Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2015 Sep;18(3):209-215. 10.5223/pghn.2015.18.3.209.
Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis Associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection in a Child
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. i101016@skku.edu
- 2Department of Critical Care Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2068800
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2015.18.3.209
Abstract
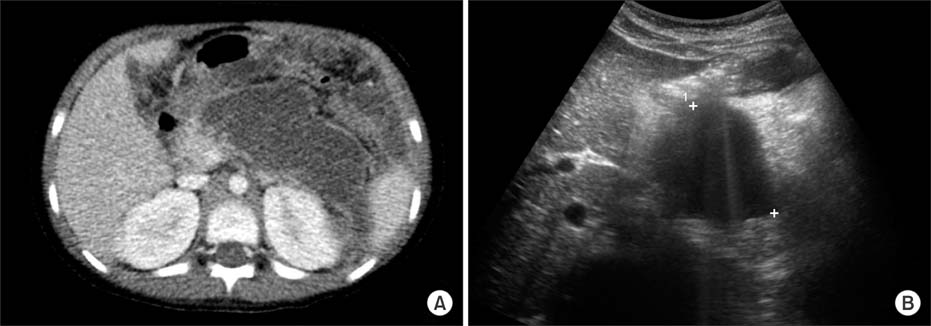
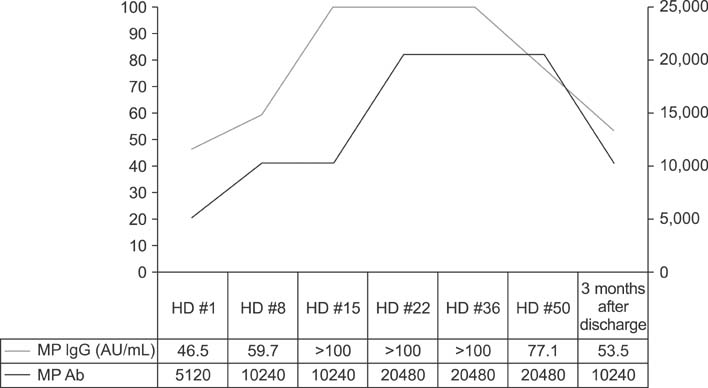
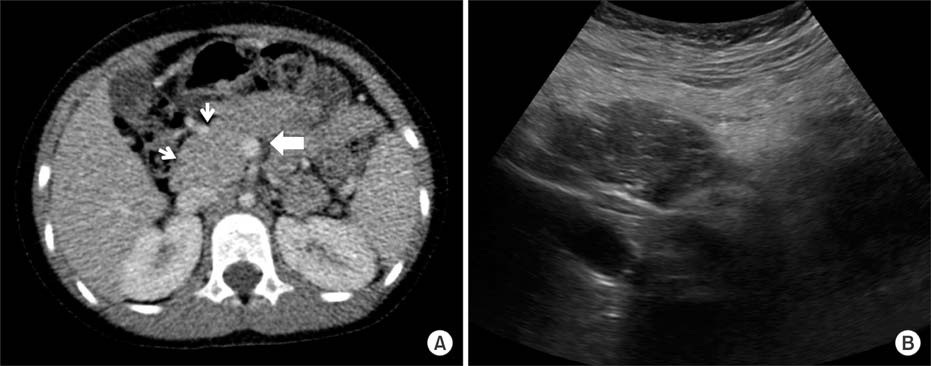
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae is responsible for approximately 20% to 30% of community-acquired pneumonia, and is well known for its diverse extrapulmonary manifestations. However, acute necrotizing pancreatits is an extremely rare extrapulmonary manifestation of M. pneumoniae infection. A 6-year-old girl was admitted due to abdominal pain, vomiting, fever, and confused mentality. Acute necrotizing pancreatitis was diagnosed according to symptoms, laboratory test results, and abdominal computed tomography scans. M. pneumoniae infection was diagnosed by a 4-fold increase in antibodies to M. pneumoniae between acute and convalescent sera by particle agglutination antibody assay. No other etiologic factors or pathogens were detected. Despite the occurrence of a large infected pseudocyst during the course, the patient was able to discharge without morbidity by early aggressive supportive care. This is the first case in Korea of a child with acute necrotizing pancreatitis associated with M. pneumoniae infection.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mårdh PA, Ursing B. The occurrence of acute pancreatitis in Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 1974; 6:167–171.
Article2. Freeman R, McMahon MJ. Acute pancreatitis and serological evidence of infection with Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Gut. 1978; 19:367–370.
Article3. Narita M. Pathogenesis of extrapulmonary manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection with special reference to pneumonia. J Infect Chemother. 2010; 16:162–169.
Article4. al-Abassi A. Acute pancreatitis associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae: a case report of missed diagnosis. Med Princ Pract. 2002; 11:112–115.
Article5. Nakagawa M, Ogino H, Shimohira M, Hara M, Shibamoto Y. Continuous regional arterial infusion therapy for acute necrotizing pancreatitis due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in a child. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009; 32:581–584.
Article6. Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013; 62:102–111.
Article7. Morinville VD, Barmada MM, Lowe ME. Increasing incidence of acute pancreatitis at an American pediatric tertiary care center: is greater awareness among physicians responsible? Pancreas. 2010; 39:5–8.
Article8. Benifla M, Weizman Z. Acute pancreatitis in childhood: analysis of literature data. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003; 37:169–172.9. Werlin SL, Kugathasan S, Frautschy BC. Pancreatitis in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2003; 37:591–595.
Article10. Lautz TB, Chin AC, Radhakrishnan J. Acute pancreatitis in children: spectrum of disease and predictors of severity. J Pediatr Surg. 2011; 46:1144–1149.
Article11. Raizner A, Phatak UP, Baker K, Patel MG, Husain SZ, Pashankar DS. Acute necrotizing pancreatitis in children. J Pediatr. 2013; 162:788–792.
Article12. Suzuki M, Sai JK, Shimizu T. Acute pancreatitis in children and adolescents. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2014; 5:416–426.
Article13. Whitcomb DC, Lowe ME. Pancreatitis: acute and chronic. In : Walker WA, editor. Pediatric gastrointestinal disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, management. 4th ed. Hamilton: BC Decker;2004. p. 1584–1597.14. Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985; 13:818–829.15. Pavlidis P, Crichton S, Lemmich Smith J, Morrison D, Atkinson S, Wyncoll D, et al. Improved outcome of severe acute pancreatitis in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Res Pract. 2013; 2013:897107.
Article16. Yasuda T, Ueda T, Takeyama Y, Shinzeki M, Sawa H, Nakajima T, et al. Treatment strategy against infection: clinical outcome of continuous regional arterial infusion, enteral nutrition, and surgery in severe acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2007; 42:681–689.
Article17. Zerem E. Treatment of severe acute pancreatitis and its complications. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:13879–13892.
Article18. Chen CC, Wang SS, Lee FY. Action of antiproteases on the inflammatory response in acute pancreatitis. JOP. 2007; 8:4 Suppl. 488–494.19. Chen CC, Wang SS, Tsay SH, Lee FY, Lu RH, Chang FY, et al. Effects of gabexate mesilate on serum inflammatory cytokines in rats with acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Cytokine. 2006; 33:95–99.
Article20. Seta T, Noguchi Y, Shimada T, Shikata S, Fukui T. Treatment of acute pancreatitis with protease inhibitors: a meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 16:1287–1293.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case Report of Acute Pancreatitis Caused by Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Infection
- A Case of Erythema Multiforme in Adults Associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection
- Mycoplasma Pneumoniae-Associated Necrotizing Pneumonia in Children: a case-report
- A Case of Cerebral Infarction Complicated by Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia
- Clinical Study of Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Infection in Children