J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2012 Sep;14(3):237-242. 10.7461/jcen.2012.14.3.237.
A Ruptured Aneurysm at the Infraoptic Azygous Anterior Cerebral Artery with the Contralateral Internal Carotid Artery Agenesis Treated by Y-stent Assisted Coil Embolization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea. paulyoonsoolee@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1808462
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2012.14.3.237
Abstract
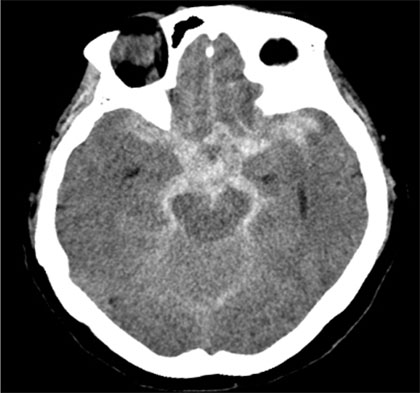
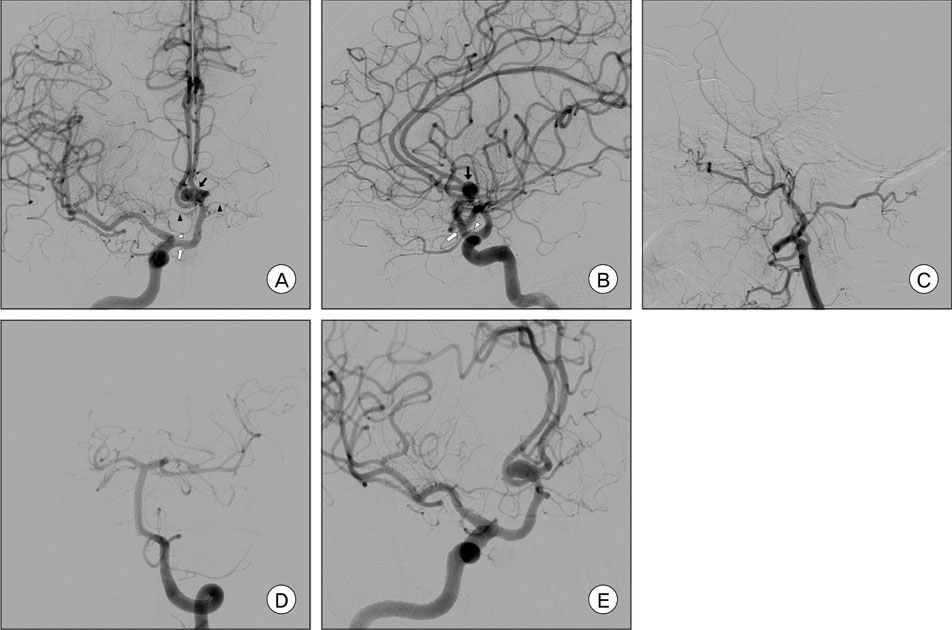
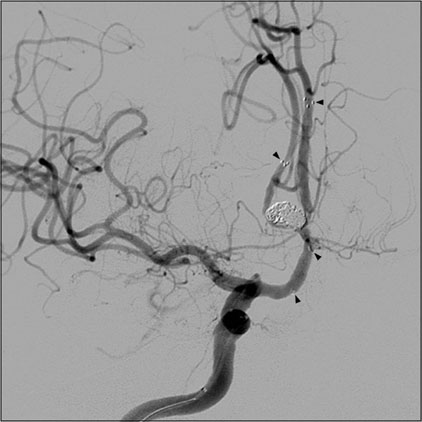
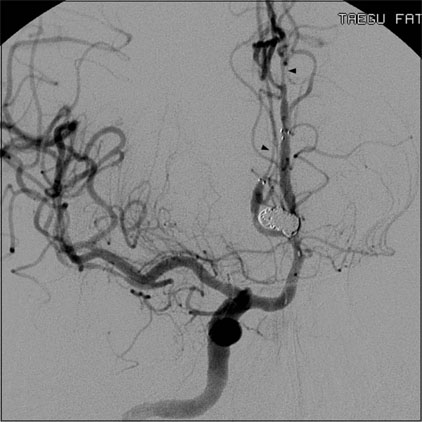
- Infraoptic anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is an extremely rare congenital anomaly. This anomalous artery usually arises from the intradural internal carotid artery (ICA) near the level of the ophthalmic artery (OA) or rarely from the extradural ICA. This anomaly frequently harbors a cerebral aneurysm, and may involve other coexisting vascular anomalies. In the case of this anomaly, surgical treatment of the aneurysm at the proximal ACA or anterior communicating artery (ACoA) may sometimes be difficult, because the veiled proximal ACA by the optic nerve would make proximal control inconvenient and the vertical midline segment of the proximal ACA would frequently form a superiorly directing aneurysm with a relatively high position. We report on an extremely rare case of a ruptured aneurysm at the infraoptic azygous ACA, possibly having an extradural origin, accompanied by contralateral ICA agenesis, and also introduce a feasible method for treatment by Y-stent assisted coil embolization.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
An Unruptured Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm with Bilateral Infraoptic Anterior Cerebral Arteries. Case Report and Review of the Literature
Michelle H. Chua, Ajith J. Thomas, Matthew R. Fusco, Christopher S. Ogilvy
J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2014;16(4):368-373. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2014.16.4.368.
Reference
-
1. Akiyama Y, Okada T, Hayashi N, Yokoi T. Infraoptic course of the anterior cerebral artery originating from the extradural internal carotid artery associated with contralateral internal carotid artery agenesis and multiple intracerebral aneurysms. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2010. 11. 50(11):984–987.2. Al-Qahtani S, Tampieri D, Brassard R, Sirhan D, Mellanson D. Coil embolization of an aneurysm associated with an infraoptic anterior cerebral artery in a child. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003. 05. 24(5):990–991.3. Fujimoto S, Murakami M. Anomalous branch of the internal carotid artery supplying circulation of the anterior cerebral artery: case report. J Neurosurg. 1983. 06. 58(6):941–946.4. Given CA II, Morris PP. Recognition and importance of an infraoptic anterior cerebral artery: case report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002. 03. 23(3):452–454.5. Gupta V, Chugh M, Vaishya S. Infraoptic azygous anterior cerebral artery. Neurol India. 2008. Oct-Dec. 56(4):487–488.
Article6. Hillard VH, Musunuru K, Nwagwu C, Das K, Murali R, Zablow B, et al. Treatment of an anterior communicating artery aneurysm through an anomalous anastomosis from the cavernous internal carotid artery. J Neurosurg. 2002. 12. 97(6):1432–1435.
Article7. Isherwood I, Dutton J. Unusual anomaly of the anterior cerebral artery. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh). 1969. 9:345–351.8. Kessler LA. Unusual anomaly of the anterior cerebral artery: report of a case. Arch Neurol. 1979. 08. 36(8):509–510.9. Ladzinski P, Maliszewski M, Majchrzak H. The accessory anterior cerebral artery: case report and anatomic analysis of vascular anomaly. Surg Neurol. 1997. 08. 48(2):171–174.10. McLaughlin N, Bojanowski MW. Infraoptic course of anterior cerebral arteries associated with abnormal gyral segmentation. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2007. 08. 107(2):430–434.11. Nutik S, Dilenge D. Carotid-anterior cerebral artery anastomosis: Case report. J Neurosurg. 1976. 03. 44(3):378–382.12. Odake G. Carotid-anterior cerebral artery anastomosis with aneurysm: case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 1988. 11. 23(5):654–658.
Article13. Osborn AG. Diagnostic cerebral angiography. 1999. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins;125. 128.14. Robinson LR. An unusual human anterior cerebral artery. J Anat. 1959. 01. 93(1):131–133.15. Senter HJ, Miller DJ. Interoptic course of the anterior cerebral artery associated with anterior cerebral artery aneurysm. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1982. 02. 56(2):302–304.16. Spinnato S, Pasqualin A, Chioffi F, Da Pian R. Infraoptic course of the anterior cerebral artery associated with an anterior communicating artery aneurysm: anatomic case report and embryological considerations. Neurosurgery. 1999. 06. 44(6):1315–1319.
Article17. Wong ST, Yuen SC, Fok KF, Yam KY, Fong D. Infraoptic anterior cerebral artery: review, report of two cases and an anatomical classification. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2008. 10. 150(10):1087–1096.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Infraoptic Course of the Anterior Cerebral Artery: Case Report
- Infraoptic Anterior Cerebral Artery Arising from Contralateral Internal Carotid Artery: Case Report
- Stent Assisted Coil Embolization of a Dissecting Aneurysm of the Vertebral Artery: A Case Involving a Patient with Hypoplasia of the Contralateral Vertebral Artery
- Emergent Endovascular Treatment of Ruptured Dissecting Aneurysm of the Intradural Vertebral Artery Using a Self-Expandable Intracranial Stent and a Bioactive Hydrophilic coil
- Dual Stent-Assisted Coil Embolization for Fusiform Aneurysm Arising From Persistent Trigeminal Artery