J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2008 Mar;15(1):39-47. 10.4078/jkra.2008.15.1.39.
Assessment of Clinical Effect and Changes of Sacroiliac Joint by CT and MRI in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis during Therapy with Etanercept
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. goldgu@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Departments of Radiology, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- 3Internal Medicine and Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 1324507
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jkra.2008.15.1.39
Abstract
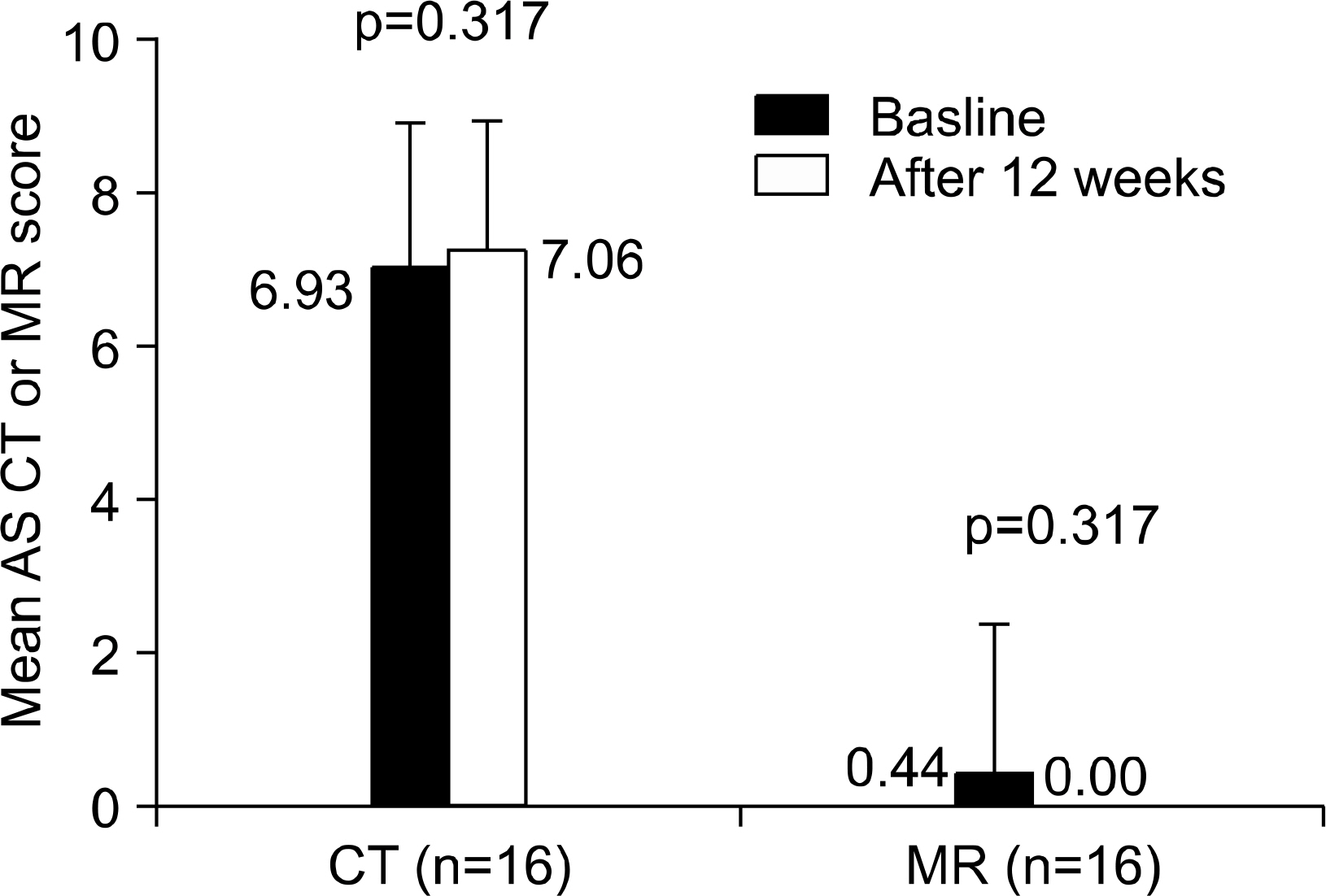
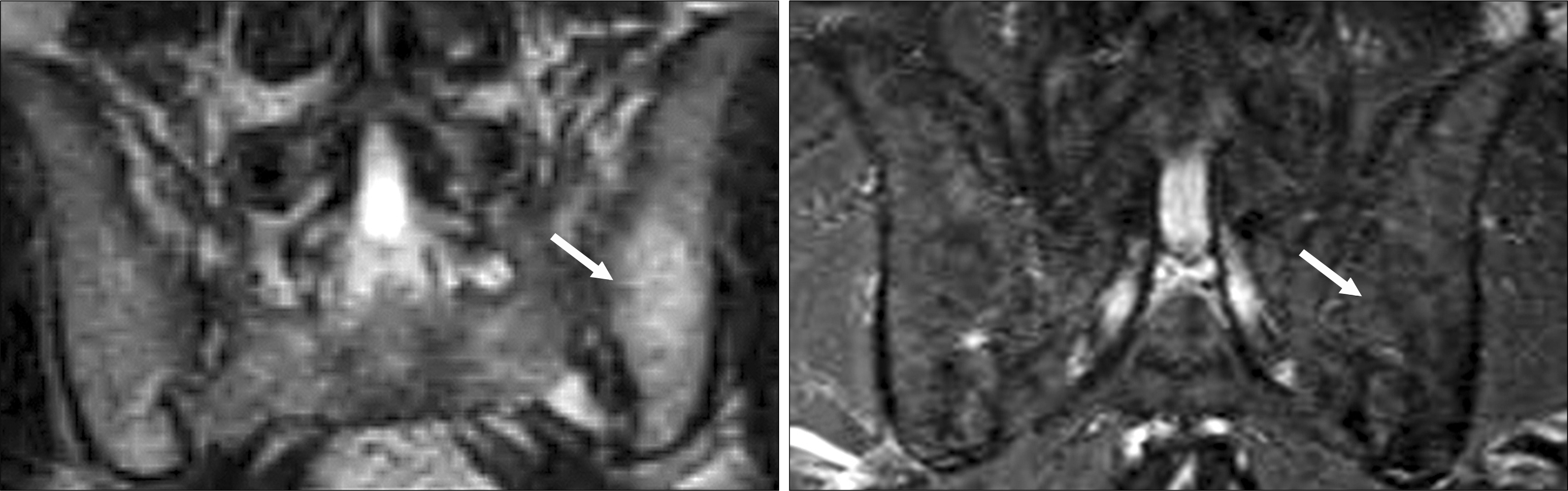
- OBJECTIVE: To assess the clinical effect and acute inflammatory and chronic bony changes of the sacroiliac (SI) joints as detected by magnetic resonance (MR) and computerized tomography (CT) imaging in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) during treatment with etanercept. METHODS: The all 16 patients with AS were treated with etanercept 25mg twice weekly subcutaneously and the clinical response was assessed by standardized parameters. Active inflammatory lesions and chronic bony changes of SI joints were assessed by the MR and CT images of the sacroiliac joints before and after treatment with etanercept. RESULTS: The mean disease duration was 13.1+/-0.69 years and the mean duration of treatment was 14.9+/-4.86 weeks. The mean BASDAI and BASFI score decreased significantly after etanercept treatment. The regression of active inflammation of sacroiliac joint was seen only in a patient with early disease stage of AS (18 months). However, no significant changes in acute inflammatory and chronic bony changes of the SI joints were found on MR and CT images after treatment of etanercept. CONCLUSION: Etanercept treatment showed good clinical response. However, no decrease in acute inflammatory and chronic bony changes of the sacroiliac joints was shown on MR and CT images in the AS patients had long-standing disease. Thus, it is suggested that etanercept should be used in early disease stage to obtain the radiographic improvement of sacroiliac joints.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Smith JA, Marker-Hermann E, Colbert RA. Ankylosing spondylitis: pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis: current concepts. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 20:571–91.2. Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, Khan MA, Braun J. Ankylosing spondylitis: concepts and epidemiology of spondyloarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 20:401–17.3. Van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984; 27:361–8.4. Maksymowych WP, Landewe R. Ankylosing spondylitis: imaging in ankylosing spondylitis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 20:507–19.5. 김태환, 전재범, 심승철, 장대국, 고희관, 정성수 등. 조기 천장골염의 자기공명영상 소견. 대한류마티스학 회지. 1998; l5:221.6. Lee YH, Hwang JY, Lee J. The clinical usefullness of multidetector computed tomography of the sacroiliac joint for evaluating spondyloarthropathies. Korean J Intern Med. 2007; 22:171–7.7. Akkoc N, van der Linden S, Khan MA. Ankylosing spondylitis and symptom-modifiying vs disease-modifying therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 20:539–57.8. Clegg DO, Reda DJ, Weisman MH, Blackburn WD, Cush JJ, CannonGW , et al. Comparison of sulfasalazine and placebo in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. A Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study. Arthritis Rheum. 1996; 39:2004–12.
Article9. Brandt J, Marzo-Ortega H, Emery P. Ankylosing spondylitis: new treatment modalities. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 20:559–70.
Article10. Gorman JD, Sack KE, Davis JC Jr. Treatment of ankylosing spondyitis by inhibition of tumor necrosis factor α. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:1349–56.11. 백유흠, 염지연, 이학현, 김태종, 배상철, 유대현 등. 국내 강직성척추염 환자를 대상으로 한 infliximab 치 료. 대한류마티스학회지. 2006; 13:279–84.12. Braun J, Brandt J, Listing J, Zink A, Alten R, Golder W, et al. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomized controlled multicentre trial. Lancet. 2002; 359:1187–93.13. van der Heijde D, Dijkmans B, Geusens P, Sieper J, DeWoody K, Williamson P, et al. Efficacy and safety of infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomized, placebocontrolled trial (AS SERT). Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:582–91.14. Davis JC, van der Heijde D, Braun J, Dougados M, Cush J, Clegg DO, et al. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor (etanercept) for treating ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized, controlled trial trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48:3230–6.15. van der Heijde D, Kivitz A, Schiff MH, Sieper J, Dijkmans BA, Braun J, et al. Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 54:2136–46.
Article16. Baraliakos X, Davis J, Tsuji W, Braun J. Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis before and after therapy with the tumor necrosis factor αreceptor fusion protein etanercept. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:1216–23.17. Braun J, Landewe R, Hermann KG, Han J, Yan S, Williamson P, et al. Major reduction in spinal inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondlyitis after treatment with infliximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 54:1646–52.18. Baraliakos X, Barndt J, Listing J, Haibel H, Sorensen H, Rudwaleit M, et al. Outcome of patients with active ankylosing spondlylitis after two years of therapy with etanercept: clinical and magnetic resonance imaging data. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 53:856–63.19. Rudwaleit M, Baraliakos X, Listing J, Brandt J, Sieper J, Braun J. Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005; 64:1305–10.
Article20. Lambert RG, Salonen D, Rahman P, Inman RD, Wong RL, Einstein SG, et al. Adalimumab significantly reduces both spinal and sacroiliac joint inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 56:4005–14.21. Baraliakos X, Hermann KG, Landewe R, Listing J, Golder W, Brandt J, et al. Assessment of acute spinal inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis by magnetic resonance imaging: a comparison between contrast enhanced T1 and short tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequences. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005; 64:1141–4.
Article22. Perry D, Stewart N, Benton N, Robinson E, Yeoman S, Crabbe J, et al. Detection of erosions in the rheumatoid hand; a comparative study of multidetector computerized tomography versus magnetic resonance scanning. J Rheumatol. 2005; 32:256–67.23. Maksymowych WP, Inman RD, Salonen D, Dhillon SS, Krishnananthan R, Stone M. Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada magnetic resonance imaging index for assessment of spinal inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 53:502–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinieal Values of Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography ( SPECT ) in Ankylosing Spondylitis
- TNF Inhibitors and Uveitis in Ankylosing Spondylitis
- MRI of Cauda Equina Syndrome in Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Case Report
- Paraplegia after Open Reduction of the Femoral Trochanteric Fracture in Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Case Report
- Successful Etanercept Therapy for Refractory Sacroiliitis in a Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis and Mixed Connective Tissue Disease