J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2012 Sep;14(3):223-227. 10.7461/jcen.2012.14.3.223.
Bilateral Approach for Stent-assisted Coiling of Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery Aneurysms: Two Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Myongji Hospital, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Myongji Hospital, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. bjkwon74@gmail.com
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Eulji Hospital, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1808459
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2012.14.3.223
Abstract
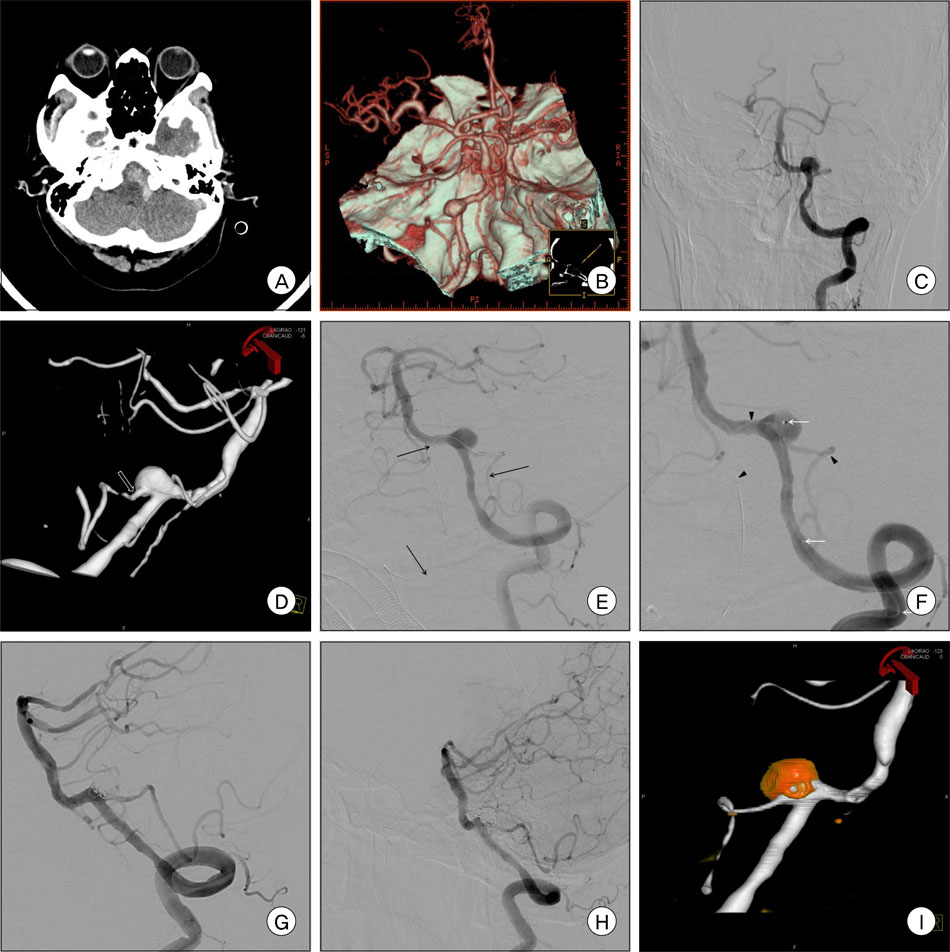
- Aneurysms of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) are rarely encountered. In particular, due to frequent anatomic complexity and the presence of nearby critical structures, PICA origin aneurysms are difficult to treat. However, recent reports of anecdotal cases using advanced endovascular instruments and skills have made the results of endovascular treatment rather outstanding. PICA preservation is the key to a successful endovascular treatment, based on the premise that a PICA origin aneurysm is well occluded. To secure PICA flow, stenting into the PICA would be the best method, however, it is nearly impossible technically via the ipsilateral vertebral artery (VA) if the PICA arose at an acute angle from the sac. In such a case, a bilateral approach for stent-assisted coiling can be a creative method for achievement of two goals of both aneurysm occlusion and PICA preservation: ipsilateral approach for coil delivery and contralateral cross-over approach for stent delivery via a retrograde smooth path into the PICA.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Coil Embolization of Ruptured Proximal Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery Aneurysm with Contralateral Retrograde Approach for LVIS Jr. Intraluminal Support Deployment
Dong Sub Kim, Jae Hoon Sung, Dong Hoon Lee, Ho Jun Yi
J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2018;20(4):235-240. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2018.20.4.235.
Reference
-
1. Al-khayat H, Al-khayat H, Beshay J, Manner D, White J. Vertebral artery-posteroinferior cerebellar artery aneurysms: clinical and lower cranial nerve outcomes in 52 patients. Neurosurgery. 2005. 01. 56(1):2–10. discussion 11.
Article2. Ates O, Ahmed AS, Niemann D, Baskaya MK. The occipital artery for posterior circulation bypass: microsurgical anatomy. Neurosurg Focus. 2008. 02. 24(2):E9.3. Bragg TM, Duckworth EA. Contralateral far-lateral approach for clipping of a ruptured vertebral artery-posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm. Neurosurg Focus. 2008. 12. 25(6):E9.
Article4. Coert BA, Chang SD, Do HM, Marks MP, Steinberg GK. Surgical and endovascular management of symptomatic posterior circulation fusiform aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2007. 05. 106(5):855–865.
Article5. Cross DT 3rd, Moran CJ, Derdeyn CP, Mazumdar A, Rivet D, Chicoine MM. Neuroform stent deployment for treatment of a basilar tip aneurysm via a posterior communicating artery route. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005. Nov-Dec. 26(10):2578–2581.6. Crowley RW, Evans AJ, Kassell NF, Jensen ME, Dumont AS. Endovascular treatment of a fusiform basilar artery aneurysm using multiple "in-stent stents". Technical note. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2009. 06. 3(6):496–500.7. D'Ambrosio AL, Kreiter KT, Bush CA, Sciacca RR, Mayer SA, Solomon RA, et al. Far lateral suboccipital approach for the treatment of proximal posteroinferior cerebellar artery aneurysms: surgical results and long-term outcome. Neurosurgery. 2004. 07. 55(1):39–50. discussion 50-4.8. Doerfler A, Wanke I, Egelhof T, Stolke D, Forsting M. Double-stent method: therapeutic alternative for small wide-necked aneurysms. Technical note. J Neurosurg. 2004. 01. 100(1):150–154.9. Ecker RD, Hanel RA, Levy EI, Hopkins LN. Contralateral vertebral approach for stenting and coil embolization of a large, thrombosed vertebral-posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2007. 12. 107(6):1214–1216.10. Hudgins RJ, Day AL, Quisling RG, Rhoton AL Jr. , Sypert GW, Garcia-Bengochea F. Aneurysms of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. J Neurosurg. 1983. 03. 58(3):381–387.11. Jeon SG, Kwon DH, Ahn JS, Kwun BD, Choi CG, Jin SC. Detachable coil embolization for saccular posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009. 09. 46(3):221–225.
Article12. Mocco J, Snyder KV, Albuquerque FC, Bendok BR, Alan SB, Carpenter JS, et al. Treatment of intracranial aneurysms with the Enterprise stent: a multicenter registry. J Neurosurg. 2009. 01. 110:35–39.
Article13. Moret J, Cognard C, Weill A, Castaings L, Rey A. [Reconstruction technique in the treatment of wide-neck intracranial aneurysms. Long-term angiographic and clinical results. Apropos of 56 cases]. J Neuroradiol. 1997. 06. 24(1):30–44. French.14. Moret J, Ross IB, Weill A, Piotin M. The retrograde approach: a consideration for the endovascular treatment of aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000. 02. 21(2):262–268.15. Peluso JP, van Rooij WJ, Sluzewski M, Beute GN, Majoie CB. Posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms: incidence, clinical presentation, and outcome of endovascular treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008. 01. 29(1):86–90.
Article16. Rodriguez-Hernandez A, Lawton MT. Anatomical triangles defining surgical routes to posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2011. 04. 114(4):1088–1094.17. Siddiqui MA, Bhattacharya J, Lindsay KW, Jenkins S. Horizontal stent-assisted coil embolisation of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms with the enterprise stent - a case series with early angiographic follow-up. Neuroradiology. 2009. 06. 51(6):411–418.18. Song HH, Won YD, Kim YJ, Kim BS. The endovascular management of saccular posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms. Korean J Radiol. 2008. Sep-Oct. 9(5):396–400.
Article19. Sundt TM Jr, Piepgras DG. Occipital to posterior inferior cerebellar artery bypass surgery. J Neurosurg. 1978. 06. 48:916–928.
Article20. Surdell DL, Hage ZA, Eddleman CS, Gupta DK, Bendok BR, Batjer HH. Revascularization for complex intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurg Focus. 2008. 02. 24(2):E21.21. Wanke I, Gizewski E, Forsting M. Horizontal stent placement plus coiling in a broad-based basilar-tip aneurysm: an alternative to the Y-stent technique. Neuroradiology. 2006. 11. 48(11):817–820.
Article22. Yavuz K, Geyik S, Saatci I, Cekirge HS. WingSpan Stent System in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: clinical experience with midterm follow-up results. J Neurosurg. 2008. 09. 109(3):445–453.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Seven Intracranial Aneurysms in One Patient: Treatment and Review of Literature
- Kissing Aneurysms at Fenestrated Proximal Basilar Artery: Double-barrel Stent-assisted Coiling Using Dual Closed-cell Stents
- Stent-Jack Technique for Ruptured Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysm Involving the Origin of Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
- Staged Approach for Stent-Assisted Coiling of Cerebral Aneurysms after Failure of Initial Intra-Saccular Catheterization
- Horizontal Stent Assisted Coiling of Wide Neck Basilar Tip Aneurysm: Comparison of Two Cases