Korean J Radiol.
2013 Aug;14(4):677-682. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.4.677.
Length and Volume of Morphologically Normal Kidneys in Korean Children: Ultrasound Measurement and Estimation Using Body Size
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiological Science, Severance Children's Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 120-752, Korea. mjl1213@yuhs.ac
- 2Biostatistics Collaboration Unit, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 120-752, Korea.
- KMID: 1715774
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.4.677
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the relationship between anthropometric measurements and renal length and volume measured with ultrasound in Korean children who have morphologically normal kidneys, and to create simple equations to estimate the renal sizes using the anthropometric measurements.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We examined 794 Korean children under 18 years of age including a total of 394 boys and 400 girls without renal problems. The maximum renal length (L) (cm), orthogonal anterior-posterior diameter (D) (cm) and width (W) (cm) of each kidney were measured on ultrasound. Kidney volume was calculated as 0.523 x L x D x W (cm3). Anthropometric indices including height (cm), weight (kg) and body mass index (m2/kg) were collected through a medical record review. We used linear regression analysis to create simple equations to estimate the renal length and the volume with those anthropometric indices that were mostly correlated with the US-measured renal sizes.
RESULTS
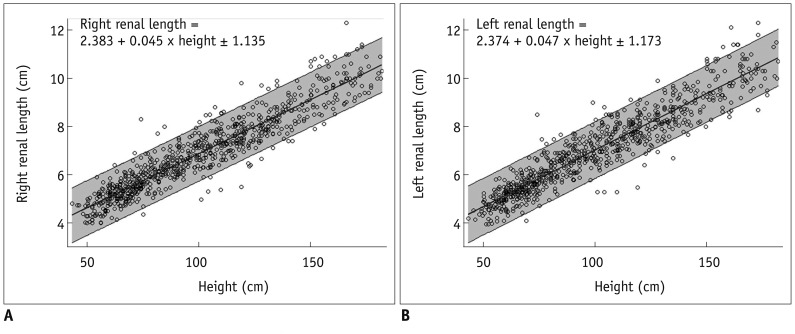
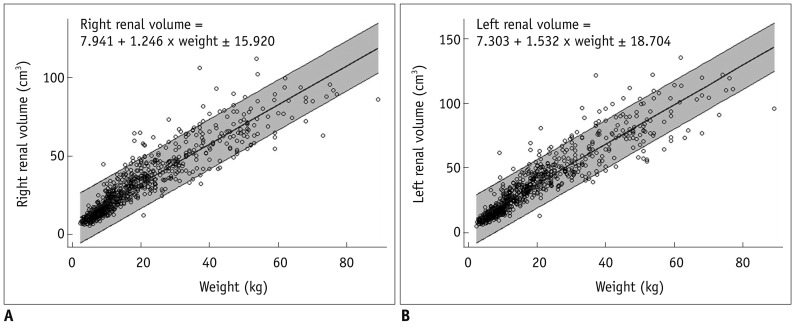
Renal length showed the strongest significant correlation with patient height (R2, 0.874 and 0.875 for the right and left kidneys, respectively, p < 0.001). Renal volume showed the strongest significant correlation with patient weight (R2, 0.842 and 0.854 for the right and left kidneys, respectively, p < 0.001). The following equations were developed to describe these relationships with an estimated 95% range of renal length and volume (R2, 0.826-0.884, p < 0.001): renal length = 2.383 + 0.045 x Height (+/- 1.135) and = 2.374 + 0.047 x Height (+/- 1.173) for the right and left kidneys, respectively; and renal volume = 7.941 + 1.246 x Weight (+/- 15.920) and = 7.303 + 1.532 x Weight (+/- 18.704) for the right and left kidneys, respectively.
CONCLUSION
Scatter plots between height and renal length and between weight and renal volume have been established from Korean children and simple equations between them have been developed for use in clinical practice.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pantoja Zuzuárregui JR, Mallios R, Murphy J. The effect of obesity on kidney length in a healthy pediatric population. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009; 24:2023–2027. PMID: 19475431.
Article2. Glodny B, Unterholzner V, Taferner B, Hofmann KJ, Rehder P, Strasak A, et al. Normal kidney size and its influencing factors - a 64-slice MDCT study of 1.040 asymptomatic patients. BMC Urol. 2009; 9:19. PMID: 20030823.
Article3. Oh K, Jang MJ, Lee NY, Moon JS, Lee CG, Yoo MH, et al. Prevalence and trends in obesity among Korean children and adolescents in 1997 and 2005. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:950–955.
Article4. Kim YS, Park MJ. Time trend in height, weight, BMI and waist circumference of Korean adolescents; from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHNES), 1998, 2001 and 2005. J Korean Soc Pediatr Endocrinol. 2007; 12:142–149.5. Blane CE, Bookstein FL, DiPietro MA, Kelsch RC. Sonographic standards for normal infant kidney length. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985; 145:1289–1291. PMID: 3904372.
Article6. Kadioglu A. Renal measurements, including length, parenchymal thickness, and medullary pyramid thickness, in healthy children: what are the normative ultrasound values? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 194:509–515. PMID: 20093617.
Article7. Moon JS, Lee SY, Nam CM, Choi JM, Choe BK, Seo JW, et al. 2007 Korean National Growth Charts: review of developmental process and an outlook. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:1–25.
Article8. Luk WH, Lo AX, Au-Yeung AW, Liu KK, Woo YH, Chiang CC, et al. Renal length nomogram in Hong Kong Asian children: sonographic measurement and multivariable approach. J Paediatr Child Health. 2010; 46:310–315. PMID: 20665930.
Article9. Klare B, Geiselhardt B, Wesch H, Schärer K, Immich H, Willich E. Radiological kidney size in childhood. Pediatr Radiol. 1980; 9:153–160. PMID: 7393670.
Article10. Hederström E, Forsberg L. Kidney size in children assessed by ultrasonography and urography. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh). 1985; 26:85–91. PMID: 3883699.
Article11. Han BK, Babcock DS. Sonographic measurements and appearance of normal kidneys in children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985; 145:611–616. PMID: 3895872.
Article12. Holloway H, Jones TB, Robinson AE, Harpen MD, Wiseman HJ. Sonographic determination of renal volumes in normal neonates. Pediatr Radiol. 1983; 13:212–214. PMID: 6888992.
Article13. Dinkel E, Ertel M, Dittrich M, Peters H, Berres M, Schulte-Wissermann H. Kidney size in childhood. Sonographical growth charts for kidney length and volume. Pediatr Radiol. 1985; 15:38–43. PMID: 3881724.
Article14. Zerin JM, Blane CE. Sonographic assessment of renal length in children: a reappraisal. Pediatr Radiol. 1994; 24:101–106. PMID: 8078709.
Article15. Scott JE, Hunter EW, Lee RE, Matthews JN. Ultrasound measurement of renal size in newborn infants. Arch Dis Child. 1990; 65(4 Spec No):361–364. PMID: 2186707.
Article16. Schmidt IM, Mølgaard C, Main KM, Michaelsen KF. Effect of gender and lean body mass on kidney size in healthy 10-year-old children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2001; 16:366–370. PMID: 11354783.
Article17. Chiara A, Chirico G, Barbarini M, De Vecchi E, Rondini G. Ultrasonic evaluation of kidney length in term and preterm infants. Eur J Pediatr. 1989; 149:94–95. PMID: 2686999.
Article18. Christophe C, Cantraine F, Bogaert C, Coussement C, Hanquinet S, Spehl M, et al. Ultrasound: a method for kidney size monitoring in children. Eur J Pediatr. 1986; 145:532–538. PMID: 3816856.
Article19. Sargent MA, Long G, Karmali M, Cheng SM. Interobserver variation in the sonographic estimation of renal volume in children. Pediatr Radiol. 1997; 27:663–666. PMID: 9252431.
Article20. Larson DB, Meyers ML, O'Hara SM. Reliability of renal length measurements made with ultrasound compared with measurements from helical CT multiplanar reformat images. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 196:W592–W597. PMID: 21512050.
Article21. Bakker J, Olree M, Kaatee R, de Lange EE, Moons KG, Beutler JJ, et al. Renal volume measurements: accuracy and repeatability of US compared with that of MR imaging. Radiology. 1999; 211:623–628. PMID: 10352583.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sonographic Measurement of the Normal Gallbladder Size in the Korean Children
- Sonographic renal length and volume of normal Thai children versus their Chinese and Western counterparts
- Measurement and Estimation of Renal Size by Computed Tomography in Korean Children
- The Change of Fetal Liver Length and Liver Volume by Ultra-sonography according to Gestational Age in Normal Pregnancy
- The Normal Renal Size of Korean Children: Radiologic Estimation