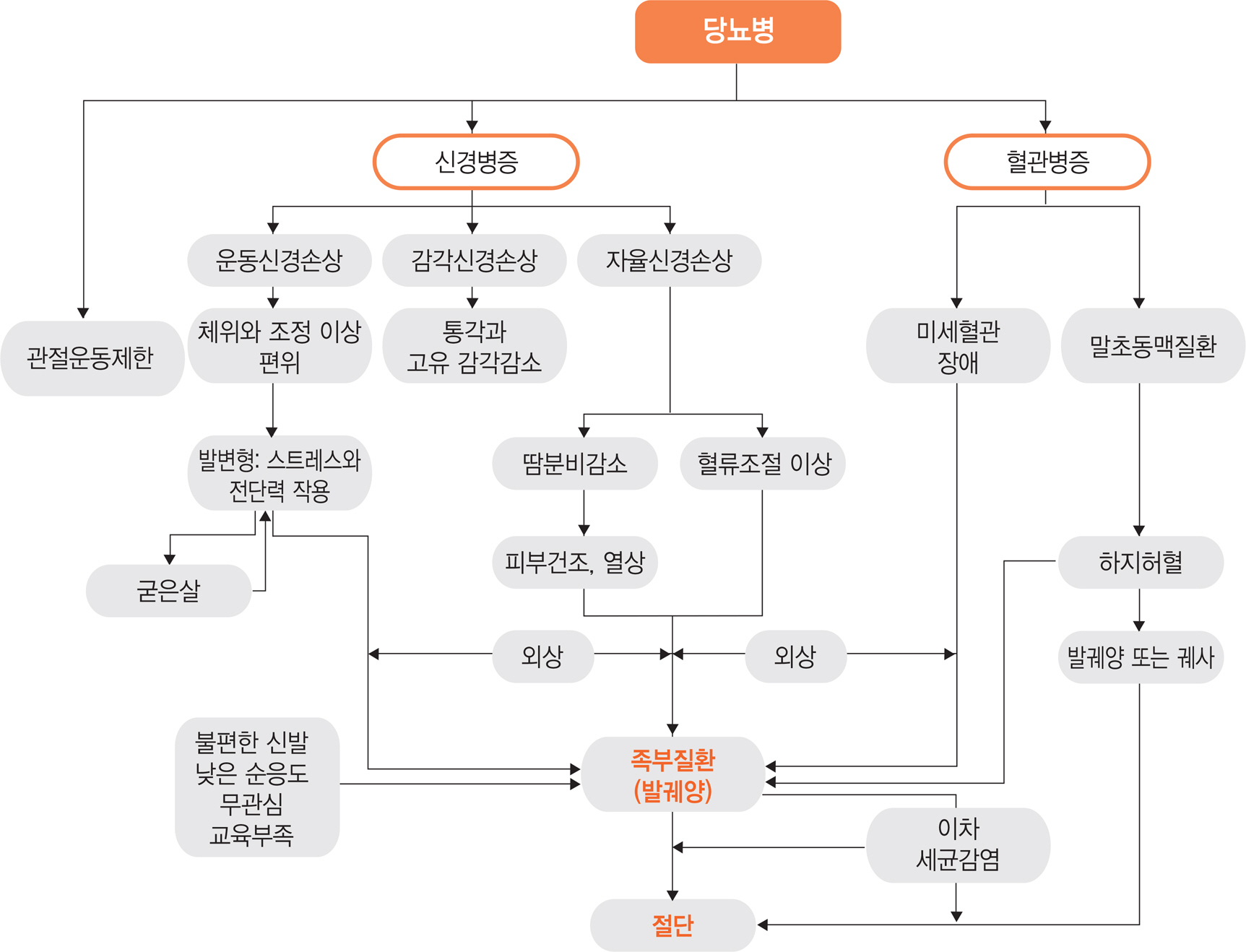
Pathogenesis of the Diabetic Foot Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Medical Center, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea. dm@hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 2137326
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2011.12.2.80
Abstract
- Diabetic foot disease is a major health problem affecting people with diabetes in developed countries, as well as in many developing countries. In people with diabetes the lifetime risk of developing diabetic foot ulcer is about 25%, and this risk may be increased in elderly people with type 2 diabetes. Although the prevalence and severity of diabetic foot disease varies in different regions, peripheral neuropathy is the common pathway leading to ulceration or diabetic foot disease across regions. The pathogenesis and related factors of diabetic foot disease are briefly described in this report.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Apelqvist J, Bakker K, van Houtum WH, Schaper NC. International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot (IWGDF) Editorial Board. Practical guidelines on the management and prevention of the diabetic foot: based upon the International Consensus on the Diabetic Foot (2007) Prepared by the International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2008; 24(Suppl 1):S181–7.2. Boulton AJ. The diabetic foot: from art to science. The 18th Camillo Golgi lecture. Diabetologia. 2004; 47:1343–53.
Article3. Boulton AJ, Armstrong DG, Albert SF, Frykberg RG, Hellman R, Kirkman MS, Lavery LA, Lemaster JW, Mills JL Sr, Mueller MJ, Sheehan P, Wukich DK. American Diabetes Association; American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. Comprehensive foot examination and risk assessment: a report of the task force of the foot care interest group of the American Diabetes Association, with endorsement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:1679–85.4. Lipsky BA. International consensus group on diagnosing and treating the infected diabetic foot. A report from the international consensus on diagnosing and treating the infected diabetic foot. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2004; 20(Suppl 1):S68–77.
Article5. Lavery LA, Peters EJ, Williams JR, Murdoch DP, Hudson A, Lavery DC. International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot. Reevaluating the way we classify the diabetic foot: restructuring the diabetic foot risk classification system of the International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:154–6.