Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2009 Aug;13(4):265-271. 10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.4.265.
Kainic Acid-induced Neuronal Death is Attenuated by Aminoguanidine but Aggravated by L-NAME in Mouse Hippocampus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 200-701, Korea. wchun@kangwon.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pharmacology, College of Pharmacy, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 200-701, Korea.
- 3Department of Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, College of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 200-701, Korea.
- 4Division of Bio-resources Technology, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 200-701, Korea.
- KMID: 2071680
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.4.265
Abstract
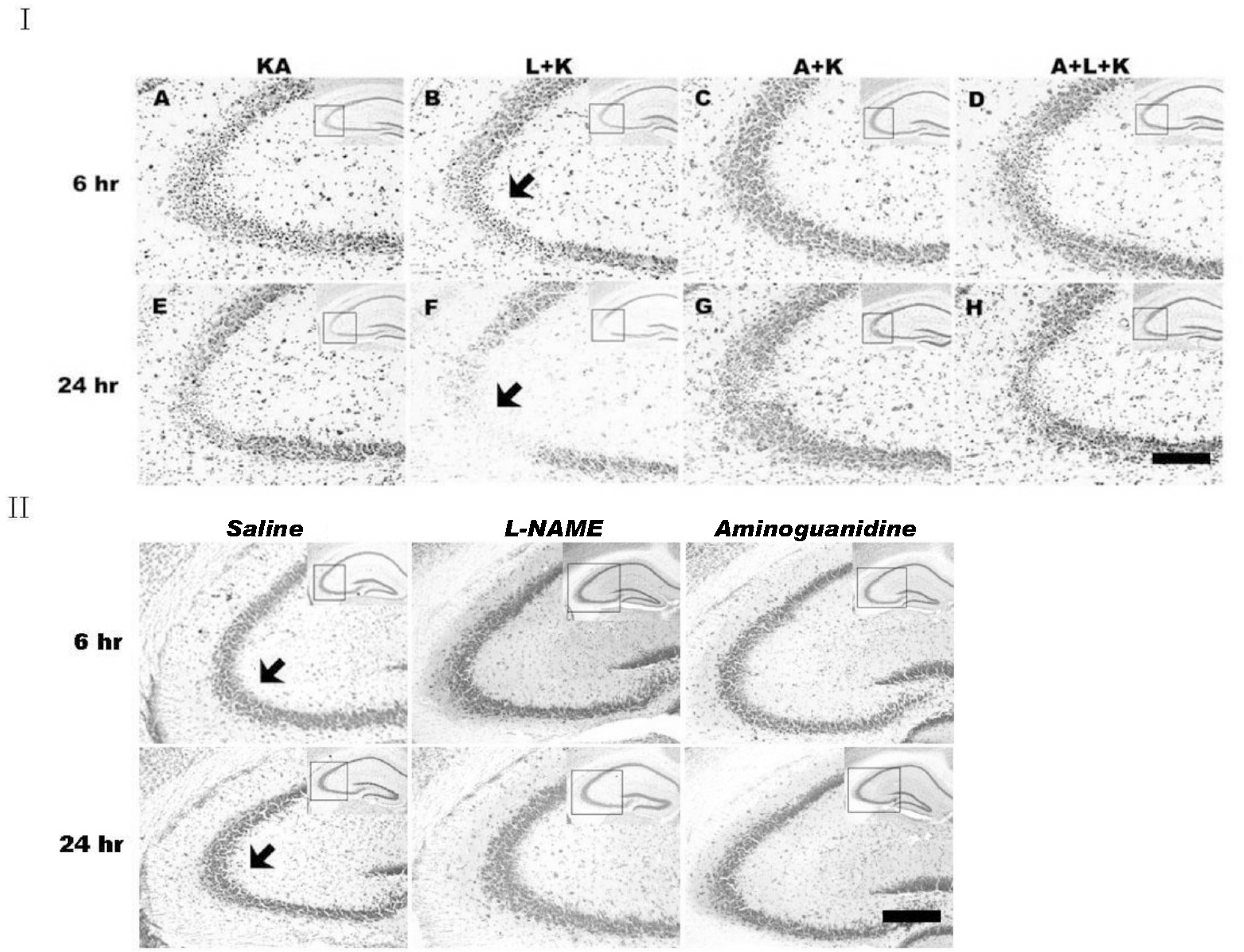
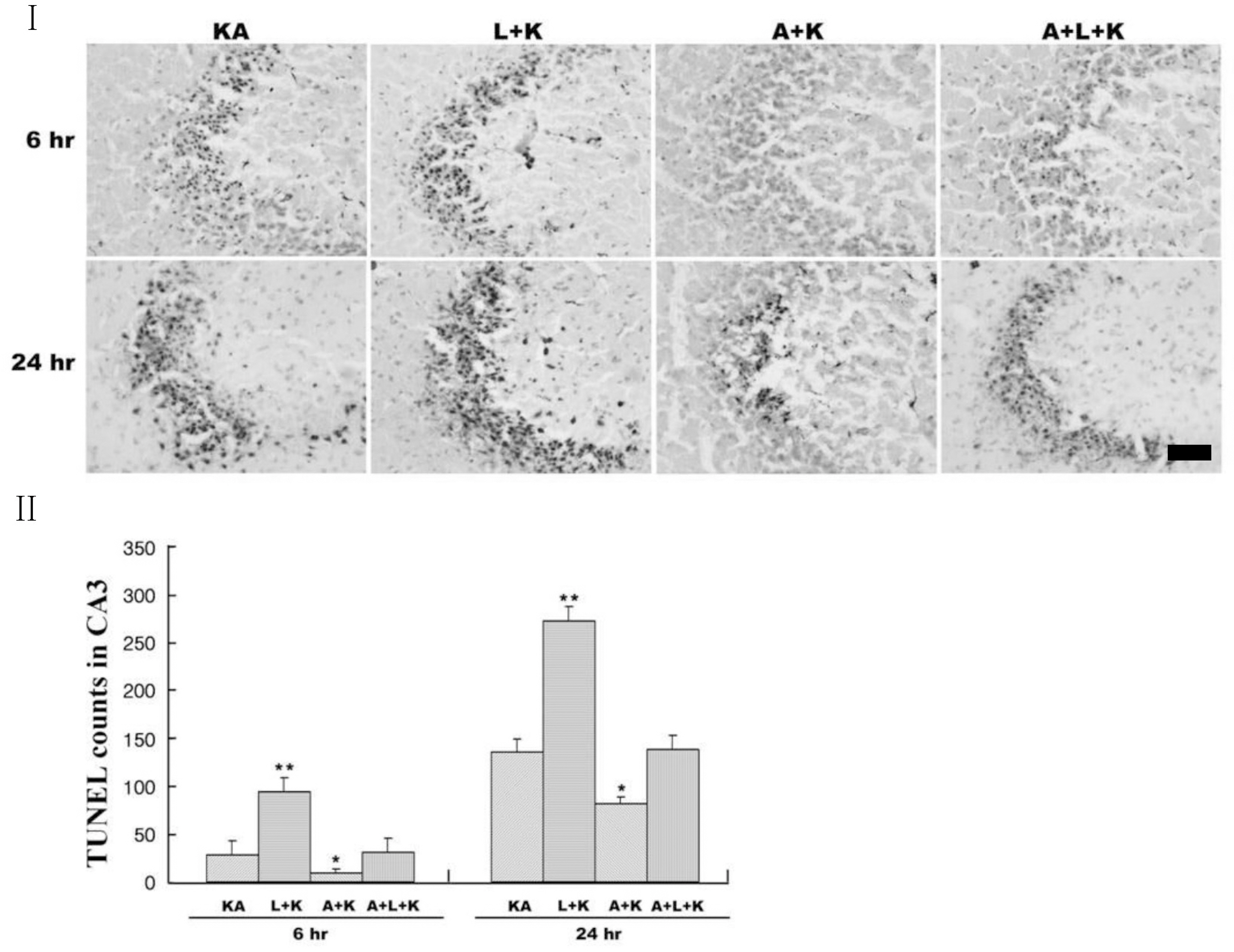
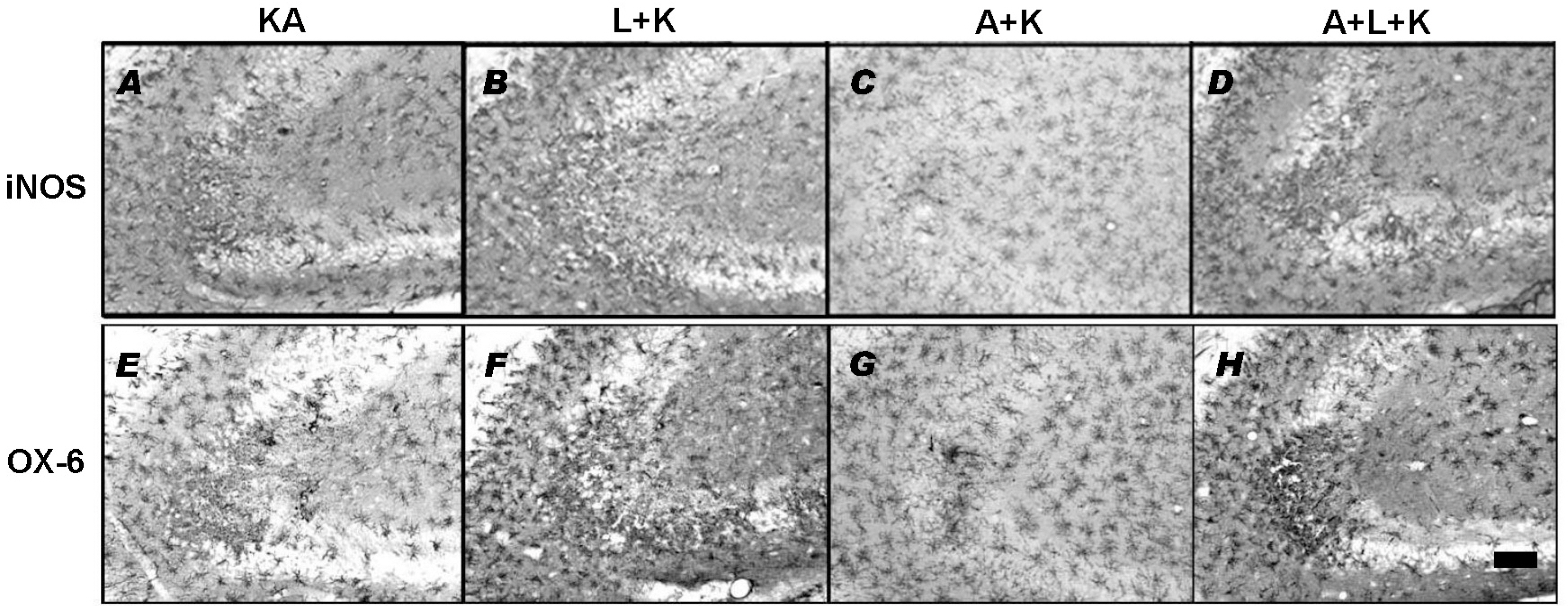
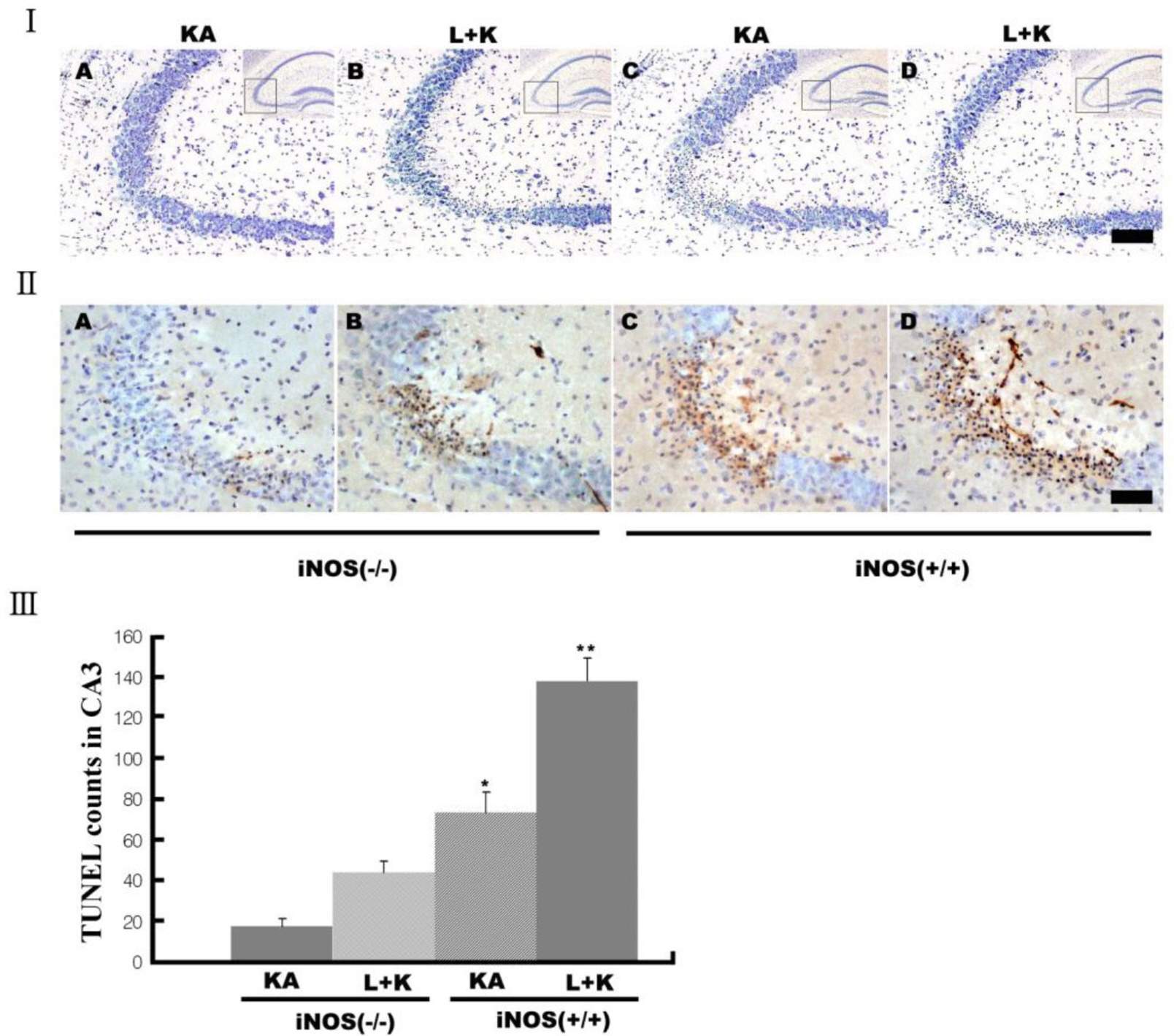
- Nitric oxide (NO) has both neuroprotective and neurotoxic effects depending on its concentration and the experimental model. We tested the effects of NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), a nonselective nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor, and aminoguanidine, a selective inducible NOS (iNOS) inhibitor, on kainic acid (KA)-induced seizures and hippocampal CA3 neuronal death. L-NAME (50 mg/kg, i.p.) and/or aminoguanidine (200 mg/kg, i.p.) were administered 1 h prior to the intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injection of KA. Pretreatment with L-NAME significantly increased KA-induced CA3 neuronal death, iNOS expression, and activation of microglia. However, pretreatment with aminoguanidine significantly suppressed both the KA-induced and L-NAME-aggravated hippocampal CA3 neuronal death with concomitant decreases in iNOS expression and microglial activation. The protective effect of aminoguanidine was maintained for up to 2 weeks. Furthermore, iNOS knockout mice (iNOS-/-) were resistant to KA-induced neuronal death. The present study demonstrates that aminoguanidine attenuates KA-induced neuronal death, whereas L-NAME aggravates neuronal death, in the CA3 region of the hippocampus, suggesting that NOS isoforms play different roles in KA-induced excitotoxicity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Bark Constituents from Mushroom-detoxified
Rhus verniciflua Suppress Kainic Acid-induced Neuronal Cell Death in Mouse Hippocampus
Jong-Seon Byun, Yoon Hee Han, Sung-Jun Hong, Sung-Mi Hwang, Yong-Soo Kwon, Hee Jae Lee, Sung-Soo Kim, Myong-Jo Kim, Wanjoo Chun
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010;14(5):279-283. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.5.279.Inhibition of eNOS/sGC/PKG Pathway Decreases Akt Phosphory-lation Induced by Kainic Acid in Mouse Hippocampus
Sang Hyun Lee, Jong Seon Byun, Pil Jae Kong, Hee Jae Lee, Duk Kyung Kim, Hae Sung Kim, Jong-Hee Sohn, Jae Jun Lee, So Young Lim, Wanjoo Chun, Sung Soo Kim
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010;14(1):37-43. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.1.37.
Reference
-
Alderton WK., Cooper CE., Knowles RG. Nitric oxide synthases: structure, function and inhibition. Biochem J. 357:593–615. 2001.
ArticleBaker H., Farbman AI. Olfactory afferent regulation of the dopamine phenotype in the fetal rat olfactory system. Neuroscience. 52:115–134. 1993.
ArticleBoer R UMPW., Klein T., Mirau B., Haas S., Baur I. The inhibitory potency and selectivity of arginine substrate site nitric-oxide synthase inhibitors is solely determined by their affinity toward the different isoenzymes. Mol Pharmacol. 58:1026–1034. 2000.
ArticleBredt DS., Snyder SH. Nitric oxide, a novel neuronal messenger. Neuron. 8:3–11. 1992.
ArticleBuisson A., Lakhmeche N., Verrecchia C., Plotkine M., Boulu RG. Nitric oxide: an endogenous anticonvulsant substance. Neuroreport. 4:444–446. 1993a.Buisson A., Margaill I., Callebert J., Plotkine M., Boulu RG. Mechanisms involved in the neuroprotective activity of a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor during focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem. 61:690–696. 1993b.
ArticleChoi DW. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron. 1:623–634. 1988.
ArticleCiani E., Baldinotti I., Contestabile A. Sustained, long-lasting inhibition of nitric oxide synthase aggravates the neural damage in some models of excitotoxic brain injury. Brain Res Bull. 56:29–35. 2001.
ArticleCoyle JT., Puttfarcken P. Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science. 262:689–695. 1993.
ArticleDanielisova V., Nemethova M., Burda J. The protective effect of aminoguanidine on cerebral ischemic damage in the rat brain. Physiol Res. 53:533–540. 2004.Du W., Harvey JA. The nitric oxide synthesis inhibitor L-NAME facilitates associative learning. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 20:1183–1195. 1996.
ArticleDu W., Weiss H., Harvey JA. Associative learning is enhanced by selective neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitors and retarded by a nitric oxide donor in the rabbit. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 150:264–271. 2000.
ArticleGarthwaite J., Boulton CL. Nitric oxide signaling in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Physiol. 57:683–706. 1995.
ArticleGross SS., Wolin MS. Nitric oxide: pathophysiological mechanisms. Annu Rev Physiol. 57:737–769. 1995.
ArticleHaberny KA., Pou S., Eccles CU. Potentiation of quinolinate-induced hippocampal lesions by inhibition of NO synthesis. Neurosci Lett. 146:187–190. 1992.
ArticleHenshall DC., Bonislawski DP., Skradski SL., Araki T., Lan JQ., Schindler CK., Meller R., Simon RP. Formation of the Apaf-1/cytochrome c complex precedes activation of caspase-9 during seizure-induced neuronal death. Cell Death Differ. 8:1169–1181. 2001.
ArticleJones PA., Smith RA., Stone TW. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors L-NAME and 7-nitroindazole protect rat hippocampus against kainate-induced excitotoxicity. Neurosci Lett. 249:75–78. 1998.
ArticleKiedrowski L., Costa E., Wroblewski JT. Glutamate receptor agonists stimulate nitric oxide synthase in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem. 58:335–341. 1992.
ArticleKim YM., Bombeck CA., Billiar TR. Nitric oxide as a bifunctional regulator of apoptosis. Circ Res. 84:253–256. 1999.
ArticleKoprowski H., Zheng YM., Heber-Katz E., Fraser N., Rorke L., Fu ZF., Hanlon C., Dietzschold B. In vivo expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in experimentally induced neurologic diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:3024–3027. 1993.
ArticleLaursen SE., Belknap JK. Intracerebroventricular injections in mice. Some methodological refinements. J Pharmacol Methods. 16:355–357. 1986.Lee JM., Zipfel GJ., Choi DW. The changing landscape of ischaemic brain injury mechanisms. Nature. 399:A7–14. 1999.
ArticleMcNamara JO. Emerging insights into the genesis of epilepsy. Nature. 399:A15–22. 1999.
ArticleMoncada S., Higgs A., Furchgott R. International Union of Pharmacology Nomenclature in Nitric Oxide Research. Pharmacol Rev. 49:137–142. 1997.Mulsch A., Busse R., Mordvintcev PI., Vanin AF., Nielsen EO., Scheel-Kruger J., Olesen SP. Nitric oxide promotes seizure activity in kainate-treated rats. Neuroreport. 5:2325–2328. 1994.
ArticlePenix LP., Davis W., Subramaniam S. Inhibition of NO synthase increases the severity of kainic acid-induced seizures in rodents. Epilepsy Res. 18:177–184. 1994.
ArticlePerez-Asensio FJ., Hurtado O., Burguete MC., Moro MA., Salom JB., Lizasoain I., Torregrosa G., Leza JC., Alborch E., Castillo J., Knowles RG., Lorenzo P. Inhibition of iNOS activity by 1400W decreases glutamate release and ameliorates stroke outcome after experimental ischemia. Neurobiol Dis. 18:375–384. 2005.Rondouin G., Bockaert J., Lerner-Natoli M. L-nitroarginine, an inhibitor of NO synthase, dramatically worsens limbic epilepsy in rats. Neuroreport. 4:1187–1190. 1993.Schulz JB., Matthews RT., Jenkins BG., Ferrante RJ., Siwek D., Henshaw DR., Cipolloni PB., Mecocci P., Kowall NW., Rosen BR. Blockade of neuronal nitric oxide synthase protects against excitotoxicity. in vivo. J Neurosci. 15:8419–8429. 1995.Shapira S., Kadar T., Weissman BA. Dose-dependent effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibition following transient forebrain ischemia in gerbils. Brain Res. 668:80–84. 1994.
ArticleSoutham E., Garthwaite J. The nitric oxide-cyclic GMP signalling pathway in rat brain. Neuropharmacology. 32:1267–1277. 1993.
ArticleStarr MS., Starr BS. Paradoxical facilitation of pilocarpine-induced seizures in the mouse by MK-801 and the nitric oxide synthesis inhibitor L-NAME. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 45:321–325. 1993.
ArticleSugimoto K., Iadecola C. Effects of aminoguanidine on cerebral ischemia in mice: comparison between mice with and without inducible nitric oxide synthase gene. Neurosci Lett. 331:25–28. 2002.
ArticleTakei Y., Takashima S., Ohyu J., Matsuura K., Katoh N., Takami T., Miyajima T., Hoshika A. Different effects between 7-nitroindazole and L-NAME on cerebral hemodynamics and hippocampal lesions during kainic acid-induced seizures in newborn rabbits. Brain Dev. 23:406–413. 2001.
ArticleTakei Y., Takashima S., Ohyu J., Takami T., Miyajima T., Hoshika A. Effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibition on the cerebral circulation and brain damage during kainic acid-induced seizures in newborn rabbits. Brain Dev. 21:253–259. 1999.
ArticleTsuda M., Suzuki T., Misawa M. Aggravation of DMCM-induced seizure by nitric oxide synthase inhibitors in mice. Life Sci. 60:339–343. 1997.
ArticleYamamoto S., Golanov EV., Berger SB., Reis DJ. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis increases focal ischemic infarction in rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 12:717–726. 1992.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Kainic Acid Treatment Increases Ca²âº-mediated Neurotoxicity in the Mouse Hippocampus
- Postischemic Treatment with Aminoguanidine Inhibits Peroxynitrite Production in the Rat Hippocampus Following Transient Forebrain Ischemia
- Bark Constituents from Mushroom-detoxified Rhus verniciflua Suppress Kainic Acid-induced Neuronal Cell Death in Mouse Hippocampus
- Effect of Pioglitazone on Excitotoxic Neuronal Damage in the Mouse Hippocampus
- Induction of alphaB-crystallin in the hippocampus of KA-treated mouse brain