Clin Orthop Surg.
2009 Mar;1(1):58-62. 10.4055/cios.2009.1.1.58.
A Case of Postoperative Tuberculous Spondylitis with a Bizarre Course
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bschang@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kangwon National University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1127916
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2009.1.1.58
Abstract
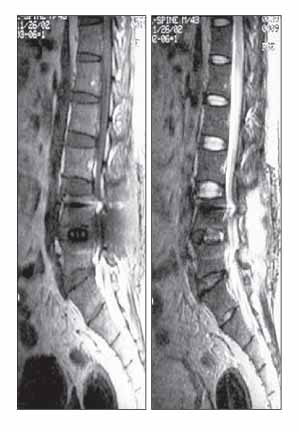
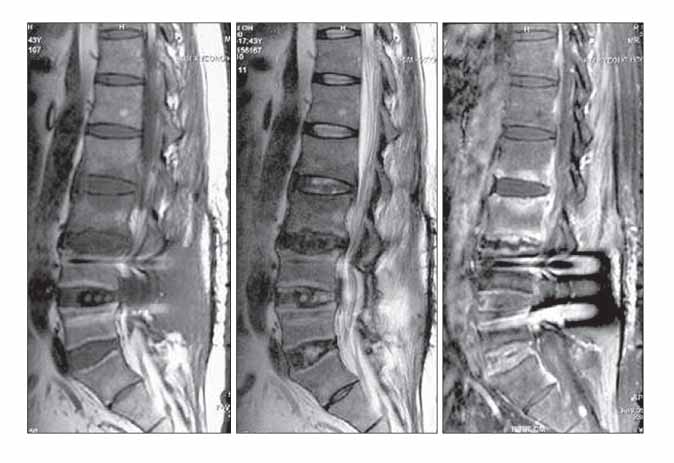
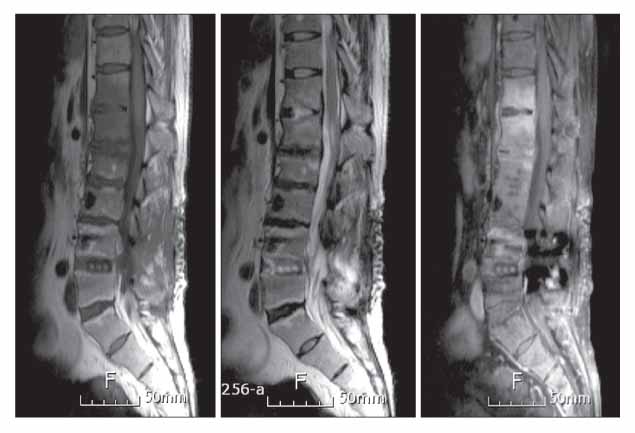
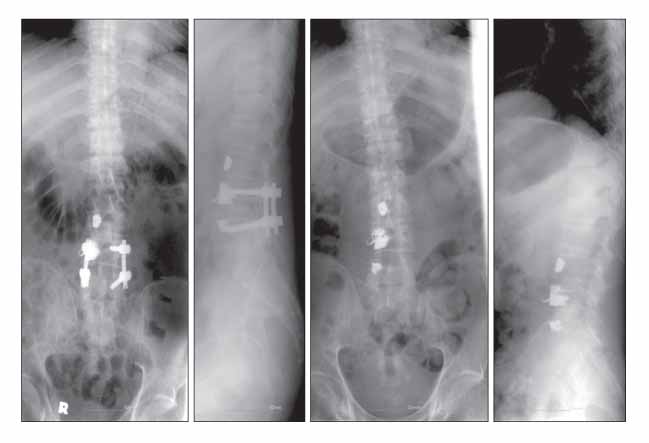
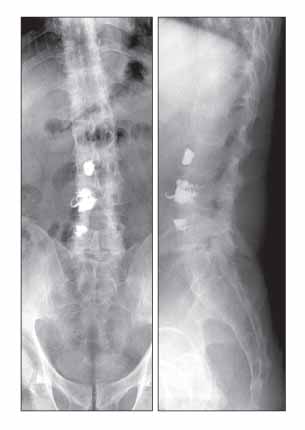
- Postoperative infections following spine surgery are usually attributable to bacterial organisms. Staphylococcus aureus is known to be the most common single pathogen leading to this infection, and the number of infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is increasing. However, there is a paucity of literature addressing postoperative infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. We encountered a case of tuberculous spondylitis after spine surgery. A man had fever with low back pain three weeks after posterior interbody fusion with instrumentation for a herniated intervertebral disc at the L4-L5 level. He had been treated with antibiotics for an extended period of time under the impression that he had a bacterial infection, but his symptoms and laboratory data had not improved. Polymerase chain reaction for Mycobacterium tuberculosis turned out to be positive. The patient's symptoms finally improved when he was treated with antituberculosis medication.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Beiner JM, Grauer J, Kwon BK, Vaccaro AR. Postoperative wound infections of the spine. Neurosurg Focus. 2003. 15(3):E14.
Article2. Ha KY, Kim YH. Postoperative spondylitis after posterior lumbar interbody fusion using cages. Eur Spine J. 2004. 13(5):419–424.
Article3. Abbey DM, Turner DM, Warson JS, Wirt TC, Scalley RD. Treatment of postoperative wound infections following spinal fusion with instrumentation. J Spinal Disord. 1995. 8(4):278–283.
Article4. Olsen MA, Nepple JJ, Riew KD, et al. Risk factors for surgical site infection following orthopaedic spinal operations. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008. 90(1):62–69.
Article5. Sucu HK, Ciçek C, Rezanko T, et al. Percutaneous computed-tomography-guided biopsy of the spine: 229 procedures. Joint Bone Spine. 2006. 73(5):532–537.
Article6. Hwang CM, Shin MJ, Kim SM, et al. The diagnostic usefulness of CT-guided needle biopsy or aspiration in infectious spondylitis. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2003. 48(6):497–504.
Article7. Lee KY, Sohn SK, Hwang KS. Comparison of pyogenic and tuberculous spondylitis. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1999. 6(3):443–450.8. Park DY, Kim JY, Choi KU, et al. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction with histopathologic features for diagnosis of tuberculosis in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded histologic specimens. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003. 127(3):326–330.
Article9. Chang MC, Wu HT, Lee CH, Liu CL, Chen TH. Tuberculous spondylitis and pyogenic spondylitis: comparative magnetic resonance imaging features. Spine. 2006. 31(7):782–788.10. Jung NY, Jee WH, Ha KY, Park CK, Byun JY. Discrimina-tion of tuberculous spondylitis from pyogenic spondylitis on MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 182(6):1405–1410.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Treatment of Tuberculous Spondylitis of the Lumbosacral Junction by Transperitoneal Approach
- Anterior lnterbody Fusion using KANEDA Instrument in Tuberculous Spondylitis: Case Report
- Comparison of Pyogenic and Tuberculous Spondylitis
- Comparison of Pyogenic Spondylitis and Tuberculous Spondylitis
- Vascularized Fibular Bone Graft for Tuberculous Spondylitis: Case Report