J Clin Neurol.
2006 Jun;2(2):118-125. 10.3988/jcn.2006.2.2.118.
Clinico-electrical Characteristics of Lateral Temporal Lobe Epilepsy; Anterior and Posterior Lateral Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Kangwon National University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sangunlee@dreamwiz.com
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurology, DongGuk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 1700744
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2006.2.2.118
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
This study aimed to determine whether there are clinicoelectrical differences between anterior lateral temporal lobe epilepsy (ALTLE) and posterior lateral temporal lobe epilepsy (PLTLE), taking medial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE) as a reference.
METHODS
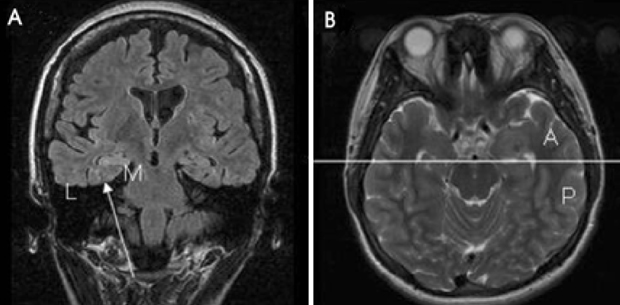
We analyzed the historical information, ictal semiologies, and ictal EEGs of temporal lobe epilepsy patients with a documented favorable surgical outcome (Engel class I or II) at follow-up after more than one year. LTLE was defined when a discrete lesion on MRI or an ictal onset zone in invasive study was located outside the collateral sulcus. LTLE was further divided into ALTLE and PLTLE by reference to the line across the cerebral peduncle. Total 107 seizures of 13 ALTLE, 8 PLTLE and 21 MTLE patients were reviewed.
RESULTS
Initial hypomotor symptom was frequently observed in PLTLE (P<0.001). Oroalimentary automatism (OAA) was not observed initially in PLTLE. Generalized tonic-clonic seizures occurred significantly earlier in PLTLE than in ALTLE or MTLE (P< 0.001). Ictal scalp EEG was not helpful in differentiating between ALTLE and PLTLE.
CONCLUSIONS
Frequent hypomotor onset, the absence of initial oroalimentary automatism, and early generalization are characteristic findings of PLTLE, although they are insufficient to differentiate it from ALTLE or MTLE.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pacia SV, Devinsky O, Perrine K, Ravdin L, Luciano D, Vazquez B, et al. Clinical features of neocortical temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1996. 40:724–730.2. O'Brien TJ, Kilpatrick C, Murrie V, Vogrin S, Morris K, Cook MJ. Temporal lobe epilepsy caused by mesial temporal sclerosis and temporal neocortical lesions. A clinical and electroencephalographic study of 46 pathologically proven cases. Brain. 1996. 119:2133–2141.3. Gil-Nagel A, Risinger MW. Ictal semiology in hippocampal versus extrahippocampal temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain. 1997. 120:183–192.
Article4. Foldvary N, Lee N, Thwaites G, Mascha E, Hammel J, Kim H, et al. Clinical and electrographic manifestation of lesional neocortical temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology. 1997. 49:757–763.
Article5. Saygi S, Spencer SS, Scheyer R, Katz A, Mattson R, Spencer DD. Differentiation of temporal lobe ictal behavior associated with hippocampal sclerosis and tumors of temporal lobe. Epilepsia. 1994. 35:737–742.
Article6. Burgerman RS, Sperling MR, French JA, Saykin AJ, O'Connor MJ. Comparison of mesial versus neocortical onset temporal lobe seizures: neurodiagnostic findings and surgical outcome. Epilepsia. 1995. 36:662–670.
Article7. Engel J Jr, Van Ness PC, Rassmussen TB, Ojemann LM. Engel J, editor. Outcome with respect to epileptic seizures. Surgical treatment of epilepsies. 1993. New York: Raven Press;609–691.8. Lee SK, Kim JY, Hong KS, Nam HW, Park SH, Chung CK. The clinical usefulness of ictal surface EEG in neocortical epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2000. 41:1450–1455.
Article9. Sperling MR, Cahan LD, Brown WJ. Relief of seizures from a predominantly posterior temporal tumor with anterior temporal lobectomy. Epilepsia. 1989. 30:559–563.
Article10. Olivier A, Gloor P, Andermann F, Ives J. Occipitotemporal epilepsy studied with stereotaxically implanted depth electrodes and successfully treated by temporal resection. Ann Neurol. 1982. 11:428–432.
Article11. Rasmussen TB. Surgical treatment of complex partial seizures: results, lessons, and problems. Epilepsia. 1983. 24:S65–S76.
Article12. Ebner A. Wolf P, editor. Lateral (neocortical) temporal lobe epilepsy. Epileptic seizures and syndromes. 1997. London: John Libbey;375–382.13. Williamson PD, Wieser HG, Delgado-Escueta AV. Engel J Jr. Clinical characteristics of partial seizures. Surgical treatment of epilepsies. 1987. New York: Raven Press;101–120.14. Penfield W, Perot P. The brain's record of auditory and visual experience. A final summary and discussion. Brain. 1963. 86:595–696.
Article15. Liegeois-Chauvel C, Musolino A, Chauvel P. Localization of the primary auditory area in man. Brain. 1991. 114:139–151.16. Schneider RC, Calhoun HD, Crosby EC. Vertigo and rotational movement in cortical and subcortical lesions. J Neurol Sci. 1968. 6:493–516.
Article17. Penfield W. The twenty-ninth Maudsley lecture: the role of the temporal cortex in certain psychical phenomena. J Ment Sci. 1955. 101:451–465.
Article18. Gloor P, Olivier A, Quesney LF, Andermann A, Horowitz S. The role of the limbic system in experiential phenomena of temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1982. 12:129–144.
Article19. Mihara T, Inoue Y, Hiyoshi T, Watanabe Y, Kubota Y, Tottori T, et al. Localizing value of seizure manifestations of temporal lobe epilepsies and the consequence of analyzing their sequential appearance. Jpn J Psychiatry Neurol. 1993. 47:175–182.
Article20. Lieb JP, Engel J Jr, Babb TL. Interhemispheric propagation time of human hippocampal seizures I Relationship to surgical outcome. Epilepsia. 1986. 27:286–293.
Article21. Duchowny M, Jayakar P, Resnick T, Levin B, Alvarez L. Posterior temporal epilepsy: electroclinical features. Ann Neurol. 1994. 35:427–431.
Article22. Ebersole JS, Pacia SV. Localization of temporal lobe foci by ictal EEG patterns. Epilepsia. 1996. 37:386–399.
Article23. Foldvary N, Klem G, Hammel J, Bingaman W, Najm I, Luders H. The localizing value of ictal EEG in focal epilepsy. Neurology. 2001. 57:2022–2028.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- THREE SUBTYPES OF TEMPORAL LOBE EPILEPSY: Clinical and Electrophysiological Characteristics of Medial, Anterior neocortical, and posterior lateral TLE
- Postictal MR Enhancement in a Patient with Lateral Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
- Asymmetry of Medial and Lateral Tempora) Regional Glucose Metabolism in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy by F-18-FDG PET
- Ictal Vomiting Associated with Temporal Lobe Epilepsy of Dominant Hemisphere
- Morphological Alterations of Hippocampus in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: Cell Loss, Synaptic Reorganization, Cell Birth