Korean J Urol.
2012 Dec;53(12):879-882. 10.4111/kju.2012.53.12.879.
Robotic Radical Nephrectomy with Vena Caval Tumor Thrombectomy: Experience of Novice Robotic Surgeons
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, University of California Irvine Medical Center, University of California Irvine, Orange, CA, USA. leejasoSMH@gmail.com
- KMID: 1988736
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.12.879
Abstract
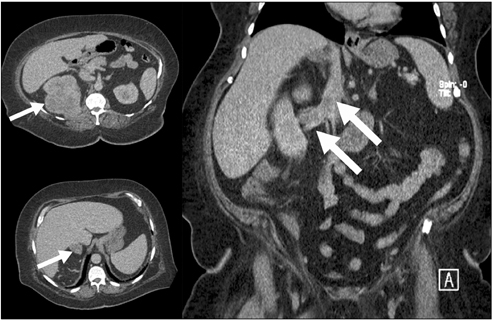
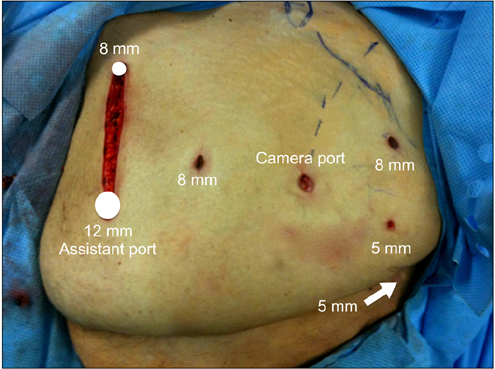
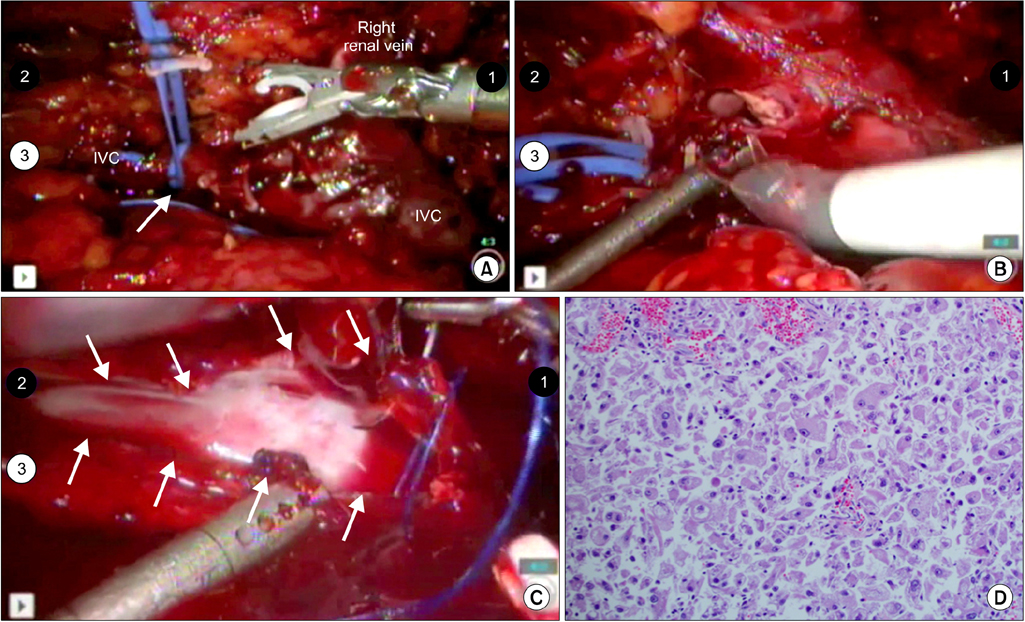
- The introduction of robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery has facilitated the application of minimally invasive surgical techniques to many complex reconstructive and extirpative procedures. Even early on in their learning experience, robotic surgeons have been able to complete procedures using a minimally invasive approach, but would not have been able to do so using a purely laparoscopic technique. Although the open surgical approach remains the standard of care in the management of large renal tumors presenting with a thrombus within the vena cava, robot-assisted surgery may provide the precision and dexterity necessary to allow for the safe application of minimally invasive techniques to such complex clinical scenarios, perhaps even by relatively novice robotic surgeons. We describe the management of a large renal mass with vena caval thrombus (cT3b), which required complete cross-clamping of the vena cava, with the use of a purely robot-assisted laparoscopic approach.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Swierzewski DJ, Swierzewski MJ, Libertino JA. Radical nephrectomy in patients with renal cell carcinoma with venous, vena caval, and atrial extension. Am J Surg. 1994. 168:205–209.2. Abaza R. Initial series of robotic radical nephrectomy with vena caval tumor thrombectomy. Eur Urol. 2011. 59:652–656.3. Van Velthoven RF, Ahlering TE, Peltier A, Skarecky DW, Clayman RV. Technique for laparoscopic running urethrovesical anastomosis: the single knot method. Urology. 2003. 61:699–702.4. Hoang AN, Vaporcyian AA, Matin SF. Laparoscopy-assisted radical nephrectomy with inferior vena caval thrombectomy for level II to III tumor thrombus: a single-institution experience and review of the literature. J Endourol. 2010. 24:1005–1012.5. Varkarakis IM, Bhayani SB, Allaf ME, Inagaki T, Gonzalgo ML, Jarrett TW. Laparoscopic-assisted nephrectomy with inferior vena cava tumor thrombectomy: preliminary results. Urology. 2004. 64:925–929.6. Disanto V, Pansadoro V, Portoghese F, Scalese GA, Romano M. Retroperitoneal laparoscopic radical nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma with infrahepatic vena caval thrombus. Eur Urol. 2005. 47:352–356.7. Sundaram CP, Rehman J, Landman J, Oh J. Hand assisted laparoscopic radical nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma with inferior vena caval thrombus. J Urol. 2002. 168:176–179.8. Martin GL, Castle EP, Martin AD, Desai PJ, Lallas CD, Ferrigni RG, et al. Outcomes of laparoscopic radical nephrectomy in the setting of vena caval and renal vein thrombus: seven-year experience. J Endourol. 2008. 22:1681–1685.9. Romero FR, Muntener M, Bagga HS, Brito FA, Sulman A, Jarrett TW. Pure laparoscopic radical nephrectomy with level II vena caval thrombectomy. Urology. 2006. 68:1112–1114.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Urologic robotic surgery in Korea: Past and present
- Anesthetic Management of Patient with Renal Cell Carcinoma Extending into the Right Atrium Using Adjunctive Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest: A case report
- Prognostic Factors for Survival in the Renal Cell Carcinoma with Tumor Thrombus
- Robotic Thyroidectomy: Pros and Cons of Various Surgical Approaches
- Comparison of transperitoneal and retroperitoneal robot partial nephrectomy for kidney tumors