Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2008 Jun;1(2):53-62. 10.3342/ceo.2008.1.2.53.
Endoscopic Skull Base Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, NC, USA. neoender@gmail.com
- KMID: 1486055
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2008.1.2.53
Abstract
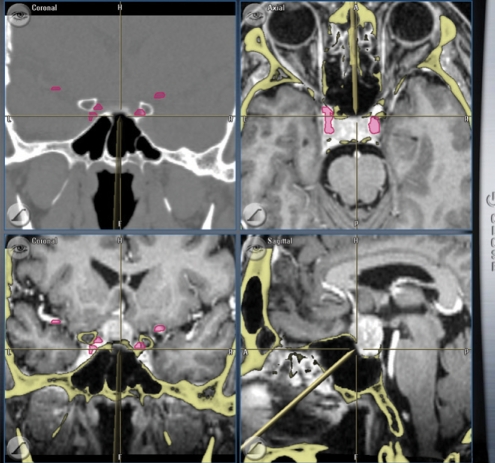
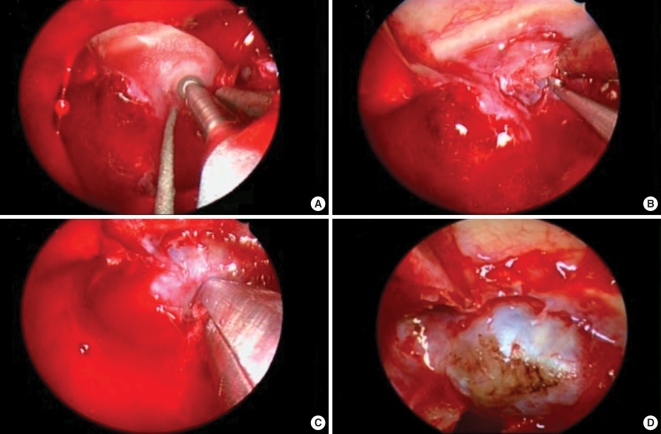
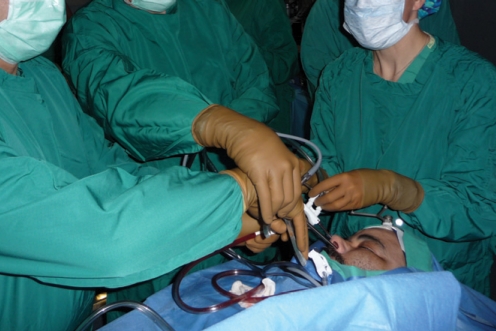
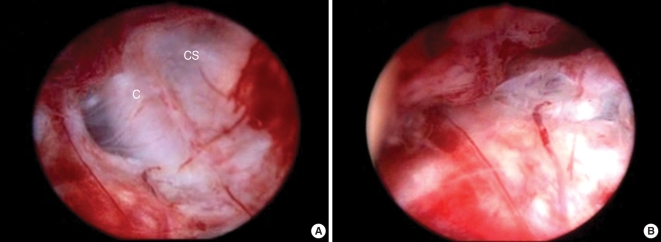
- Endoscopic skull base surgery has undergone rapid advancement in the past decade moving from pituitary surgery to suprasellar lesions and now to a myriad of lesions extending from the cribriform plate to C2 and laterally out to the infratemporal fossa and petrous apex. Evolution of several technological advances as well as advances in understanding of endoscopic anatomy and the development of surgical techniques both in resection and reconstruction have fostered this capability. Management of benign disease via endoscopic methods is largely accepted now but more data is needed before the controversy on the role of endoscopic management of malignant disease is decided. Continued advances in surgical technique, navigation systems, endoscopic imaging technology, and robotics assure continued brisk evolution in this expanding field.
Keyword
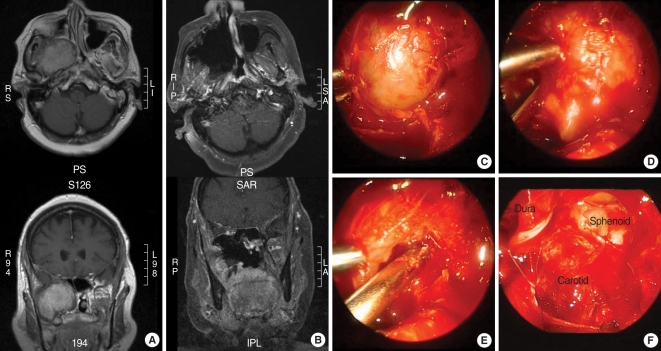
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Correlation between Pituitary Insufficiency and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding in Non-Functioning Pituitary Adenomas
Hyun Min Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Eun Young Lee, Woo Kyung Lee, Jung Soo Lim, Sena Hwang, Mi Jung Lee, Seung Ku Lee, Sun Ho Kim, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2010;25(4):310-315. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2010.25.4.310.
Reference
-
1. Pollock JR, Akinwunmi J, Scaravilli F, Powell MP. Transcranial surgery for pituitary tumors performed by Sir Victor Horsley. Neurosurgery. 2003; 4. 52(4):914–925. PMID: 12657189.
Article2. Caton R, Paul FT. Notes of a case of acromegaly treated by operation. Br Med J. 1893; 2:1421–1423.
Article3. Schloffer H. On the problem of surgery on the pituitary gland. Beitr Klin Chir. 1906; 50:767–817.4. Schloffer H. Further report on the patient operated upon for a pituitary tumor. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1907; 20:1075–1078.5. Hirsch O. Endonasal method of removal of hypophyseal tumors: With a report of two successful cases. JAMA. 1910; 55:772–774.6. Cushing H. Partial hypophysectomy for acromegaly: With remarks on function of the hypophysis. Ann Surg. 1909; 50:1002–1017. PMID: 17862444.7. Cushing H. The Weir Mitchell Lecture: Surgical experiences with pituitary disorders. JAMA. 1914; 63:1515–1525.8. Maroon JC. Skull base surgery: past, present, and future trends. Neurosurg Focus. 2005; 7. 19(1):E1. PMID: 16078812.
Article9. Senior BA, Ebert CS, Kolln K, Bassim MK, Younes M, Sigounas DG, et al. Minimally invasive pituitary surgery. Laryngoscope. in press.
Article10. Liu JK, Das K, Weiss MH, Laws ER Jr, Couldwell WT. The history and evolution of transsphenoidal surgery. J Neurosurg. 2001; 12. 95(6):1083–1096. PMID: 11765830.
Article11. Landolt AM. History of pituitary surgery from the technical aspect. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2001; 1. 12(1):37–44. PMID: 11175987.
Article12. Doglietto F, Prevedello DM, Jane JA Jr, Han J, Laws ER Jr. Brief history of endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery-from Philipp Bozzini to the First World Congress of Endoscopic Skull Base Surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2005; 12. 15. 19(6):E3. PMID: 16398480.13. Mouton WG, Bessell JR, Maddern GJ. Looking back to the advent of modern endoscopy: 150th birthday of Maximilian Nitze. World J Surg. 1998; 12. 22(12):1256–1258. PMID: 9841754.
Article14. Linder TE, Simmen D, Stool SE. Revolutionary inventions in the 20th century. The history of endoscopy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997; 11. 123(11):1161–1163. PMID: 9366694.
Article15. Messerklinger W. Diagnosis and endoscopic surgery of the nose and its adjoining structures. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg. 1980; 34(2):170–176. French. PMID: 7457127.16. Jankowski R, Auque J, Simon C, Marchal JC, Hepner H, Wayoff M. Endoscopic pituitary tumor surgery. Laryngoscope. 1992; 2. 102(2):198–202. PMID: 1738293.
Article17. Jho HD, Carrau RL. Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery: experience with 50 patients. J Neurosurg. 1997; 7. 87(1):44–51. PMID: 9202264.
Article18. Cappabianca P, Alfieri A, de Divitiis E. Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach to the sella: towards functional endoscopic pituitary surgery (FEPS). Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 1998; 6. 41(2):66–73. PMID: 9651913.
Article19. Laws ER Jr. Transsphenoidal microsurgery in the management of craniopharyngioma. J Neurosurg. 1980; 5. 52(5):661–666. PMID: 7373393.
Article20. Zhang Q, Kong F, Yan B, Ni Z, Liu H. Endoscopic endonasal surgery for clival chordoma and chondrosarcoma. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2008; 4. 70(2):124–129. PMID: 18408411.
Article21. Georgalas C, Kania R, Guichard JP, Sauvaget E, Tran Ba Huy P, Herman P. Endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery for cholesterol granulomas involving the petrous apex. Clin Otolaryngol. 2008; 2. 33(1):38–42. PMID: 18302553.
Article22. Fortes FS, Sennes LU, Carrau RL, Brito R, Ribas GC, Yasuda A, et al. Endoscopic anatomy of the pterygopalatine fossa and the transpterygoid approach: development of a surgical instruction model. Laryngoscope. 2008; 1. 118(1):44–49. PMID: 17989582.
Article23. de Notaris M, Esposito I, Cavallo LM, Burgaya AC, Galino AP, Esposito F, et al. Endoscopic endonasal approach to the ethmoidal planum: anatomic study. Neurosurg Rev. 2008; 7. 31(3):309–317. PMID: 18338185.
Article24. Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Esposito F, De Divitiis O, Messina A, De Divitiis E. Extended endoscopic endonasal approach to the midline skull base: the evolving role of transsphenoidal surgery. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 2008; 33:151–199. PMID: 18383814.
Article25. Solari D, Magro F, Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Samii A, Esposito F, et al. Anatomical study of the pterygopalatine fossa using an endoscopic endonasal approach: spatial relations and distances between surgical landmarks. J Neurosurg. 2007; 1. 106(1):157–163. PMID: 17236502.
Article26. Kassam AB, Thomas AJ, Zimmer LA, Snyderman CH, Carrau RL, Mintz A, et al. Expanded endonasal approach: a fully endoscopic completely transnasal resection of a skull base arteriovenous malformation. Childs Nerv Syst. 2007; 5. 23(5):491–498. PMID: 17226032.
Article27. Stamm AM. Transnasal endoscopy-assisted skull base surgery. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 2006; 9. 196(45):53.
Article28. Stamm AC, Pignatari SS, Vellutini E. Transnasal endoscopic surgical approaches to the clivus. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2006; 6. 39(3):639–656. PMID: 16757236.
Article29. Kassam AB, Gardner P, Snyderman C, Mintz A, Carrau R. Expanded endonasal approach: fully endoscopic, completely transnasal approach to the middle third of the clivus, petrous bone, middle cranial fossa, and infratemporal fossa. Neurosurg Focus. 2005; 7. 15. 19(1):E6. PMID: 16078820.
Article30. Kassam A, Snyderman CH, Mintz A, Gardner P, Carrau RL. Expanded endonasal approach: the rostrocaudal axis. Part I. Crista galli to the sella turcica. Neurosurg Focus. 2005; 7. 15. 19(1):E3. PMID: 16078817.
Article31. Kassam A, Snyderman CH, Mintz A, Gardner P, Carrau RL. Expanded endonasal approach: the rostrocaudal axis. Part II. Posterior clinoids to the foramen magnum. Neurosurg Focus. 2005; 7. 15. 19(1):E4. PMID: 16078818.
Article32. Cavallo LM, Cappabianca P, Galzio R, Iaconetta G, de Divitiis E, Tschabitscher M. Endoscopic transnasal approach to the cavernous sinus versus transcranial route: anatomic study. Neurosurgery. 2005; 4. 56(2 Suppl):379–389. PMID: 15794834.
Article33. Casler JD, Doolittle AM, Mair EA. Endoscopic surgery of the anterior skull base. Laryngoscope. 2005; 1. 115(1):16–24. PMID: 15630358.
Article34. Kingdom TT, Delgaudio JM. Endoscopic approach to lesions of the sphenoid sinus, orbital apex, and clivus. Am J Otolaryngol. 2003; Sep–Oct. 24(5):317–322. PMID: 13130444.
Article35. Alfieri A, Jho HD, Schettino R, Tschabitscher M. Endoscopic endonasal approach to the pterygopalatine fossa: anatomic study. Neurosurgery. 2003; 2. 52(2):374–378. PMID: 12535367.
Article36. Unger F, Walch C, Stammberger H, Papaefthymiou G, Haselsberger K, Pendl G. Olfactory neuroblastoma (esthesioneuroblastoma): report of six cases treated by a novel combination of endoscopic surgery and radiosurgery. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2001; 6. 44(2):79–84. PMID: 11487789.
Article37. Hartnick CJ, Myseros JS, Myer CM 3rd. Endoscopic access to the infratemporal fossa and skull base: a cadaveric study. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001; 11. 127(11):1325–1327. PMID: 11701068.38. Casiano RR, Numa WA, Falquez AM. Endoscopic resection of esthesioneuroblastoma. Am J Rhinol. 2001; Jul–Aug. 4:271–279. PMID: 11554661.
Article39. Kassam AB, Snyderman C, Gardner P, Carrau R, Spiro R. The expanded endonasal approach: a fully endoscopic transnasal approach and resection of the odontoid process: technical case report. Neurosurgery. 2005; 7. 57(1 Suppl):E213. PMID: 15987596.
Article40. Griffith AJ, Terrell JE. Transsphenoid endoscopic management of petrous apex cholesterol granuloma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996; 1. 114(1):91–94. PMID: 8570257.
Article41. Fucci MJ, Alford EL, Lowry LD, Keane WM, Sataloff RT. Endoscopic management of a giant cholesterol cyst of the petrous apex. Skull Base Surg. 1994; 4(1):52–58. PMID: 17170927.
Article42. Poetker DM, Toohill RJ, Loehrl TA, Smith TL. Endoscopic management of sinonasal tumors: a preliminary report. Am J Rhinol. 2005; May–Jun. 19(3):307–315. PMID: 16011140.
Article43. Lund V, Howard DJ, Wei WI. Endoscopic resection of malignant tumors of the nose and sinuses. Am J Rhinol. 2007; Jan–Feb. 21(1):89–94. PMID: 17283568.
Article44. Zafereo ME, Fakhri S, Prayson R, Batra PS, Lee J, Lanza DC, et al. Esthesioneuroblastoma: 25-year experience at a single institution. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; 4. 138(4):452–458. PMID: 18359353.
Article45. Castelnuovo P, Bignami M, Delu G, Battaglia P, Bignardi M, Dallan I. Endonasal endoscopic resection and radiotherapy in olfactory neuroblastoma: our experience. Head Neck. 2007; 9. 29(9):845–850. PMID: 17427966.
Article46. Dave SP, Bared A, Casiano RR. Surgical outcomes and safety of transnasal endoscopic resection for anterior skull tumors. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 6. 136(6):920–927. PMID: 17547980.
Article47. Suriano M, De Vincentiis M, Colli A, Benfari G, Mascelli A, Gallo A. Endoscopic treatment of esthesioneuroblastoma: a minimally invasive approach combined with radiation therapy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 1. 136(1):104–107. PMID: 17210343.
Article48. Patel SG, Singh B, Polluri A, Bridger PG, Cantu G, Cheesman AD, et al. Craniofacial surgery for malignant skull base tumors: report of an international collaborative study. Cancer. 2003; 9. 15. 98(6):1179–1187. PMID: 12973841.49. Batra PS, Citardi MJ, Worley S, Lee J, Lanza DC. Resection of anterior skull base tumors: comparison of combined traditional and endoscopic techniques. Am J Rhinol. 2005; Sep–Oct. 19(5):521–528. PMID: 16270609.
Article50. McCutcheon IE, Blacklock JB, Weber RS, DeMonte F, Moser RP, Byers M, et al. Anterior transcranial (craniofacial) resection of tumors of the paranasal sinuses: surgical technique and results. Neurosurgery. 1996; 3. 38(3):471–479. PMID: 8837798.
Article51. Har-El G, Casiano RR. Endoscopic management of anterior skull base tumors. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2005; 2. 38(1):133–144. PMID: 15649504.
Article52. Snyderman CH, Carrau RL, Kassam AB, Zanation A, Prevedello D, Gardner P, et al. Endoscopic skull base surgery: principles of endonasal oncological surgery. J Surg Oncol. 2008; 6. 15. 97(8):658–664. PMID: 18493946.
Article53. Lund VJ, Howard D, Wei W, Spittle M. Olfactory neuroblastoma: past, present, and future? Laryngoscope. 2003; 3. 113(3):502–507. PMID: 12616204.
Article54. Sonnenburg RE, White D, Ewend MG, Senior B. The learning curve in minimally invasive pituitary surgery. Am J Rhinol. 2004; Jul–Aug. 18(4):259–263. PMID: 15490574.
Article55. Karavitaki N, Brufani C, Warner JT, Adams CB, Richards P, Ansorge O, et al. Craniopharyngiomas in children and adults: systematic analysis of 121 cases with long-term follow-up. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2005; 4. 62(4):397–409. PMID: 15807869.
Article56. Kassam AB, Gardner PA, Snyderman CH, Carrau RL, Mintz AH, Prevedello DM. Expanded endonasal approach, a fully endoscopic transnasal approach for the resection of midline suprasellar craniopharyngiomas: a new classification based on the infundibulum. J Neurosurg. 2008; 4. 108(4):715–728. PMID: 18377251.57. Kassam AB, Prevedello DM, Thomas A, Gardner P, Mintz A, Snyderman C, et al. Endoscopic endonasal pituitary transposition for a transdorsum sellae approach to the interpeduncular cistern. Neurosurgery. 2008; 3. 62(3 Suppl 1):57–72. PMID: 18424968.
Article58. Laufer I, Anand VK, Schwartz TH. Endoscopic, endonasal extended transsphenoidal, transplanum transtuberculum approach for resection of suprasellar lesions. J Neurosurg. 2007; 3. 106(3):400–406. PMID: 17367062.
Article59. Frank G, Pasquini E, Doglietto F, Mazzatenta D, Sciarretta V, Farneti G, et al. The endoscopic extended transsphenoidal approach for craniopharyngiomas. Neurosurgery. 2006; 7. 59(1 Suppl 1):ONS75–ONS83. PMID: 16888556.
Article60. de Divitiis E, Cavallo LM, Cappabianca P, Esposito F. Extended endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach for the removal of suprasellar tumors: Part 2. Neurosurgery. 2007; 1. 60(1):46–58. PMID: 17228252.61. de Divitiis E, Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Esposito F, de Divitiis O, Messina A. Extended endoscopic transsphenoidal approach for extrasellar craniopharyngiomas. Neurosurgery. 2007; 11. 61(5 Suppl 2):219–227. PMID: 18091236.
Article62. Stamm AC, Vellutini E, Harvey RJ, Nogeira JF Jr, Herman DR. Endoscopic transnasal craniotomy and the resection of craniopharyngioma. Laryngoscope. 2008; 118(7):1142–1148. PMID: 18438262.
Article63. Colli B, Al-Mefty O. Chordomas of the craniocervical junction: follow-up review and prognostic factors. J Neurosurg. 2001; 12. 95(6):933–943. PMID: 11765837.
Article64. Hug EB, Loredo LN, Slater JD, DeVries A, Grove RI, Schaefer RA, et al. Proton radiation therapy for chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the skull base. J Neurosurg. 1999; 9. 91(3):432–439. PMID: 10470818.
Article65. Frank G, Sciarretta V, Calbucci F, Farneti G, Mazzatenta D, Pasquini E. The endoscopic transnasal transsphenoidal approach for the treatment of cranial base chordomas and chondrosarcomas. Neurosurgery. 2006; 7. 59(1 Suppl 1):ONS50–ONS57. PMID: 16888551.
Article66. Solares CA, Fakhri S, Batra PS, Lee J, Lanza DC. Transnasal endoscopic resection of lesions of the clivus: a preliminary report. Laryngoscope. 2005; 11. 115(11):1917–1922. PMID: 16319599.
Article67. Jho HD, Carrau RL, McLaughlin MR, Somaza SC. Endoscopic transsphenoidal resection of a large chordoma in the posterior fossa. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1997; 139(4):343–347. PMID: 9202775.
Article68. Alfieri A, Jho HD, Tschabitscher M. Endoscopic endonasal approach to the ventral cranio-cervical junction: anatomical study. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2007; 3. 144(3):219–225. PMID: 11956934.69. Nayak JV, Gardner PA, Vescan AD, Carrau RL, Kassam AB, Snyderman CH. Experience with the expanded endonasal approach for resection of the odontoid process in rheumatoid disease. Am J Rhinol. 2007; Sep–Oct. 21(5):601–606. PMID: 17999797.
Article70. Fraser JF, Anand VK, Schwartz TH. Endoscopic biopsy sampling of tophaceous gout of the odontoid process. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007; 7. 7(1):61–64. PMID: 17633489.71. Messina A, Bruno MC, Decq P, Coste A, Cavallo LM, de Divittis E, et al. Pure endoscopic endonasal odontoidectomy: anatomical study. Neurosurg Rev. 2007; 7. 30(3):189–194. PMID: 17492320.
Article72. Gardner PA, Kassam AB, Rothfus WE, Snyderman CH, Carrau RL. Preoperative and intraoperative imaging for endoscopic endonasal approaches to the skull base. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2008; 2. 41(1):215–230. PMID: 18261533.
Article73. Chen MK, Lai JC, Chang CC, Liu MT. Minimally invasive endoscopic nasopharyngectomy in the treatment of recurrent T1-2a nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2007; 5. 117(5):894–896. PMID: 17473691.
Article74. Oyama K, Ikezono T, Tahara S, Shindo S, Kitamura T, Teramoto A. Petrous apex cholesterol granuloma treated via the endoscopic transsphenoidal approach. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2007; 3. 149(3):299–302. PMID: 17273887.
Article75. Presutti L, Villari D, Marchioni D. Petrous apex cholesterol granuloma: transsphenoid endoscopic approach. J Laryngol Otol. 2006; 6. 120(6):e20. PMID: 16700957.
Article76. DiNardo LJ, Pippin GW, Sismanis A. Image-guided endoscopic transsphenoidal drainage of select petrous apex cholesterol granulomas. Otol Neurotol. 2003; 11. 24(6):939–941. PMID: 14600478.
Article77. Mouadeb DA, Chandra RK, Kennedy DW, Feldman M. Sinonasal paraganglioma: endoscopic resection with a 4-year follow-up. Head Neck. 2003; 12. 25(12):1077–1081. PMID: 14648867.
Article78. Zimmer LA, Hirsch BE, Kassam A, Horowitz M, Snyderman CH. Resection of a recurrent paraganglioma via an endoscopic transnasal approach to the jugular fossa. Otol Neurotol. 2006; 4. 27(3):398–402. PMID: 16639280.
Article79. Robinson S, Patel N, Wormald PJ. Endoscopic management of benign tumors extending into the infratemporal fossa: a two-surgeon transnasal approach. Laryngoscope. 2005; 10. 115(10):1818–1822. PMID: 16222202.
Article80. Douglas R, Wormald PJ. Endoscopic surgery for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: where are the limits? Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; 2. 14(1):1–5. PMID: 16467630.
Article81. White DR, Dubin MG, Senior BA. Endoscopic repair of cerebrospinal fluid leaks after neurosurgical procedures. Am J Otolaryngol. 2003; Jul–Aug. 24(4):213–216. PMID: 12884209.
Article82. Martin TJ, Loehrl TA. Endoscopic CSF leak repair. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 2. 15(1):35–39. PMID: 17211181.
Article83. Lopatin AS, Kapitanov DN, Potapov AA. Endonasal endoscopic repair of spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leaks. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003; 8. 129(8):859–863. PMID: 12925345.
Article84. Schlosser RJ, Bolger WE. Nasal cerebrospinal fluid leaks. J Otolaryngol. 2002; 8. 31(Suppl 1):S28–S37. PMID: 12243241.
Article85. Zweig JL, Carrau RL, Celin SE, Snyderman CH, Kassam A, Hegazy H. Endoscopic repair of acquired encephaloceles, meningoceles, and meningo-encephaloceles: predictors of success. Skull Base. 2002; 8. 12(3):133–139. PMID: 17167667.
Article86. Kassam A, Carrau RL, Snyderman CH, Gardner P, Mintz A. Evolution of reconstructive techniques following endoscopic expanded endonasal approaches. Neurosurg Focus. 2005; 7. 15. 19(1):E8. PMID: 16078822.
Article87. Hadad G, Bassagasteguy L, Carrau RL, Mataza JC, Kassam A, Snyderman CH, et al. A novel reconstructive technique after endoscopic expanded endonasal approaches: vascular pedicle nasoseptal flap. Laryngoscope. 2006; 10. 116(10):1882–1886. PMID: 17003708.
Article88. Fortes FS, Carrau RL, Snyderman CH, Kassam A, Prevedello D, Vescan A, et al. Transpterygoid transposition of a temporoparietal fascia flap: a new method for skull base reconstruction after endoscopic expanded endonasal approaches. Laryngoscope. 2007; 6. 117(6):970–976. PMID: 17417106.
Article89. Rasmussen IA Jr, Lindseth F, Rygh OM, Berntsen EM, Selbekk T, Xu J, et al. Functional neuronavigation combined with intra-operative 3D ultrasound: initial experiences during surgical resections close to eloquent brain areas and future directions in automatic brain shift compensation of preoperative data. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2007; 4. 149(4):365–378. PMID: 17308976.
Article90. Hong J, Hata N, Konishi K, Hashizume M. Real-time magnetic resonance imaging driven by electromagnetic locator for interventional procedure and endoscopic therapy. Surg Endosc. 2008; 2. 22(2):552–556. PMID: 18189156.
Article91. Levy ML, Nguyen A, Aryan H, Jandial R, Meltzer HS, Apuzzo ML. Robotic virtual endoscopy: development of a multidirectional rigid endoscope. Neurosurgery. 2006; 7. 59(1 Suppl 1):ONS134–ONS141. PMID: 16888544.
Article92. O'Malley BW Jr, Weinstein GS. Robotic skull base surgery: preclinical investigations to human clinical application. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 12. 133(12):1215–1219. PMID: 18086962.93. Hanna EY, Holsinger C, DeMonte F, Kupferman M. Robotic endoscopic surgery of the skull base: a novel surgical approach. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 12. 133(12):1209–1214. PMID: 18086961.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Iatrogenic Skull Base Defect Accompanied by Brain Injury After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: A Report of Two Cases
- Endoscopic Endonasal Transsphenoidal Skull Base Surgery
- A Case of Extracranial Chondroma of the Skull Base
- Endoscopic Endonasal Skull Base Repair with Nasoseptal Flap
- Book Review: Transnasal Endoscopic Skull Base and Brain Surgery: Tips and Pearls