Korean J Orthod.
2014 May;44(3):105-112. 10.4041/kjod.2014.44.3.105.
Effect of silica coating on bond strength between a gold alloy and metal bracket bonded with chemically cured resin
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. 022bracket@gmail.com
- KMID: 1974995
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2014.44.3.105
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of three different surface conditioning methods on the shear bond strength (SBS) of metal brackets bonded directly to gold alloy with chemically cured resin.
METHODS
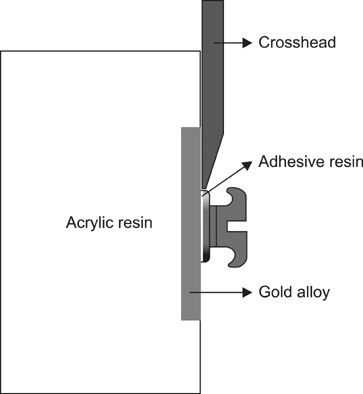
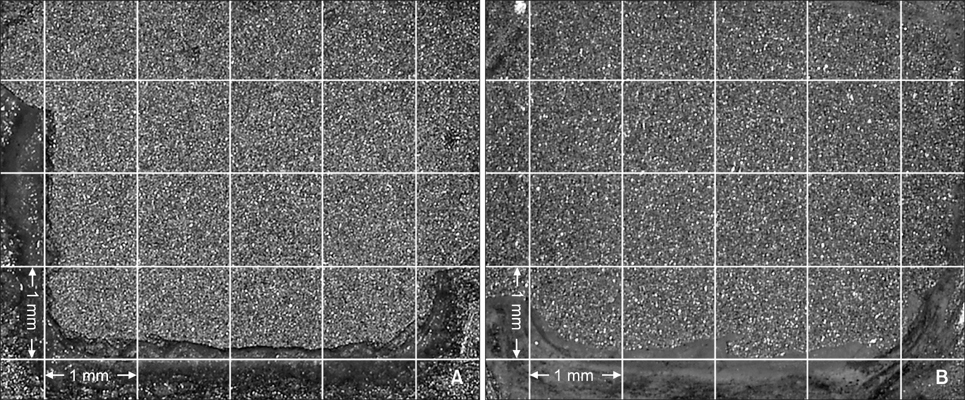
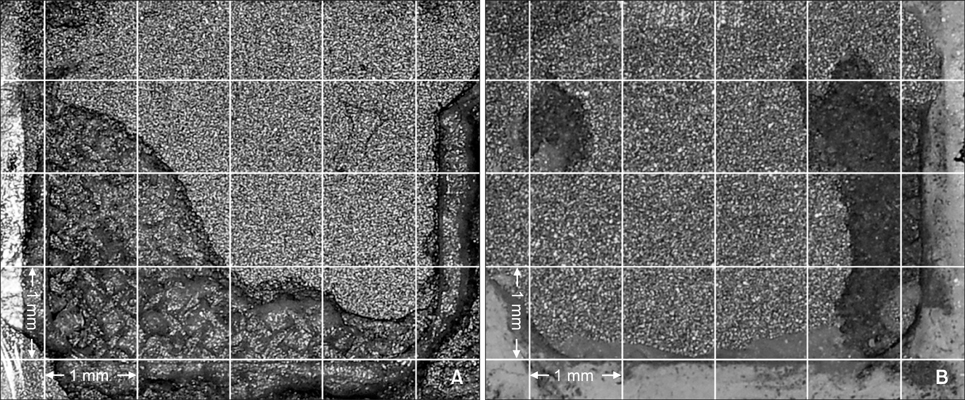
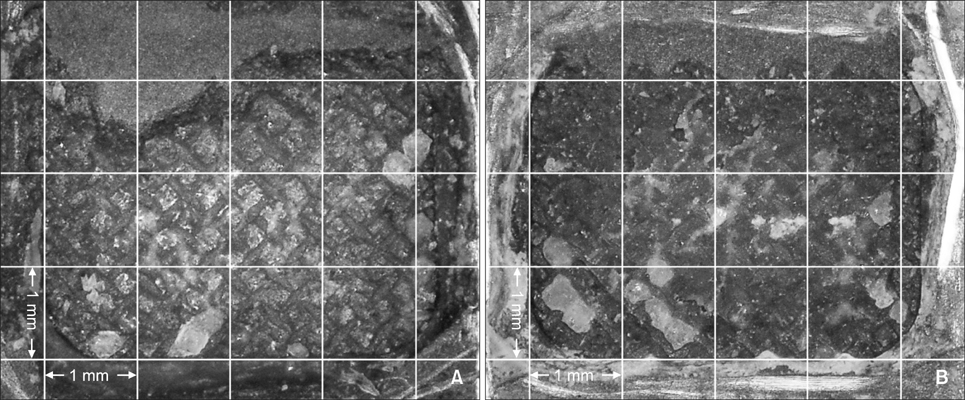
Two hundred ten type III gold alloy specimens were randomly divided into six groups according to the combination of three different surface conditioning methods (aluminum oxide sandblasting only, application of a metal primer after aluminum oxide sandblasting, silica coating and silanation) and thermocycling (with thermocycling, without thermocycling). After performing surface conditioning of specimens in accordance with each experimental condition, metal brackets were bonded to all specimens using a chemically cured resin. The SBS was measured at the moment of bracket debonding, and the resin remnants on the specimen surface were evaluated using the adhesive remnant index.
RESULTS
Application of metal primer after aluminum oxide sandblasting yielded a higher bond strength than that with aluminum oxide sandblasting alone (p < 0.001), and silica coating and silanation yielded a higher bond strength than that with metal primer after aluminum oxide sandblasting (p < 0.001). There was no significant change in SBS after thermocycling in all groups.
CONCLUSIONS
With silica coating and silanation, clinically satisfactory bond strength can be attained when metal brackets are directly bonded to gold alloys using a chemically cured resin.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison of shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets using various zirconia primers
Ji-Yeon Lee, Jin-Seok Kim, Chung-Ju Hwang
Korean J Orthod. 2015;45(4):164-170. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2015.45.4.164.
Reference
-
1. Boyd RL, Baumrind S. Periodontal considerations in the use of bonds or bands on molars in adolescents and adults. Angle Orthod. 1992; 62:117–126.2. Van Meerbeek B, De Munck J, Yoshida Y, Inoue S, Vargas M, Vijay P, et al. Buonocore memorial lecture. Adhesion to enamel and dentin: current status and future challenges. Oper Dent. 2003; 28:215–235.3. Wood DP, Jordan RE, Way DC, Galil KA. Bonding to porcelain and gold. Am J Orthod. 1986; 89:194–205.
Article4. Zachrisson BU, Buyukyilmaz T. Recent advances in bonding to gold, amalgam and porcelain. J Clin Orthod. 1993; 27:661–675.5. Antoniadou M, Kern M, Strub JR. Effect of a new metal primer on the bond strength between a resin cement and two high-noble alloys. J Prosthet Dent. 2000; 84:554–560.
Article6. Lee YK, Cha JY, Yu HS, Hwang CJ. Effect of metal primer and thermocycling on shear bonding strength between the orthodontic bracket and gold alloy. Korean J Orthod. 2009; 39:320–329.
Article7. Nergiz I, Schmage P, Herrmann W, Ozcan M. Effect of alloy type and surface conditioning on roughness and bond strength of metal brackets. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004; 125:42–50.
Article8. Jung MH, Chung SH, Shon WJ. Shear bond strength between gold alloy and orthodontic metal bracket using light emitting diode curing light. Korean J Orthod. 2010; 40:27–33.
Article9. Shon WJ, Kim TW, Chung SH, Jung MH. The effects of primer precuring on the shear bond strength between gold alloy surfaces and metal brackets. Eur J Orthod. 2012; 34:72–76.
Article10. Artun J, Bergland S. Clinical trials with crystal growth conditioning as an alternative to acid-etch enamel pretreatment. Am J Orthod. 1984; 85:333–340.
Article11. Bishara SE, Ajlouni R, Laffoon JF. Effect of thermocycling on the shear bond strength of a cyanoacrylate orthodontic adhesive. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003; 123:21–24.
Article12. Büyükyilmaz T, Zachrisson BU. Improved orthodontic bonding to silver amalgam. Part 2. Lathe-cut, admixed, and spherical amalgams with different intermediate resins. Angle Orthod. 1998; 68:337–344.13. Büyükyilmaz T, Zachrisson YO, Zachrisson BU. Improving orthodontic bonding to gold alloy. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1995; 108:510–518.
Article14. Bulbul M, Kesim B. The effect of primers on shear bond strength of acrylic resins to different types of metals. J Prosthet Dent. 2010; 103:303–308.
Article15. Matsumura H, Shimoe S, Nagano K, Atsuta M. Effect of noble metal conditioners on bonding between prosthetic composite material and silver-palladium-copper-gold alloy. J Prosthet Dent. 1999; 81:710–714.
Article16. Yoshida K, Atsuta M. Effect of MMA-PMMA resin polymerization initiators on the bond strengths of adhesive primers for noble metal. Dent Mater. 1999; 15:332–336.
Article17. Sun R, Suansuwan N, Kilpatrick N, Swain M. Characterisation of tribochemically assisted bonding of composite resin to porcelain and metal. J Dent. 2000; 28:441–445.
Article18. Atsü SS, Gelgör IE, Sahin V. Effects of silica coating and silane surface conditioning on the bond strength of metal and ceramic brackets to enamel. Angle Orthod. 2006; 76:857–862.19. Watanabe T, Ino S, Okada S, Katsumata Y, Hamano N, Hojo S, et al. Influence of simplified silica coating method on the bonding strength of resin cement to dental alloy. Dent Mater J. 2008; 27:16–20.
Article20. Matinlinna JP, Lassila LV, Ozcan M, Yli-Urpo A, Vallittu PK. An introduction to silanes and their clinical applications in dentistry. Int J Prosthodont. 2004; 17:155–164.21. Jung MH, Shon WJ, Park YS, Chung SH. Effects of silanation time on shear bond strength between a gold alloy surface and metal bracket. Korean J Orthod. 2013; 43:127–133.
Article22. Schneider W, Powers JM, Pierpont HP. Bond strength of composites to etched and silica-coated porcelain fusing alloys. Dent Mater. 1992; 8:211–215.
Article23. Cozza P, Martucci L, De Toffol L, Penco SI. Shear bond strength of metal brackets on enamel. Angle Orthod. 2006; 76:851–856.24. Patusco VC, Montenegro G, Lenza MA, Alves de Carvalho A. Bond strength of metallic brackets after dental bleaching. Angle Orthod. 2009; 79:122–126.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of chemically cured resin and light cured resin on shear bond strength of metal bracket and ceramic bracket
- EFFECT OF GOLD ELECTRODEPOSIT ON THE BOND STRENGTH BETWEEN ALLOYS AND VENEERED RESIN
- Shear bond strength between gold alloy and orthodontic metal bracket using light emitting diode curing light
- Shear bond strength of metal brackets bonded with light-cured adhesive: an in vitro comparative study
- Shear bond strength and failure patterns according to the material of resin base in indirect racket bonding