Infect Chemother.
2010 Aug;42(4):241-243. 10.3947/ic.2010.42.4.241.
A Case of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum Bacteremia and Osteomyelitis Diagnosed by 16s rRNA Sequencing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. haroc153@naver.com
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1457385
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2010.42.4.241
Abstract
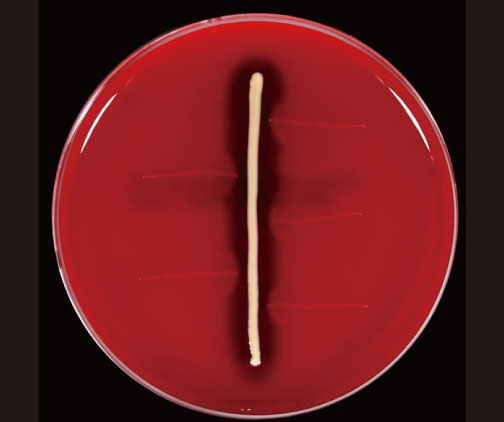
- Arcanobacterium haemolyticum is a catalase-negative, aerobic gram-positive rod. It causes pharyngitis, skin and soft tissue infection, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, and septicemia. We experienced a case of A. haemolyticum bacteremia and osteomyelitis in a diabetic patient. The organism was misidentified as Cellulomonas species by automated system but correctly identified as A. haemolyticum by 16s rRNA sequencing.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
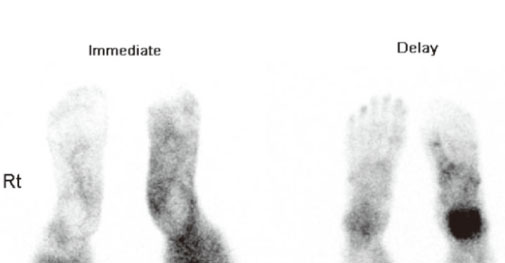
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Two Cases of Invasive Infections Caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum in Immunocompetent Adult
Seong Yeon Park, Ki Hyoung Koo, Hee Jin Huh, Seok Lae Chae
Infect Chemother. 2012;44(6):481-484. doi: 10.3947/ic.2012.44.6.481.
Reference
-
1. MacLean PD, Liebow AA, Rosenberg AA. A hemolytic Corynebacterium resembling Corynebacterium ovis and corynebacterium pyogenes in man. J Infect Dis. 1946. 79:69–90.
Article2. Collins MD, Jones D, Schofield GM. Reclassification of 'Corynebacterium haemolyticum' (MacLean, Liebow & Rosenberg) in the genus Arcanobacterium gen. nov. as Arcanobacterium haemolyticum nom. rev., comb. nov. J Gen Microbiol. 1982. 128:1279–1281.
Article3. Mackenzie A, Fuite LA, Chan FT, King J, Allen U, MacDonald N, Diaz-Mitoma F. Incidence and pathogenicity of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum during a 2-year study in Ottawa. Clin Infect Dis. 1995. 21:177–181.
Article4. Dobinsky S, Noesselt T, Rücker A, Maerker J, Mack D. Three cases of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum associated with abscess formation and cellulitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1999. 18:804–806.
Article5. Esteban J, Zapardiel J, Soriano F. Two cases of soft-tissue infection caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum. Clin Infect Dis. 1994. 18:835–836.
Article6. Skov RL, Sanden AK, Danchell VH, Robertsen K, Ejlertsen T. Systemic and deep-seated infect ions caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998. 17:578–582.
Article7. Vargas J, Hernandez M, Silvestri C, Jiménez O, Guevara N, Carballo M, Rojas N, Riera J, Alayo E, Fernández M, Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Silva M. Brain abscess due to Arcanobacterium haemolyticum after dental extraction. Clin Infect Dis. 2006. 42:1810–1811.
Article8. Waller KS, Johnson J, Wood BP. Radiological case of the month. Cavitary pneumonia due to Arcanobacterium hemolytic. Am J Dis Child. 1991. 145:209–210.9. Alós JI, Barros C, Gómez-Garcés JL. Endocarditis caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1995. 14:1085–1088.10. Ford JG, Yeatts RP, Givner LB. Orbital cellulitis, subperiosteal abscess, sinusitis, and septicemia caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995. 120:261–262.
Article11. Adderson EE, Boudreaux JW, Cummings JR, Pounds S, Wilson DA, Procop GW, Hayden RT. Identification of clinical coryneform bacterial isolates: comparison of biochemical methods and sequence analysis of 16S rRNA and rpoB genes. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. 46:921–927.
Article12. Carlson P, Kontiainen S, Renkonen OV. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994. 38:142–143.
Article13. Carlson P, Korpela J, Walder M, Nyman M. Antimicrobial susceptibilities and biotypes of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum blood isolates. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1999. 18:915–917.
Article14. Nyman M, Banck G, Thore M. Penicillin tolerance in Arcanobacterium haemolyticum. J Infect Dis. 1990. 161:261–265.15. Malini A, Deepa EK, Manohar PV, Borappa K, Prasad SR. Soft tissue infections with Arcanobacterium haemolyticum: report of three cases. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2008. 26:192–195.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Invasive Infections Caused by Arcanobacterium haemolyticum in Immunocompetent Adult
- A Case of Bacteremia Due to Microbacterium oleivorans Identified by 16S rRNA Sequencing Analysis
- Five Cases of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum Isolated from Skin Ulcer and Peritonsillar Abscess
- A Case of Bacteremia Caused by Leuconostoc lactis Identified by 16S rRNA Sequencing
- Catheter-related Bacteremia due to Microbacterium oxydans Identified by 16S rRNA Sequencing Analysis and Biochemical Characteristics